Exhibit 99.2
LICHEN INTERNATIONAL LIMITED
INDEX TO INTERIM UNAUDITED CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
F-1
LICHEN INTERNATIONAL LIMITED
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF JUNE 30, 2025 AND DECEMBER 31, 2024
(UNAUDITED)
(All amounts in thousands of USD, except for share and per share data, unless otherwise noted)
| June 30, 2025 | December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| Assets | ||||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | $ | ||||||
| Accounts receivable and contract assets | ||||||||
| Inventories | ||||||||
| Prepayments, deposits, and other current assets | ||||||||
| Total current assets | ||||||||
| Long-term investment | ||||||||
| Property and equipment, net | ||||||||
| Intangible assets, net | ||||||||
| Right-of-use assets | ||||||||
| Goodwill | ||||||||
| Prepaid and other assets | ||||||||
| Total assets | $ | $ | ||||||
| Liabilities And Shareholders’ Equity | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | $ | ||||||
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | ||||||||
| Contract liabilities | ||||||||
| Taxes payable | ||||||||
| Due to the related parties | ||||||||
| Lease liabilities | ||||||||
| Total current liabilities | ||||||||
| Lease liabilities | ||||||||
| Total non-current liability | ||||||||
| Total Liabilities | ||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | ||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity: | ||||||||
| Class A Ordinary Share, $ | ||||||||
| Class B Ordinary Share, $ | ||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | ||||||||
| Statutory surplus reserves | ||||||||
| Retained earnings | ||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Total Lichen International Limited’s shareholders’ equity | ||||||||
| Non-controlling interest | ||||||||
| Total shareholders’ equity | ||||||||
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | $ | ||||||
| * | represents amount less than $1,000. |
| 1 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-2
LICHEN INTERNATIONAL LIMITED
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME AND COMPREHENSIVE (LOSS) INCOME
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED JUNE 30, 2025 AND 2024
(UNAUDITED)
(All amounts in thousands of USD, except for share and per share data, unless otherwise noted)
| June 30, 2025 | June 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Revenues | ||||||||
| Financial and taxation solution services | $ | $ | ||||||
| Education support services | ||||||||
| Software and maintenance services | ||||||||
| Pre-IPO advisory services | ||||||||
| Total revenues | ||||||||
| Cost of revenues | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Gross profit | ||||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||
| Selling and marketing | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| General and administrative | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Total operating expenses | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| (Loss) Income from operations | ( | ) | ||||||
| Other income (expense) | ||||||||
| Other (expense) income, net | ( | ) | ||||||
| Interest income | ||||||||
| (Loss) Income before income taxes | ( | ) | ||||||
| Income tax expenses | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net (loss) income | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||
| Less: Net income attributable to non-controlling interests | ||||||||
| Net (loss) income attributable to Lichen International Limited | ( | ) | ||||||
| Comprehensive (loss) income: | ||||||||
| Net (loss) income | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | ( | ) | ||||||
| Comprehensive (loss) income | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||
| Weighted average number of ordinary shares outstanding – basic and diluted1 | ||||||||
| (Loss) Earnings per ordinary share – basic and diluted1 | ( | ) | ||||||
| 1 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-3
LICHEN INTERNATIONAL LIMITED
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(UNAUDITED)
(All amounts in thousands of USD, except for share and per share data, unless otherwise noted)
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED JUNE 30, 2025 and 2024
| Class
A Ordinary Shares (US$ 0.008 par value)1 | Class
B Ordinary Shares (US$ 0.008 par value) 1 | Additional paid-in capital | Statutory surplus reserve | Retained Earnings | Accumulated other comprehensive loss | Total
Lichen International Limited shareholders’ equity | Non- controlling interests | Total Shareholders’ equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | $ | | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | - | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ordinary shares issue for cash | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share based compensation (Note 16) | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ( | ) | ( | ) | - | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of June 30, 2024 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | - | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class
