Exhibit 99.1
Huachen AI Parking Management Technology Holding Co., Ltd
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(Expressed in U.S. Dollars, except for the number of shares)
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, 2025 | December 31, 2024 | |||||||
Unaudited US$ | US$ | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current assets | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | ||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net | ||||||||
| Other receivables - related parties | ||||||||
| Other receivables, net | ||||||||
| Prepayments | ||||||||
| Inventories, net | ||||||||
| Total current assets | ||||||||
| Non-current assets | ||||||||
| Plant and equipment, net | ||||||||
| Right-of-use assets, net | ||||||||
| Deferred tax assets | ||||||||
| Land-use rights, net | ||||||||
| Intangible assets, net | ||||||||
| Total non-current assets | ||||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | ||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Current liabilities | ||||||||
| Short-term bank loans | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | ||||||||
| Accrued liabilities and other payables | ||||||||
| Contract liabilities | ||||||||
| Taxes payable | ||||||||
| Other payables - related parties | ||||||||
| Lease liabilities | ||||||||
| Total current liabilities | ||||||||
| Non-current liabilities | ||||||||
| Long-term bank loan | ||||||||
| Long-term account payable | ||||||||
| Total non-current liabilities | ||||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | ||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity | ||||||||
| Class A ordinary shares (par value of US$ | ||||||||
| Class B ordinary shares (par value of US$ | ||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | ||||||||
| Statutory reserves | ||||||||
| Retained earnings | ||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| TOTAL HUACHEN CAYMAN SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Non-controlling interest | ||||||||
| TOTAL SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
Huachen AI Parking Management Technology Holding Co., Ltd
UNAUDITED CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(Expressed in U.S. Dollars, except for the number of shares)
| For the six months ended, June 30 | ||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Unaudited | Unaudited | |||||||
| US$ | US$ | |||||||
| Revenues | ||||||||
| Cost of revenues | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Gross profit | ||||||||
| Operating expenses | ||||||||
| Selling and marketing expenses | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| General and administrative expenses | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Research and development expenses | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Total operating expenses | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Income from operations | ||||||||
| Other expenses, net | ||||||||
| Interest expense, net | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Other (expenses) income, net | ( | ) | ||||||
| Total other expenses, net | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Income before income taxes | ||||||||
| Income tax expenses | ( | ) | ||||||
| Net income | ||||||||
| Net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest | ||||||||
| Net income attributable to common shareholders | ||||||||
| OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation income (loss) | ( | ) | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | ( | ) | ||||||
| Total comprehensive income | ||||||||
| Net profit per share - Basic and diluted | ||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding used in calculating basic and diluted earnings per share | ||||||||
2
Huachen AI Parking Management Technology Holding Co., Ltd
UNAUDITED CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(Expressed in U.S. Dollars, except for the number of shares)
| Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class A Ordinary Shares | Class
B | Additional Paid in | Statutory | Other Retained | Non- Comprehensive | Controlling | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares* | Amount | Shares | Amount | Capital | Reserves | Earnings | Income (Loss) | Interests | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allocation to non-controlling interests | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation gain | - | - | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of June 30, 2024 (Unaudited) | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2024 | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of shares for cash | - | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Re-designation of shares | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional Paid-in Capital | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allocation to non-controlling interests | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation gain | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of June 30, 2025 (Unaudited) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3
Huachen AI Parking Management Technology Holding Co., Ltd
UNAUDITED CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Expressed in U.S. Dollars, except for the number of shares)
| For the Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2025 (Unaudited) | 2024 (Unaudited) | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||
| Net income | $ | $ | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation of plant and equipment | ||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets and land-use rights | ||||||||
| Amortization of right-of-use assets | ||||||||
| Reversal of allowance for credit losses | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| (Reversal) provision of allowance for inventory impairment | ( | ) | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts receivable | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Other receivables | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Other receivables - related parties | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Inventories | ( | ) | ||||||
| Prepayments | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Accounts payables | ||||||||
| Accrued liabilities and other payables | ||||||||
| Lease liabilities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Contract liabilities | ||||||||
| Taxes payable | ||||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities | ( | ) | ||||||
| Cash flows from investing activity: | ||||||||
| Purchase of plant and equipment | ( | ) | ||||||
| Net cash used in investing activity | ( | ) | ||||||
| Cash flows from financing activity: | ||||||||
| Repayments of short-term bank loans | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Proceeds from additional paid-in capital | ||||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activity | ( | ) | ||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | ||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | ( | ) | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | $ | ||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | ||||||||
| Cash paid for interest | $ | $ | ||||||
4
Huachen AI Parking Management Technology Holding Co., Ltd AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO UNAUDITED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Six Months Ended June 30, 2025 and 2024
Note 1 — ORGANIZATION AND BUSINESS DESCRIPTION
Huachen AI Parking Management Technology Holding Co., Ltd (“Huachen” or the “Company”) is a company that was established under the laws of Cayman Islands as a holding company on September 30, 2021. Our main business operations are conducted through our subsidiaries in the People’s Republic of China. We are a technology company related to design, manufacture, sales, installation and maintenance of intelligent cubic parking garage and equipment.
As of June 30, 2025, the Company’s subsidiaries are as follows:
| Percentage of | ||||||||
| direct/indirect | ||||||||
| Date of | Jurisdiction of | Economic | ||||||
| Subsidiaries | Incorporation | Formation | Ownership | |||||
| Hua Chen Intelligent Technology Co., Limited (“Huachen HK”) | % | |||||||
| Huachen AI Technology (Zhejiang) Co., Ltd (“Hua Chen WFOE”) | % | |||||||
| Zhejiang Huachen Technology Co., Ltd (“Zhejiang Hua Chen Tech”) | % | |||||||
| Shanghai Tiandidaochuan Parking Equipment Manufacturing Co., Ltd (“Shanghai TD Manufacturing”) | % | |||||||
| Shanghai Tiandiricheng Parking Lots Management Co., Ltd (“Shanghai TD Parking”) | % | |||||||
| Zhejiang Tiandidaochuan Parking Equipment Co., Ltd (“Zhejiang TD Parking”) | % | |||||||
| Shanghai Yufeng Information Technology Co., Ltd (“Shanghai Yufeng”) | % | |||||||
| Shanghai Tiandi Puji Parking Management Co., Ltd (“Shanghai TP Parking”) | % | |||||||
| Shanghai Tiandi Daochuan Parking Equipment Installation Co., Ltd (“Shanghai TD Installation”) | % | |||||||
| Zhejiang Xinfeng Trade Co., Ltd (“Zhejiang Xinfeng”) | % | |||||||
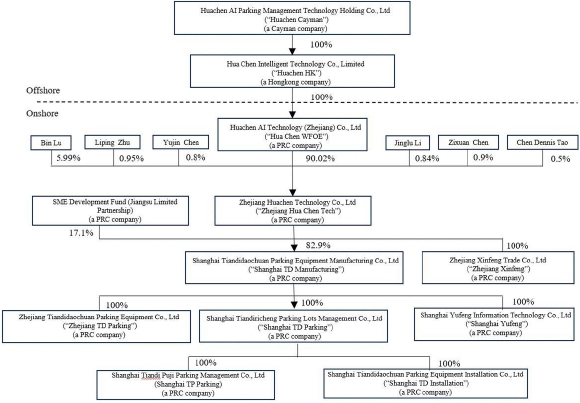
5
The Company, through a series of transactions which are accounted for as a reorganization of entities under common control (the “Reorganization”), became the ultimate parent of its subsidiaries. The reorganization involved: the formation of the Company’s wholly-owned subsidiary-Huachen HK and Huachen HK’s wholly owned subsidiary — Hua Chen WFOE.
Before and after the reorganization, the Company, together with its subsidiaries, is effectively controlled by the same shareholders, and therefore the reorganization is considered as a recapitalization of entities under common control in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 805-50-25. The consolidation of the Company and its subsidiaries have been accounted for at historical cost and prepared on the basis as if the aforementioned transactions had become effective as of the beginning of the first period presented in the accompanying consolidated financial statements in accordance with ASC 805-50-45-5.
Note 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Method of accounting
The accompanying audited consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries (collectively the “Company”). Management has eliminated all significant inter-company balances and transactions in preparing the accompanying audited consolidated financial statements.
Management has prepared the accompanying audited consolidated financial statements and these notes in accordance to generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“US GAAP”). The Company maintains its general ledger and journals with the accrual method accounting.
Principles of consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the financial statements of the Company and its subsidiaries. All intercompany transactions and balances are eliminated upon consolidation. All intercompany transactions and balances between the Company and its subsidiaries are eliminated upon consolidation.
Subsidiaries are those entities in which the Company, directly or indirectly, controls more than one half of the voting power; or has the power to govern the financial and operating policies, to appoint or remove the majority of the members of the board of directors, or to cast a majority of votes at the meeting of directors.
Non-controlling interest represents the portion of the net assets of subsidiaries attributable to interests that are not owned by the Company. The non-controlling interest is presented in the consolidated balance sheets, separately from equity attributable to the shareholders of the Company. Non-controlling interest’s operating result is presented on the face of the consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income as an allocation of the total income for the year between non-controlling shareholders and the shareholders of the Company.
6
Uses of estimates
In preparing the consolidated financial statements in conformity with US GAAP, management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. These estimates are based on information as of the date of the consolidated financial statements. Significant estimates required to be made by management include, but are not limited to, the valuation of accounts receivable and inventories, useful lives of plant and equipment, land use right, the recoverability of long-lived assets, provision necessary for contingent liabilities, and realization of deferred tax assets. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and cash equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investment instruments with an original maturity of three months or less from the date of purchase to be cash equivalents. The Company maintains most of its bank accounts in the PRC.
Accounts receivable, net
Accounts receivable, net are recorded at the gross billing amount less an allowance for expected credit losses from the customers. Accounts receivable do not bear interest.
Since July 1, 2022, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments-Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments (“ASU 2016-13”), using the modified retrospective transition method. ASU 2016-13 replaces the existing incurred loss impairment model with an expected loss methodology, which will result in more timely recognition of credit losses. Upon adoption, the Company changed the impairment model to utilize a forward-looking current expected credit losses (CECL) model in place of the incurred loss methodology for financial instruments measured at amortized cost and receivables resulting from the application of ASC 606.
The Company maintains an allowance for credit losses in accordance with ASC Topic 326, Credit Losses (“ASC 326”) and records the allowance for credit losses as an offset to accounts receivable, and the estimated credit losses charged to the allowance in the combined statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss). The Company assesses collectability by reviewing accounts receivable on a collective basis where similar characteristics exist, primarily based on similar business lines, services or product offerings and on an individual basis when the Company identifies specific customers with known disputes or collectability issues. In determining the amount of the allowance for credit losses, the Company considers historical collectability based on past due status, the age of the accounts receivable balances, credit quality of the Company’s customers based on ongoing credit evaluations, current economic conditions, reasonable and supportable forecasts of future economic conditions, and other factors that may affect the Company’s ability to collect from customer.