A Ordinary Shares (US$ 0.008 par value)1 | Class
B Ordinary Shares (US$ 0.008 par value) 1 | Additional paid-in capital | Statutory surplus reserve | Retained Earnings | Accumulated other comprehensive loss | Total
Lichen International Limited shareholders’ equity | Non- controlling interests | Total
Shareholders’ equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2024 | $ | | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net (loss) income | - | - | - | - | - | - | ( | ) | - | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ordinary shares issue for cash | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Business acquisition | - | - | - | - | ( | ) | - | - | - | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Round-up shares | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of June 30, 2025 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | - | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| * |
| 1 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-4
LICHEN INTERNATIONAL LIMITED
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED JUNE 30, 2025 AND 2024
(UNAUDITED)
(All amounts in thousands of USD, except for share and per share data, unless otherwise noted)
| June 30, 2025 | June 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||
| Net (loss) income | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation of property and equipment | ||||||||
| Amortization of other assets | ||||||||
| Amortization of right-of-use assets | ||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets | ||||||||
| Investment loss | ||||||||
| Share-based compensation | ||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts receivable and contract assets | ||||||||
| Prepayments and other current assets | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Right-of-use assets | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Accounts payable | ( | ) | ||||||
| Contract liabilities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | ||||||||
| Tax payables | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Inventories | ||||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities | ( | ) | ||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||
| Investment in potential company | ( | ) | ||||||
| Disposal of the subsidiary | ||||||||
| The deposits for software | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Acquisition of Bondly HK | ( | ) | ||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||
| Ordinary shares issued for cash | ||||||||
| Due to the related parties | ( | ) | ||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | ||||||||
| Effects of foreign currency exchange rate changes on cash | ( | ) | ||||||
| Net (decrease) increase in cash | ( | ) | ||||||
| Cash, beginning of period | ||||||||
| Cash, end of period | $ | $ | ||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flows information: | ||||||||
| Cash paid for income taxes | $ | $ | ||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of non-cash information: | ||||||||
| Obtaining right-of-use assets in exchange for operating lease liabilities | $ | $ | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-5
LICHEN INTERNATIONAL LIMITED
NOTES TO INTERIM UNAUDITED CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| 1. | ORGANIZATION AND NATURE OF OPERATIONS |
Legend China Limited was incorporated in the Cayman
Islands on
Lichen is an investment holding company. Through its wholly owned subsidiaries, Lichen is principally engaged in the provision of: (i) financial and taxation solution services; (ii) education support services to partnered institutions; and (iii) software and maintenance services.
Lichen owns
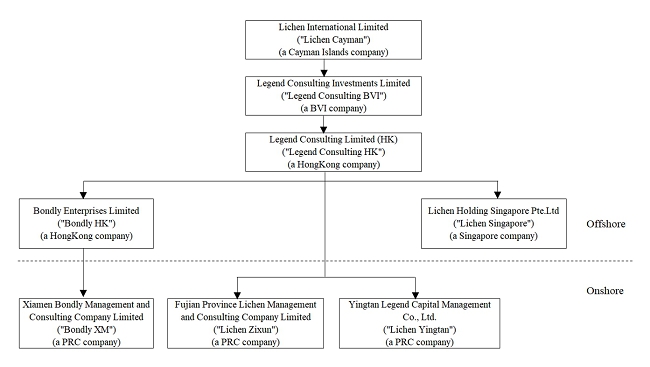
F-6
During the reporting periods, the Company has several subsidiaries in PRC. Details of the Company and its operating subsidiaries are set out below:
| Name of subsidiaries | Place of | Date of | Percentage | Principal activities | |||||
| Legend Consulting Investments Limited (“Legend Consulting BVI”) | % | ||||||||
| Legend Consulting Limited (“Legend Consulting HK”) | % | ||||||||
| Lichen Holding Singapore Pte. Ltd. (“Lichen Singapore”) | % | ||||||||
| Fujian Province Lichen Management and Consulting Company Limited (“Lichen Zixun”) | % | ||||||||
| Bondly Enterprises Limited (“Bondly HK”) | % | ||||||||
| Xiamen Bondly Management and Consulting Company Limited (Bondly XM) | % | ||||||||
| Yingtan Legend Capital Management Co., Ltd. (“Lichen Yingtan”) | % |
Legend Consulting BVI is an investment holding company wholly owned by Lichen.
Legend Consulting HK is an investment holding company wholly owned by Legend Consulting BVI.
Lichen Zixun, which is wholly owned by Legend Consulting HK, is engaged in providing financial and taxation solution services and education support services.
Lichen Singapore, which is wholly owned and established by Legend Consulting HK on December 28, 2023, is engaged in providing financial and taxation solution services and education support services.
The acquisition of
Bondly XM, which is wholly owned and established by Bondly HK on August 25, 2022, is engaged in providing financial and taxation solution services.
Lichen Yingtan, which is wholly owned by Legend Consulting HK.
Reorganization and Share Issuance
On April 28, 2021, Lichen passed a resolution
to increase the share capital. Pursuant to such resolution, the authorized share capital of Lichen was increased from HK$
On December 15, 2021, Lichen executed a special
resolution to change the par value of the ordinary shares from $
F-7
The consideration paid by Lichen and its subsidiaries has been accounted for at historical cost and prepared on the basis as if the aforementioned transactions had become effective as of the beginning of the first period presented in the unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements. As all the entities involved in the process of the Reorganization are under common control before and after the Reorganization, the Reorganization is accounted for in a manner similar to a pooling-of-interest with the assets and liabilities of the parties to the Reorganization carried over at their historical amounts.
Initial Public Offering
On February 8, 2023, the Company closed its initial
public offering of
| 2. | SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
Basis of presentation
The accompanying unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”) for information pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Securities Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
Principles of consolidation
The accompanying unaudited condensed consolidated
financial statements include the unaudited financial statements of the Company and its subsidiaries, which include the BVI-registered
entity, Hong Kong-registered entity, Singapore-registered entity, and PRC-registered entities directly or indirectly owned by the Company.
All transactions and balances among the Company and its subsidiaries have been eliminated upon consolidation. The results of subsidiaries
acquired or disposed of are recorded in the consolidated income statements from the effective date of acquisition or up to the effective
date of disposal, as appropriate. A subsidiary is an entity in which (i) the Company directly or indirectly controls more than
Use of estimate and assumptions
The preparation of the Company’s unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods presented. Estimates are adjusted to reflect actual experience when necessary. Significant accounting estimates reflected in the Company’s unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements include, allowance for doubtful accounts, useful lives of long-lived assets, impairment of long-lived assets and uncertain tax position. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
Business combination
Business combinations are recorded using the acquisition method of accounting. The assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any non-controlling interests of the acquiree at the acquisition date, if any, are measured at their fair values as of the acquisition date. Goodwill is recognized and measured as the excess of the total consideration transferred plus the fair value of any non-controlling interest of the acquiree and fair value of previously held equity interest in the acquiree, if any, at the acquisition date over the fair values of the identifiable net assets acquired. Common forms of the consideration made in acquisitions include cash and common equity instruments. Consideration transferred in a business acquisition is measured at the fair value as of the date of acquisition. Acquisition-related expenses and restructuring costs are expensed as incurred.
Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”)
805 establishes a measurement period to provide the Company with a reasonable amount of time to obtain the information necessary to identify
and measure various items in a business combination and cannot extend beyond
Functional currency and foreign currency translation
The reporting currency of the Company is the United States dollar (“US$”). The Company’s operations are principally conducted through its subsidiaries in PRC in the local currency, Renminbi (RMB), as its functional currency. The functional currency of the Company’s entities incorporated in Hong Kong is the Hong Kong dollars (“HK$”). The determination of the respective functional currency is based on the criteria of Accounting Standard Codification (“ASC”) 830, Foreign Currency Matters. Assets and liabilities are translated at the unified exchange rate as quoted by the PBOC (“The People’s Bank of China”) at the balance sheet date. The statement of income accounts is translated at the average exchange rates for the periods and the equity accounts are translated at historical rates. Translation adjustments resulting from this process are included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). Transaction gains and losses that arise from exchange rate fluctuations on transactions denominated in a currency other than the functional currency are included in the results of operations as incurred.
Translation adjustments included in accumulated
other comprehensive loss amounted to $
F-8
Translation of foreign currencies into US$
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| Period-end RMB: US$1 exchange rate | ||||||||
| Period-end HK$: US$1 exchange rate | ||||||||
| For the six months ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Period-average RMB: US$1 exchange rate | ||||||||
| Period-average HK$: US$1 exchange rate | ||||||||
Related parties
Parties, which can be a corporation or individual, are considered to be related if the Company has the ability, directly or indirectly, to control the other party or exercise significant influence over the other party in making financial and operating decisions. Companies are also considered to be related if they are subject to common control or common significant influence, such as a family member or relative, shareholder, or a related corporation.