7
As of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, allowance
for credit losses balances amounted to $
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value. Costs include the cost of raw materials, freight, direct labor and related production overhead. The cost of inventories is calculated using the weighted average method. Any excess of the cost over net realizable value of each item of inventories is recognized as a provision for diminution in the value of inventories. Net realizable value is estimated using selling price in the normal course of business less any costs to Complete and sell products. The Company evaluates inventories on a quarterly basis for its realizable value adjustments and reduces the carrying value of those inventories that are obsoletes or in excess of the forecasted usage to their estimated net realizable value based on various factors including aging and future demand of each type of inventories.
Prepayments
Prepayments consist of balances paid to suppliers for services and materials that have not been provided or received. Advance to suppliers is short-term in nature and is reviewed periodically to determine whether their carrying value has become impaired.
Plant and equipment, net
Plant and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated
depreciation.
| Useful life | ||
| Office equipment and furniture | ||
| Transportation vehicles | ||
| Mechanical equipment | ||
| Buildings |
Repair and maintenance costs are charged to expenses as incurred, whereas the cost of renewals and betterments that extend the useful lives of property and equipment are capitalized as additions to the related assets. Retirements, sales and disposals of assets are recorded by removing the costs, accumulated depreciation and impairment with any resulting gain or loss recognized in the consolidated statements of income in other income or expenses.
8
Intangible Assets, net
Intangible assets consist primarily of software
and membership. Intangible assets are stated at cost less accumulated amortization.
| Useful life | ||
| ERP- Zhituo software | ||
| Nasdaq membership |
The software is amortized on a monthly basis. Its cost was recorded
as an asset in January 2019 with the original purchase value approximately $
Land use rights, net
Under the PRC law, all land in the PRC is owned
by the government and cannot be sold to an individual or company. The government grants individuals and companies the right to use the
parcels of land for specified periods of time. These land use rights are sometimes referred to informally as “ownership.”
Land use rights are stated at cost less accumulated amortization. The estimated useful life for land use right is
The land use rights were recorded as an asset in March 2018 with the
original value approximately $
Leases
From January 1, 2022, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-02, Lease (FASB ASC Topic 842). The adoption of Topic 842 resulted in the presentation of operating lease right-of-use (“ROU”) assets and operating lease liabilities on the consolidated balance sheet. The Company has elected the package of practical expedients, which allows the Company not to reassess (1) whether any expired or existing contracts as of the adoption date are or contain a lease, (2) lease classification for any expired or existing leases as of the adoption date and (3) initial direct costs for any expired or existing leases as of the adoption date. Lastly, the Company elected the short-term lease exemption for all contracts with lease terms of 12 months or less.
At inception of a contract, the Company assesses whether a contract is, or contains, a lease. A contract is or contains a lease if it conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange of a consideration. To assess whether a contract is or contains a lease, the Company assess whether the contract involves the use of an identified asset, whether it has the right to obtain substantially all the economic benefits from the use of the asset and whether it has the right to control the use of the asset.
The right-of-use assets and related lease liabilities are recognized at the lease commencement date. The Company recognizes operating lease expenses on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
9
Right-of-use of assets
The Company recognises right-of-use assets at the commencement date of the lease (i.e. the date the underlying asset is available for use). Right-of-use assets are measured at cost, less any accumulated depreciation and impairment losses and adjusted for any remeasurement of lease liabilities. The cost of right-of-use assets includes the amount of lease liabilities recognised, initial direct costs incurred, and lease payments made at or before the commencement date less any lease incentives received. Right-of-use assets are depreciated on a straight-line basis over the shorter of the lease term and the estimated useful lives of the assets. All right-of-use assets are reviewed for impairment annually. There was no impairment for right-of-use lease assets for the years ended December 31, 2024.
Lease liabilities
Lease liability is initially measured at the present value of the outstanding lease payments at the commencement date, discounted using the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. Lease payments included in the measurement of the lease liability comprise fixed lease payments, variable lease payments that depend on an index or a rate, amounts expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee and any exercise price under a purchase option that the Company is reasonably certain to exercise. Lease liability is measured at amortized cost using the effective interest rate method. It is re-measured when there is a change in future lease payments, if there is a change in the estimate of the amount expected to be payable under a residual value guarantee, or if there is any change in the Company assessment of option purchases, contract extensions or termination options.
As of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, there
were approximately $ and $
Impairment of Long-lived Assets
The Company reviews long-lived assets, including definitive-lived intangible assets, for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. If the estimated cash flows from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition below are the asset’s carrying value, then the asset is deemed to be impaired and written down to its fair value. There were impairments of these assets as of December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022.
10
Fair value of financial instruments
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. A three-level fair value hierarchy prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value. The hierarchy requires entities to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The three levels of inputs used to measure fair value are as follows:
| ● | Level 1 — inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets. |
| ● | Level 2 — inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, quoted market prices for identical or similar assets in markets that are not active, inputs other than quoted prices that are observable and inputs derived from or corroborated by observable market data. |
| ● | Level 3 — inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable. |
Unless otherwise disclosed, the fair value of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash, short-term investments, accounts receivable, due from related parties, accounts payable, due to related parties, accrued liabilities and other payable, taxes payable and short-term bank loans, approximate the fair value of the respective assets and liabilities as of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024 based upon the short-term nature of the assets and liabilities.