Fair value of financial instruments
ASC 825-10 requires certain disclosures regarding the fair value of financial instruments. Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. A three-level fair value hierarchy prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value. The hierarchy requires entities to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The three levels of inputs used to measure fair value are as follows:
| ● | Level 1 — inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets. |
| ● | Level 2 — inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, quoted market prices for identical or similar assets in markets that are not active, inputs other than quoted prices that are observable and inputs derived from or corroborated by observable market data. |
| ● | Level 3 — inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable. |
The fair value of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued expenses and other current liabilities, approximate their recorded values due to their short-term maturities as of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024.
Cash
Cash consist of cash on hand, cash in banks, which are unrestricted as to withdrawal or use, and have insignificant risk of changes in value. The Company maintains most of its bank accounts in the Cayman and mainland of China.
Accounts receivable and allowance for credit losses
Accounts receivable represents the Company’s right to consideration in exchange for goods and services that the Company has transferred to the customers before payment is due. Accounts receivable is stated at the historical carrying amount, net of an estimated allowance for uncollectible accounts. The allowance for credit losses for accounts receivable is based upon the current expected credit losses (“CECL”) model. The CECL model requires an estimate of the credit losses expected over the life of accounts receivable since initial recognition, and accounts receivable with similar risk characteristics are grouped together when estimating CECL. In assessing the CECL, the Company applies a roll rate-based method that considers historical collectability based on past due status, the age of the balances, credit quality of the Company’s customers based on ongoing credit evaluations, current economic conditions, reasonable and supportable forecasts of future economic conditions, and other factors that may affect the Company’s ability to collect from customers. There was no allowance for credit losses set up by the Company as of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, respectively.
F-9
Contract assets
Contract assets represent the Company’s right to consideration in exchange for goods and service performed, which invoice has not been issued.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost and net realizable value. Cost elements of inventories comprise the purchase price of products, shipping charges to receive products from the suppliers when they are embedded in the purchase price. Cost is determined using the weighted average method. Provisions are made for excessive, slow moving, expired and obsolete inventories as well as for inventories with carrying values in excess of market. Certain factors could impact the realizable value of inventory, so the Company continually evaluates the recoverability based on assumptions about customer demand and market conditions. The evaluation may take into consideration historical usage, inventory aging, expiration date, expected demand, anticipated sales price, product obsolescence and other factors. The reserve or write-down is equal to the difference between the cost of inventory and the estimated net realizable value based upon assumptions about future demand and market conditions. If actual market conditions are less favorable than those projected by management, additional inventory reserves or write-downs may be required that could negatively impact the Company’s gross margin and operating results. If actual market conditions are more favorable, the Company may have higher gross margin when products that have been previously reserved or written down are eventually sold. As of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, management compared the cost of inventories with their net realizable value and determined no inventory write-down was necessary.
Prepayments, deposits and other current assets
Represents cash deposited for software development service. The deposits are refundable and bear no interest pursuant to terms of contract. The software development service is in progress and anticipated to be completed by 2026.
Long-term investments
The Company’s long-term investments primarily consist of equity investments accounted for using the equity method and other investments accounted for at fair value.
Equity investments accounted for using the equity method
The Group applies the equity method of accounting to account for equity investments and limited partnership in a private equity fund, according to ASC 323 Investment—Equity Method and Joint Ventures, over which it has significant influence but does not own a majority equity interest or otherwise control. Under the equity method, the Group initially records the investments at cost and the difference between the cost of the equity investee and the fair value of the underlying equity in the net assets of the equity investee is recognized as equity method goodwill, which is included in the equity method investments on the consolidated balance sheets. The Group subsequently adjusts the carrying amount of the investments to recognize its proportionate share of each equity investee’s net income or loss into earnings and cash distributions from investees, after the date of investment. The Group evaluates the equity method investments for impairment under ASC 323. An impairment loss on the equity method investments is recognized as “Investment loss, net (including impairments)” in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss when the decline in value is determined to be other-than-temporary.
Investments accounted for at fair value
In accordance with ASC 825, Financial Instruments, for financial products with variable interest rates referenced to performance of underlying assets and with original maturities greater than one year, the Group elected the fair value method at the date of initial recognition and carries these investments at fair value. Changes in the fair value of these investments are reflected on the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss as “Investment loss, net (including impairments)”.