Bank borrowings and unsecured senior notes
Bank borrowings and unsecured senior notes are recognized initially at fair value, net of upfront fees, debt discounts or premiums, debt issuance costs and other incidental fees. Upfront fees, debt discounts or premiums, debt issuance costs and other incidental fees are recorded as a reduction of the proceeds received and the related accretion is recorded as interest expense in the consolidated income statements over the estimated term of the facilities using the effective interest method.
Revenue recognition
The Company adopted ASC 606 “Revenue Recognition.” It recognizes revenue when control of the promised goods or services is transferred to customers, in an amount that reflects the consideration we expect to be entitled to in exchange for those goods or services. The Company recognizes revenue based on the consideration specified in the applicable agreement.
Revenue from contracts with customers is recognized using the following five steps:
| 1. | Identify the contract(s) with a customer; |
| 2. | Identify the performance obligations in the contract; |
| 3. | Determine the transaction price; |
| 4. | Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract; and |
| 5. | Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation. |
11
Generally, revenues are recognized when the Company has negotiated the terms of the transaction, which includes determining either the overall price, or price for each performance obligation in the form of a service or a product, the service or product has been delivered to the customer, no obligation is outstanding regarding that service or product, and the Company is reasonably assured that funds have been or will be collected from the customer.
A summary of each of the Company’s revenue streams under ASC 606 is as follows:
Performance obligations satisfied at a point in time
Equipment structural parts income
Revenue from sales of equipment structural parts is recognized when the products are delivered and accepted by customers, which is the point when title has transferred and risk of ownership has passed. Return allowances is determined by an estimate of expected customer merchandise returns, which is calculated based on historical return patterns, and recorded as a refund liability included in accrued expenses and other liabilities.
For equipment structural parts sales, the Company passed the control of the goods to the customers at a point in time, typically occurs at the delivery. Revenue from sales of equipment structural parts is recognized when the products are delivered and accepted by customers, which is the point when title has transferred and risk of ownership has passed. There are no other performance obligations in the contract, so we consider there is only one performance obligation for each contract.
For equipment structural parts sales, the transaction price was set up when customer places the purchase order, which in some cases are governed by master sales agreements. Total amount of each transaction was determined based on the unit price multiplied with the delivery quantity of the products ordered, or based on the services priced that was agreed between the parties.
For equipment sales, the Company’s payment terms are generally less than one year. The Company has elected the practical expedient under ASC 606-10-32-18 to not assess whether a contract has a significant financing component.
Cubic parking garage income
This revenue is recognized after the garage project has been completed and successfully accepted by the client.
According to 5-Step revenue analysis, the Company considers customer purchase orders, which in some cases are governed by master sales agreements, to be the contracts with a customer. This purchase order determination guided both product (garage and equipment) sales and maintenance service sales. The Company signs master agreement with its customers which include the customer’s name, the products’ specifications, or service type if for maintenance service, payment terms, product acceptance criteria, or service acceptance criteria, and other necessary information. The purchase orders, both product or service, which in some cases are governed by master sales agreements, would be sent to the Company at each time of the purchase. For product (garage and equipment), the PO (purchase order) includes types and quantities of goods to be purchased, the place of delivery, and other information relating to the purchase. The master agreement and purchase order signed between the parties create enforceable rights and obligations.
12
From time to time, the Company and its customers may renegotiate existing contracts to reflect changes of price and other terms. Such modifications are treated as separate contract if both of the following conditions are met:
| ● | The scope of the contract increases because of the addition of promised goods or services that are distinct. |
| ● | The price of the contract increases by an amount of consideration that reflects the entity’s standalone selling prices of the additional promised goods or services and any appropriate adjustments to that price to reflect the circumstances of the particular contract. |
The Company considers customer purchase orders, which in some cases are governed by master sales agreements, to be the contracts with a customer. As part of its consideration of the contract, the Company evaluates certain factors including the customer’s ability to pay (or credit risk). For each contract, the Company considers the promise to transfer products or service delivery, each of which are distinct, to be the identified performance obligations.
For cubic parking garage, when the contract was signed, the garage project began to be executed. First, the equipment selection was made according to the design institute drawings, and then the construction and installation were carried out on site. Revenues from the installation and sale of garage equipment are combined and treated as one performance obligation. The commitments for garage equipment and installation are not separately identifiable, as evidenced by the fact that the customer does not acquire control of the garage until after acceptance of the completed garage installation, and the customer can only utilize and benefit from the garage after the installation is completed, and the customer cannot benefit from a single element. The Company does not currently have any contract modifications and the contract does not currently have any variable consideration. The transaction price is clearly identifiable within the Company’s sales and installation contracts in the context of the Company’s performance obligations for equipment and installation revenues. When the project is completed, the customer accepts the garage. Once the customer acceptance is complete, the Company recognizes revenue for this contract. According to ASC 606-10-25-27, first, the customer simultaneously does not receive and consume the benefits provided by the Company’s performance. Second, the Company’s performance does not create or enhance an asset that the customer controls as the asset is created or enhanced. Third, the Company’s performance does create an asset with an alternative use (selling to a different customer) to the Company. In summary, the Company recognizes cubic parking garage income at a point in time.
The Company negotiates with customers for agreed-upon specifications for products or services customer ordered, and such agreed-upon terms are usually documented in the master sales agreement between the Company and its customers.