F-10
Property and equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost less
accumulated depreciation and impairment if any.
| Useful Life | Estimated Residual Value |
|||||
| Building | % | |||||
| Motor vehicles | % | |||||
| Furniture and equipment | % | |||||
| Office improvements | % | |||||
The cost and related accumulated depreciation of assets sold or otherwise retired are eliminated from the accounts and any gain or loss is included in the unaudited condensed consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income (loss). Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are charged to earnings as incurred, while additions, renewals and betterments, which are expected to extend the useful life of assets, are capitalized. The Company also re-evaluates the periods of depreciation to determine whether subsequent events and circumstances warrant revised estimates of useful lives.
Intangible assets
Intangible assets consist primarily of software
acquired, which are stated at cost less accumulated amortization and impairment, if any. Intangible assets are amortized using the straight-line
method over the estimated useful lives, which are generally
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the identifiable assets and liabilities acquired in a business combination.
Goodwill is not depreciated or amortized but is tested for impairment on an annual basis as of December 31, and in between annual tests when an event occurs or circumstances change that could indicate that the asset might be impaired. In accordance with the FASB ASC 350 guidance on “Testing of Goodwill for Impairment”, a company first has the option to assess qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If the company decides, as a result of its qualitative assessment, that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, the quantitative impairment test is mandatory. Otherwise, no further testing is required. The quantitative impairment test consists of a comparison of the fair value of each reporting unit with its carrying amount, including goodwill. If the carrying amount of each reporting unit exceeds its fair value, an impairment loss equal to the difference between the fair value of the reporting unit and the carrying amount will be recorded. Application of a goodwill impairment test requires significant management judgment, including the identification of reporting units, assigning assets and liabilities to reporting units, assigning goodwill to reporting units, and determining the fair value of each reporting unit. The judgment in estimating the fair value of reporting units includes estimating future cash flows, determining appropriate discount rates and making other assumptions. Changes in these estimates and assumptions could materially affect the determination of fair value for each reporting unit.
F-11
Prepaid and other assets
Mainly represents the deposit of the new purchased
property, cash deposited for software development service and prepaid renovation expense. The deposits are refundable and bear no interest
pursuant to terms of contract. The property under development is commitment to be completed by the end of 2028. The amortization period
of the renovation is
Impairment of long-lived assets
The Company evaluates its long-lived assets, including property and equipment and intangibles with finite lives, for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances, such as a significant adverse change to market conditions that will impact the future use of the assets, indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be fully recoverable. When these events occur, the Company evaluates the recoverability of long-lived assets by comparing the carrying amount of the assets to the future undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use of the assets and their eventual disposition. If the sum of the expected undiscounted cash flows is less than the carrying amount of the assets, the Company recognizes an impairment loss based on the excess of the carrying amount of the assets over their fair value. Fair value is generally determined by discounting the cash flows expected to be generated by the assets, when the market prices are not readily available. The adjusted carrying amount of the assets become new cost basis and are depreciated over the assets’ remaining useful lives. Long-lived assets are grouped with other assets and liabilities at the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are largely independent of the cash flows of other assets and liabilities. Given no events or changes in circumstances indicating the carrying amount of long-lived assets may not be recovered through the related future net cash flows, the Company did not recognize any impairment loss on long-lived assets for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024. There can be no assurance that future events will not have impact on the Company’s revenue or financial position which could result in impairment in the future.
Operating leases
The Company, through its subsidiary, leases its office, which are classified as operating leases in accordance with ASC 842. Operating leases are required to record in the balance sheet as right-of-use assets and lease liabilities, initially measured at the present value of the lease payments. The Company has elected the package of practical expedients, which allows the Company not to reassess (1) whether any expired or existing contracts as of the adoption date are or contain a lease, (2) lease classification for any expired or existing leases as of the adoption date, and (3) initial direct costs for any expired or existing leases as of the adoption date. The Company elected the short-term lease exemption for the lease terms that are 12 months or less.
At inception of a contract, the Company assesses whether a contract is, or contains, a lease. A contract is or contains a lease if it conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange of a consideration. To assess whether a contract is or contains a lease, the Company assesses whether the contract involves the use of an identified asset, whether it has the right to obtain substantially all the economic benefits from the use of the asset and whether it has the right to control the use of the asset. The right-of-use assets and related lease liabilities are recognized at the lease commencement date. The Company recognizes operating lease expenses on a straight-line basis over the lease term and had no finance leases for any of the periods stated herein.