13
For product, the Company typically provides
For cubic parking garage price, the Company will consider the cost of the civil foundation, the cost of the mechanical parking equipment, the cost of the installation of the parking equipment, the cost of the construction and installation of the parking equipment, and the cost of the maintenance of the garage. The price of the price parking garage depends on the supply and demand relationship between the number of parking spaces demanded and the number of cubic garage manufacturers, and also depends on the number of floors and configuration of the cubic garage. The more layers of the garage, the higher the price of the garage, while the higher the configuration of the garage, the higher the price of the garage.
For cubic garage, The Company’s payment
terms are normally
For product sales (garage or equipment), the transaction price of a contract is allocated to each distinct goods stated in the purchase order. The price of each distinct goods is determined by the ordered quantities and price quotation.
Performance obligations satisfied over time
Maintenance services income
Garage maintenance service contracts require our company to perform repairs or maintenance on any equipment failures during the contract maintenance period, typically ranging from to years. The transfer of control of maintenance services occurs at the time the services are provided; this is the moment when the customer benefits and assumes the risks and rewards associated with the services. This forms the basis for the recognition of revenue from maintenance services, which are recognized on a straight-line basis over the coverage period for garage repairs.
Our maintenance services are governed by contracts that are independently executed, separate from any other contractual arrangements. The maintenance service contracts are specifically tailored to meet the unique needs of our clients. The maintenance services for such contracts can be distinctly identified and are determined as separate performance obligations within the contracts
14
The summary of the Company’s total revenues by product categories for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024 was as follows:
| For the Six Months Ended | ||||||||
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Equipment structural parts | $ | |||||||
| Cubic parking garage | ||||||||
| Maintenance services | ||||||||
| Others | ||||||||
| Total revenue | $ | $ | ||||||
| Timing of Revenue Recognition: | ||||||||
| Performance obligations satisfied over time | $ | $ | ||||||
| Performance obligations satisfied at a point in time | ||||||||
| Total Revenue | $ | $ | ||||||
Research and development expenses
In connection with the design and development
of cubic parking garage and related equipment products, the Company expense all internal research costs as incurred, which primarily comprise
employee costs, internal and external costs related to execution of studies, including manufacturing costs, facility costs of the research
center, amortization to intangible assets, and depreciation to plant and equipment used in the research and development activities. For
the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024, research and development expenses were $
Income taxes
The Company accounts for current income taxes in accordance with the laws of the relevant tax authorities. Deferred income taxes are recognized when temporary differences exist between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts in the consolidated financial statements. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period including the enactment date. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
An uncertain tax position is recognized as a benefit
only if it is “more likely than not” that the tax position would be sustained in a tax examination. The amount recognized
is the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than
15
The Company’s subsidiaries in China are subject to the income tax laws of the PRC. income was generated outside the PRC for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024. As of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, all of the Company’s tax returns of its PRC operating entities remain open for statutory examination by PRC tax authorities.
Value added tax (“VAT”)
Sales revenue is reported net of VAT. The VAT
is based on gross sales price and VAT rates range up to
Earnings per Share
The Company computes earnings per share (“EPS”) in accordance with ASC 260, “Earnings per Share” (“ASC 260”). ASC 260 requires companies with complex capital structures to present basic and diluted EPS. Basic EPS is measured as net income divided by the weighted average common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted presents the dilutive effect on a per share basis of potential common shares (e.g., convertible securities, options and warrants) as if they had been converted at the beginning of the periods presented, or issuance date, if later. Potential common shares that have an anti-dilutive effect (i.e., those that increase income per share or decrease loss per share) are excluded from the calculation of diluted EPS. For the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024, there were dilutive shares.
Foreign currency translation
Since the Company operates all in the PRC, the Company’s functional currency is the Chinese Yuan (“RMB”). The Company’s consolidated financial statements have been translated into the reporting currency U.S. Dollars (“US$”). Assets and liabilities of the Company are translated at the exchange rate at each reporting period end date. Equity is translated at historical rates. Income and expense accounts are translated at the average rate of exchange during the reporting period. The resulting translation adjustments are reported under other comprehensive income (loss). Gains and losses resulting from the translations of foreign currency transactions and balances are reflected in the results of operations.
The RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currency and all foreign exchange transactions must take place through authorized institutions. No representation is made that the RMB amounts could have been, or could be, converted into US$ at the rates used in translation.
The following table outlines the currency exchange rates that were used in creating the consolidated financial statements in this report:
| For the Six Months Ended | ||||||||
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Year-end spot rate | US$1=RMB |
US$1=RMB |
||||||
| Average rate | US$1=RMB |
US$1=RMB |
||||||
16
Comprehensive income
Comprehensive income consists of two components, net income/(loss) and other comprehensive income /(loss). Other comprehensive income/(loss) refers to revenue, expenses, gains and losses that under GAAP are recorded as an element of shareholders’ equity but are excluded from net income. Other comprehensive income consists of a foreign currency translation adjustment resulting from the Company not using US$ as its functional currency.
Risks and uncertainties
The main operation of the Company is located in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company’s business, financial condition, and results of operations may be influenced by political, economic, and legal environments in the PRC, as well as by the general state of the PRC economy. The Company’s results may be adversely affected by changes in the political, regulatory and social conditions in the PRC. Although the Company has not experienced losses from these situations and believes that it is in compliance with existing laws and regulations including its organization and structure disclosed in Note 1, this may not be indicative of future results.
The Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations may also be negatively impacted by risks related to natural disasters, extreme weather conditions, health epidemics and other catastrophic incidents, which could significantly disrupt the Company’s operations.