The right-of-use of asset is initially measured at cost, which comprises the initial amount of the lease liability adjusted for any lease payments made at or before the commencement date, plus any initial direct costs incurred and less any lease incentive received. All right-of-use assets are reviewed for impairment annually. There was no impairment for right-of-use assets as of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024.
Share-based compensation
The Company accounts for stock-based compensation to employees in accordance with ASC 718, “Compensation-Stock Compensation”. ASC 718 requires companies to measure the cost of employee services received in exchange for an award of equity instruments, including the equity incentive plan, based on the grant date fair value of the award and to recognize it as compensation expense over the period the employee is required to provide service in exchange for the award, usually the vesting period. Stock option forfeitures are recognized at the date of employee termination. Effective January 1, 2024, the Company adopted ASU 2018-07 for the accounting of share-based payments granted to non-employees for goods and services and no material impacts to the Financial Statements.
F-12
Contingencies
From time to time, the Company is a party to various legal actions arising in the ordinary course of business. The Company accrues costs associated with these matters when they become probable and the amount can be reasonably estimated. Legal costs incurred in connection with loss contingencies are expensed as incurred. The Company’s management does not expect any liability from the disposition of such claims and litigation individually or in the aggregate would have a material adverse impact on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of operations and cash flows.
Revenue recognition
The Company adopted ASC Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, effective as of January 1, 2019. Accordingly, the unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024 are presented under ASC 606. The core principle of the guidance is that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. Revenue is the transaction price the Company expects to be entitled to in exchange for the promised goods or services in a contract in the ordinary course of the Company’s activities and is recorded net of value-added tax (“VAT”). To achieve that core principle, the Company applies the following steps:
Step 1: Identify the contract (s) with a customer
Step 2: Identify the performance obligations in the contract
Step 3: Determine the transaction price
Step 4: Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract
Step 5: Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation
No practical expedients were used when the Company adopted the ASC 606. Revenue recognition policies for each type of revenue stream are as follow:
Financial and taxation solution services
Revenues from financial and taxation solution services for which control of services is transferred over time is recognized progressively based on the contract costs incurred to date (primarily comprising staff costs and industry expert cost by reference to the time as recorded in the monthly working record incurred to date) as compared to the total costs to be incurred under the transaction (by reference to the total budgeted time of the respective project) to depict the Company’s performance in transferring control of services promised to a customer. The Company recognizes revenues over time only if it can reasonably measure its progress toward complete satisfaction of the performance obligation. The Company normally requires the customers to pay a deposit upon entering into the service contracts.
Education support services - sales of teaching and learning materials
Revenues from the sales of educational materials for which control of assets is transferred at a point in time is recognized when the goods are delivered to customers. The Company does not provide any sales-related warranties. There is no right of return by customers under the Company’s standard contract terms.
F-13
Education support services - Provision of marketing, operation and technical support services
Revenues from provision of marketing, operation and technical support services from the partnered institutions is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the agreement. The transaction price inclusive of value added tax as received from customers in advance is recognized as a contract liability at the time of the initial transaction and is released on a straight-line basis over the period of service (usually one year).
Software and maintenance services
Standard software is a right to use license because the software has standalone functionality and the customer can use the software as it is available at a point in time. The Company recognizes revenues for such licenses at a point in time when the customer has received licenses and thus has control over the software. In case there is an update of the standard software, end customers or distributors are required to pay additional consideration to buy upgraded version. Revenues from maintenance services is recognized over time within the service period.
Pre-IPO advisory services
Revenues from Pre-IPO advisory services for which control of services is transferred over time is recognized progressively based on the contract costs incurred to date (primarily comprising staff costs and industry expert cost by reference to the time as recorded in the monthly working record incurred to date) as compared to the total costs to be incurred under the transaction (by reference to the total budgeted time of the respective project) to depict the Company’s performance in transferring control of services promised to a customer. The Company recognizes revenues over time only if it can reasonably measure its progress toward complete satisfaction of the performance obligation. The Company normally requires the customers to pay a deposit upon entering into the service contracts.