In December 2019, a sudden coronavirus epidemic swept through China and then spread to the rest of the world. For parking field, whether parking equipment manufacturing enterprises or parking management and operation enterprises, due to the significant delay in the working time, normal production cannot be produced, resulting in a decrease in the order volume of parking equipment manufacturing enterprises. Due to the basic stop of travel, parking income has been greatly reduced, and some cities have reduced parking fees, which has further extended the impact on parking income. The extent of the impact on the Company’s future financial results will be dependent on future developments such as the length and severity of the crisis, the potential resurgence of the crisis, future government actions in response to the crisis and the overall impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global economy and capital markets, among many other factors, all of which remain highly uncertain and unpredictable. Given this uncertainty, the Company is currently unable to quantify the expected impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on its future operations, financial condition, liquidity and results of operations if the current situation continues.
Recent accounting pronouncements
We consider the applicability and impact of all accounting standards updates (“ASUs”). Management periodically reviews new accounting standards that are issued.
17
In May 2025, the FASB issued ASU No. 2025-04, Compensation — Stock Compensation (Topic 718) and Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Clarifications to Share-Based Consideration Payable to a Customer. The amendments revise the ASC Master Glossary definition of the term performance condition for share-based consideration payable to a customer, incorporating conditions that are based on the volume or monetary amount of a customer’s purchases (or potential purchases) of goods or services from the grantor, and performance targets based on purchases made by other parties that purchase the grantor’s goods or services from the grantor’s customers. For awards with service conditions, the amendments of the ASU eliminate the policy election permitting a grantor to account for forfeitures as they occur; thus, a grantor will be required to estimate the number of expected forfeitures when measuring share-based consideration payable to a customer. The ASU clarifies that share-based consideration encompasses the same instruments as share-based payment arrangements, but the grantee does not need to be a supplier of goods or services to the grantor. The ASU also clarifies that a grantor should not apply the guidance in Topic 606 on constraining estimates of variable consideration to share-based consideration payable to a customer; only to assess the probability that an award will vest using the guidance in Topic 718. The ASU is effective for all entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2026. The Company plans to adopt this guidance effective January 1, 2027, and the adoption of this ASU is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
In May 2025, the FASB issued No. 2025-03, Business Combinations (Topic 805) and Consolidation (Topic 810): Determining the Accounting Acquirer in the Acquisition of a Variable Interest Entity. This ASU was issued to revise current guidance for determining the accounting acquirer for a transaction effected primarily by exchanging equity interests in which the legal acquiree is a variable interest entity (VIE) that meets the definition of a business. The amendments of the ASU require that an entity involved in this type of transaction consider the same factors currently required for determining which entity is the accounting acquirer in other acquisition transactions, as provided in ASC 805-10-55-12 through 55-15. The ASU is effective for all entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2026. The Company plans to adopt this guidance effective January 1, 2027. The Company believes the future adoption of this ASU is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
In March 2025, the FASB issued No. 2025-02, Liabilities (405): Amendments to SEC Paragraphs Pursuant to SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 122. This ASU was issued pursuant to SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 122, which rescinds the interpretive guidance included in Section FF of Topic 5 in the Staff Accounting Bulletin Series entitled Accounting for Obligations to Safeguard Crypto-Assets an Entity Holds for its Platform Users. This ASU has no impact on non-PBEs. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. The Company plans to adopt this guidance effective January 1, 2025, and the adoption of this ASU is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
In January 2025, the FASB issued ASU No. 2025-01, Income Statement—Reporting Comprehensive Income—Expense Disaggregation Disclosures (Subtopic 220-40): Clarifying the Effective Date. This ASU amends the effective date of ASU 2024-03 to clarify that all public business entities are required to adopt the guidance in annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim periods within annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2027. Early adoption of Update 2024-03 is permitted. The Company plans to adopt this guidance effective January 1, 2025, and the adoption of this ASU is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
18
In November 2024, the FASB issued No. 2024-04, Debt—Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20): Induced Conversions of Convertible Debt Instruments. This ASU clarify the requirements for determining whether certain settlements of convertible debt instruments should be accounted for as an induced conversion. The ASU is effective for all entities for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2025, and interim reporting periods within those annual reporting periods. The Company believes the future adoption of this ASU is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
In November 2024, the FASB issued No. 2024-03, Income Statement—Reporting Comprehensive Income—Expense Disaggregation Disclosures (Subtopic 220-40): Disaggregation of Income Statement Expenses. The ASU requires Public Business Entities (PBEs) to make detailed disclosure of relevant expense captions presented on the face of the income statement within continuing operations into specified categories in the notes to financial statements within a new tabular disclosure requirement. The amendments in this Update are effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2027. Early adoption is permitted. The Company plans to adopt this guidance effective January 1, 2025, and the adoption of this ASU is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
In March 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-02, “Codification Improvements — Amendments to Remove References to the Concepts Statements”. This update contains amendments to the Codification that remove references to various FASB Concepts Statements. These changes remove references to various Concepts Statements and the amendments apply to all reporting entities within the scope of the affected accounting guidance. The amendments in this Update are effective for public business entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. Early application of the amendments in this Update is permitted for any fiscal year or interim period for which financial statements have not yet been issued (or made available for issuance). The Company believes the future adoption of this ASU is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
We do not believe other recently issued but not yet effective accounting standards, if currently adopted, would have a material effect on the unaudited condensed consolidated financial position, statements of operations and cash flows.
NOTE 3 — ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE, NET
Accounts receivable consist of the following:
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Accounts receivable: | $ | $ | ||||||
| Retention receivable | ||||||||
| Less: allowance for credit losses | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Accounts receivable, net | $ | $ | ||||||
19
As of June 30, 2025, accounts receivable, net
were approximately $
For accounts receivable, approximately
Allowance for credit losses movement:
As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | $ | ||||||
| Additions/(reversal) | ( | ) | ||||||
| Exchange rate effect | ( | ) | ||||||
| Ending balance | $ | $ | ||||||
The expenses of allowances for credit losses was
$
NOTE 4 — INVENTORIES, NET
Inventories consist of the following:
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Raw materials | $ | $ | ||||||
| Working in process | ||||||||
| Finished goods | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
As of June 30, 2025 inventories, net were approximately
$
20
The Company has inventory falling price reserve
policy. According to it, the inventory falling price will be accrued by
Inventories, net consist of the following:
As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Gross inventories | $ | $ | ||||||
| Less: allowance for impairment | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Inventories, net | $ | $ | ||||||
Allowance for impairment movement:
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | $ | ||||||
| (Reversal) /additions | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Exchange rate effect | ( | ) | ||||||
| Ending balance | $ | $ | ||||||
NOTE 5 — OTHER RECEIVABLES
Other receivables consist of the following:
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Other receivables | ||||||||
| Short-term capital borrowing | $ | $ | ||||||
| Reserve fund | ||||||||
| Deposit | ||||||||
| Trade accounts | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
21
Other receivables are mainly composed of short-term
capital loans, financial lease deposits, financial leases, bankers’ acceptances, temporary borrowings for employees, consulting
fees and other items. The largest proportion is short-term capital borrowing with customers and suppliers in their daily operations, accounting
for
For other receivables, approximately
NOTE 6 — PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Plant and equipment, net, consist of the following:
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, 2025 | December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| Office equipment and furniture | $ | $ | ||||||
| Transportation vehicles | ||||||||
| Mechanical equipment | ||||||||
| Building | ||||||||
| Subtotal | ||||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Plant and equipment, net | $ | $ | ||||||
Depreciation expense were $
NOTE 7 — INTANGIBLE ASSETS, NET
Intangible assets, net, consisted of the following:
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| ERP-Zhituo software | ||||||||
| Nasdaq membership | ||||||||
| Less: accumulated amortization | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Intangible assets, net | $ | $ | ||||||
For the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024,
the Company amortized approximately $
22
NOTE 8 — LAND-USE RIGHTS, NET
Land-use rights, net, consisted of the following:
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Land-use rights | $ | $ | ||||||
| Less: accumulated amortization | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Land-use rights, net | $ | $ | ||||||
For the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024,
the Company amortized approximately $
Estimated future amortization expenses are as follows:
| Amortization | ||||
| expenses | ||||
| Fiscal year 2025 | ||||
| Fiscal year 2026 | ||||
| Fiscal year 2027 | ||||
| Thereafter | ||||
| Total | $ | |||
NOTE 9 — LEASE
The Company has two lease contracts were for the
company’s office space, located on the same floor in Yangpu District of Shanghai, the original leases are from February 1, 2020
to January 31, 2023, and the leaseholders are both Aml Fong (Shanghai) Co., LTD. The Company resigned the agreement and the leases are
from February 1, 2023 to January 31, 2025. In January 2025, the Company entered into a new lease agreement for office space located in
Pudong New Area, Shanghai. The lease term runs from January 11, 2025, to January 10, 2026. The leaseholder is Shanghai TaiRun Investment
Group Co., Ltd. Given that the lease term is
23
Supplemental balance sheet information related to operating leases was as follows:
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Right-of-use assets, net | $ | $ | ||||||
| Operating lease liabilities – current | ||||||||
| Operating lease liabilities – non-current | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
The weighted average discount rates and lease cost for all of operating leases were as follows as of June 30, 2025
| For the Six Months Ended | ||||||||
| June 30 | June 30 | |||||||
| Weighted average discount rates and lease cost: | 2025 | 2024 | ||||||
| Weighted average discount rate | % | % | ||||||
| Operating lease cost | ||||||||
Lease Commitment:
In January 2025, the Company entered into a lease of offices in an
area of
24
NOTE 10 — SHORT-TERM BANK LOAN
Short-term bank loans consist of the following:
| As of | ||||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||||
| Note | 2025 | 2024 | ||||||||
| Loans payable to Zhejiang Rural Commercial Bank | (1) | |||||||||
| Loan payable to Beijing Bank | (2) | |||||||||
| Loan payable to Jiaxing Bank | (3) | |||||||||
| Loan payable to Shanghai Bank | (4) | |||||||||
| Loan payable to China Merchants Bank | (5) | |||||||||
| Loan payable to Mingtai Bank | (6) | |||||||||
| Car loan (Due on October 31, 2025) | (7) | |||||||||
| Total short-term loans | $ | $ | ||||||||
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) | On
On |
25
| (4) |
| (5) |
| (6) |
| (7) |
NOTE 11 — LONG-TERM BANK LOANS
| As of | ||||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||||
| Note | 2025 | 2024 | ||||||||
| Loan from Jiaxing Bank (Effective interest rate at | (1) | |||||||||
| Car loan (Due on | (2) | |||||||||
| Total | ||||||||||
| (1) |
| (2) |
26
NOTE 12 — RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Due from related parties consists of the following:
| As of | ||||||||||
| Name | Related party relationship | June 30, 2025 | December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| Zhaohui Chen | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Yun Zhang | ||||||||||
| Qi Qin | ||||||||||
| Shanghai Muling Industry Co., LTD | ||||||||||
| Total due from related parties | $ | $ | ||||||||
The Company has, in the past, advanced cash to related parties for business purpose and recorded advances as due from related parties in the consolidated financial statements. Such advances are non-interest bearing and due upon demand. Since the large amount is recovered, there is no impairment. As of June 30, 2025, all of the balance of other receivable from related party have been subsequently collected.