Contract liabilities
Contract liability is recorded when a payment is received from a customer before the Company transfers the related services. Contract liability is recognized as revenue when the Company performs the services under the contract.
Disaggregated information of revenues by services:
| For the six months ended June 30 | ||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Financial and taxation solution services | $ | $ | ||||||
| Education support services | ||||||||
| Software and maintenance services | ||||||||
| Pre-IPO advisory services | ||||||||
| Revenues | $ | $ | ||||||
Segment reporting
Operating segments are reported in a manner consistent
with the internal reporting provided to the chief operating decision-maker. The chief operating decision-maker has been identified as
the Chief Executive Officer who allocates resources to and assesses the performance of the operating segments of an entity. The Company’s
reporting segments are decided based on its operating segments while taking full consideration of various factors such as products and
services, geographic location and regulatory environment related to administration of the management. Operating segments meeting the same
qualifications are allocated as
F-14
Value added tax (“VAT”)
Revenue represents the invoiced value of goods
and service, net of VAT. The VAT is based on gross sales price and VAT rates range up to
Income taxes
The Company follows the liability method of accounting for income taxes in accordance with ASC 740 (“ASC 740”), Income Taxes. The Company accounts for current income taxes in accordance with the laws of the relevant tax authorities. Deferred income taxes are recognized when temporary differences exist between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts in the consolidated financial statements. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period including the enactment date. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
The Company is not subject to tax on income or capital gain under the current tax laws of U.S. And the Company is subject to tax on income or capital gain under the tax laws of PRC.
An uncertain tax position is recognized as a benefit
only if it is “more likely than not” that the tax position would be sustained in a tax examination. The amount recognized
is the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than
Statutory surplus reserves
The Company’s PRC subsidiaries are required
to allocate at least
Advertising expenses
Advertising expenditures are expensed as incurred
and such expenses were included as part of selling and marketing expenses. For the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024, the advertising
expenses amounted to approximately $
Comprehensive (loss) income
Comprehensive (loss) income consists of two components, net (loss) income and other comprehensive income (loss). Other comprehensive income (loss) refers to revenue, expenses, gains and losses that under GAAP are recorded as an element of equity but are excluded from net income. Other comprehensive income (loss) consists of a foreign currency translation adjustment resulting from the Company not using the U.S. dollar as its functional currencies.
(Loss) Earnings per ordinary share
The Company computes earnings per share (“EPS”) in accordance with ASC 260, Earnings per Share. ASC 260 requires companies to present basic and diluted EPS. Basic EPS is measured as net income divided by the weighted average common share outstanding for the period. Diluted EPS presents the dilutive effect on a per-share basis of the potential Ordinary Shares (e.g., convertible securities, options and warrants) as if they had been converted at the beginning of the periods presented, or issuance date, if later. Potential Ordinary Shares that have an anti-dilutive effect (i.e., those that increase income per share or decrease loss per share) are excluded from the calculation of diluted EPS. There were no dilutive or anti-dilutive potential Ordinary Shares or effect for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024.
F-15
Recent accounting pronouncements
The Company considers the applicability and impact of all accounting standards updates (“ASUs”). Management periodically reviews new accounting standards that are issued. Under the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, as amended (the “JOBS Act”), the Company meets the definition of an emerging growth company, or EGC, and has elected the extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards, which delays the adoption of these accounting standards until they would apply to private companies.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-03, “Income Statement—Reporting Comprehensive Income (Subtopic 220-40): Disaggregation of Income Statement Expenses.” This pronouncement introduces new disclosure requirements aimed at enhancing transparency in financial reporting by requiring disaggregation of specific income statement expense captions. Under the new guidance, entities are required to disclose a breakdown of certain expense categories, such as: employee compensation; depreciation; amortization, and other material components. The disaggregated information can be presented either on the face of the income statement or in the notes to the financial statements, often using a tabular format. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2025, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating these new disclosure requirements and does not expect the adoption to have a material impact. In January 2025, the FASB issued ASU 2025-01, which revises the effective date of ASU 2024-03 (on disclosures about disaggregation of income statement expenses) “to clarify that all public business entities are required to adopt the guidance in annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim periods within annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2027.” Entities within the ASU’s scope are permitted to early adopt the ASU.