Due to related parties consists of the following:
| As of | ||||||||||
| Name | Related party relationship | June 30, 2025 | December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| Yue Xu | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Jiling Cheng | ||||||||||
| Zhejiang Xinghang Precision Machinery Co., LTD | ||||||||||
| Shanghai Liqing Information Technology Co. LTD | ||||||||||
| Bin Lu | ||||||||||
| Total due to related parties | $ | $ | ||||||||
As of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, the balance due to related parties was used for working capital during the Company’s normal course of business. These advances are non-interest bearing and due on demand.
27
NOTE 13 — TAXES
Corporate Income Taxes (“CIT”)
The Company is subject to income taxes on an entity basis on income arising in or derived from the tax jurisdiction in which each entity is domiciled.
Under the current laws of the Cayman Islands, the Company is not subject to tax on income or capital gain. In addition, no Cayman Islands withholding tax will be imposed upon the payment of dividends by the Company to its shareholders.
Huachen HK is subject to Hong Kong profits tax
at a rate of
Other subsidiaries are incorporated in the PRC,
and are subject to the PRC Enterprise Income Tax. Under the Enterprise Income Tax (“EIT”) Law of PRC, domestic enterprises
and Foreign Investment Enterprises (“FIE”) are subject to a unified
According to the Law of Company income, the company
belong to the general taxpayer, the VAT tax rate is
Allowable VAT on purchases = purchase price *
rate. VAT on sales = sales price * rate. For medium and large company, the tax rate is
28
Taxes payable consist of the following:
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Income tax payable | $ | $ | ||||||
| Other taxes payable | ||||||||
| Total taxes payable | $ | $ | ||||||
Deferred tax assets consist of the following:
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets | $ | $ | ||||||
Income tax expenses consist of the following:
For the Six Months Ended | ||||||||
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Income tax expense | $ | $ | ||||||
29
NOTE 14 — CONCENTRATIONS
The Company’s revenue and expense transactions are denominated in RMB and of the Company and its subsidiaries’ assets and liabilities are denominated in RMB. RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currencies. In the PRC, foreign exchange transactions are required by law to be transacted only by authorized financial institutions at exchange rates set by the People’s Bank of China (“PBOC”). Remittances in currencies other than RMB may require certain supporting documentation to affect the remittance.
As of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, $
As of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, there is no restricted cash was on deposit at financial institutions in the PRC. Restricted cash represents cash that cannot be withdrawn without the permission of third parties. The Company’s restricted cash is substantially a cash balance on deposit required by its business partners and commercial banks.
As of June 30, 2025, four suppliers accounted
for approximately
As of June 30, 2025, four customers accounted
for
NOTE 15 — SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Ordinary Shares
Huachen Cayman was established under the laws
of the Cayman Islands on September 30, 2021. The original authorized number of Ordinary Shares was
On August 12, 2024, Huachen Cayman effected a
30
Immediately upon the completion of the forward
split, cancellation of authorized but unissued Ordinary Shares and diminution of authorized share capital, the board of directors of the
Company approved the surrender of a total of
On
February 4, 2025, the Company entered into an underwriting agreement (the “Underwriting
Agreement”) with Benjamin Securities, Inc., as the representative
of the underwriters listed on Schedule 1 thereto, in connection with the initial public of
On March 7, 2025, the underwriters fully exercised
the Over-Allotment Option to purchase an additional
On
May 20, 2025, the Company decided to increase the Company’s authorized share capital from $
As of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, the Company had
Statutory reserve
The Company is required to make appropriations
to certain reserve funds, comprising the statutory surplus reserve and the discretionary surplus reserve, based on after-tax net income
determined in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles of the PRC (“PRC GAAP”). Appropriations to the statutory
surplus reserve are required to be at least
31
NOTE 16 — SEGMENT REPORTING
An operating segment is a component of the Company that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses, and is identified on the basis of the internal financial reports that are provided to and regularly reviewed by the Company’s chief operating decision maker in order to allocate resources and assess performance of the segment.
NOTE 17 — COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
The Company may be involved in certain legal proceedings, claims and other disputes arising from the commercial operations, projects, employees and other matters which, in general, are subject to uncertainties and in which the outcomes are not predictable. The Company determine whether an estimated loss from a contingency should be accrued by assessing whether a loss is deemed probable and can be reasonably estimated. Although the outcomes of these legal proceedings cannot be predicted, the Company does not believe these actions, in the aggregate, will have a material adverse impact on its financial position, results of operations or liquidity.
Lease Commitments
The company’s subsidiary, Shanghai TD Parking
has entered into
The total future minimum lease payments of property management fee and short-term lease under the non-cancellable operating lease with respect to the office as of June 30, 2025 are payable as follows:
| Lease Commitment | ||||
| Within 1 year | $ | |||
| Total | $ | |||
NOTE 18 — SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
The Company has evaluated subsequent events through September 19, 2025, the date the financial statements were issued and filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. Based on the Company’s evaluation, except as disclosed in the financial statements, no other event has occurred requiring adjustment or disclosure in the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
32