In January 2025, the FASB issued ASU 2025-01 Income Statement—Reporting Comprehensive Income—Expense Disaggregation Disclosures (Subtopic 220-40). The Board issued Update 2024-03 on November 4, 2024. Update 2024-03 states that the amendments are effective for public business entities for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2027. Following the issuance of Update 2024-03, the Board was asked to clarify the initial effective date for entities that do not have an annual reporting period that ends on December 31 (referred to as non-calendar year-end entities). Because of how the effective date guidance was written, a non-calendar year-end entity may have concluded that it would be required to initially adopt the disclosure requirements in Update 2024-03 in an interim reporting period, rather than in an annual reporting period. The Board’s intent in the basis for conclusions of Update 2024-03 is clear that all public business entities should initially adopt the disclosure requirements in the first annual reporting period beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim reporting periods within annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2027. However, the Board acknowledges that there was ambiguity between the intent in the basis for conclusions in Update 2024-03 and the transition guidance that was included in the Codification when Update 2024-03 was issued. We do not expect the adoption of this accounting standard to have an impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In April 2025, the FASB issued ASU 2025-04 – Compensation—Stock Compensation (Topic 718) and Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Clarifications to Share-Based Consideration Payable to a Customer, which revises the definition of performance condition for share-based consideration payable to a customer, eliminates the forfeiture policy election for awards granted to customers (unless granted in exchange for a distinct good or service), and clarifies applicability of the variable consideration constraint. The ASU will be effective for annual reporting periods (including interim periods within annual reporting periods) beginning after December 15, 2026, for all entities. Early adoption is permitted for both interim and annual financial statements that have not yet been issued. The Company is evaluating the impact of the adoption of this guidance.
In July 2025, the FASB issued ASU 2025-05 - Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (Topic 326). The amendments in this Update provide (1) all entities with a practical expedient and (2) entities other than public business entities with an accounting policy election when estimating expected credit losses for current accounts receivable and current contract assets arising from transactions accounted for under Topic 606. An entity that elects the practical expedient and the accounting policy election, if applicable, should apply the amendments in this Update prospectively. The amendments will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2025, and interim reporting periods within those annual reporting periods. Early adoption is permitted in both interim and annual reporting periods in which financial statements have not yet been issued or made available for issuance. The Company is evaluating the impact of the adoption of this guidance. We believe the future adoption of this ASU is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
F-16
Except for the above-mentioned pronouncements, there are no new recent issued accounting standards that will have a material impact on the unaudited condensed consolidated financial position, statements of operations and cash flows.
| 3. | Cash |
Cash consist of cash on hand, cash in banks, which
are unrestricted as to withdrawal or use, and have insignificant risk of changes in value.
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| RMB | $ | $ | ||||||
| HKD | ||||||||
| SGD | ||||||||
| USD | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
| * | represents amount less than $1,000. |
| 4. | Accounts receivable and contract assets |
Accounts receivables and unbilled receivables consisted of the following as of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024:
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Accounts receivables | $ | $ | ||||||
| Unbilled receivables | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
There was allowance for doubtful accounts recognized
as of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, respectively. The accounts receivable and unbilled receivable amounted to $
F-17
| 5. | Prepayments, deposits and other current assets |
Prepayments, deposits and other current assets consisted of the following:
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Deposits to software developer2 | $ | $ | ||||||
| Cash due from the issuance1 | ||||||||
| Prepaid service fee | ||||||||
| Other current assets | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
On December 29, 2024, the Company entered into
a securities purchase agreement with certain institutional investors named thereto (the “Purchasers”). Pursuant to the Securities
Purchase Agreements, the Purchasers agreed to subscribe for and purchase, and the Company agreed to issue and sell to the Purchasers,
an aggregate of
On
May 12, 2025, the Company made the first deposit of $
| 6. | Property and equipment, net |
Property and equipment, net consisted of the following:
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Buildings | $ | $ | ||||||
| Furniture and equipment | ||||||||
| Motor vehicles | ||||||||
| Office improvements | ||||||||
| Subtotal | ||||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Property and equipment, net | $ | $ | ||||||
Depreciation expenses
for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024 amounted to approximately $
The Company did not recognize any impairment loss on property and equipment for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and year ended December 31, 2024.
F-18
| 7. | Intangible assets |
The Company’s intangible assets with definite useful lives primarily consisted of licensed software and customer relationship, which are for sales or support the Company’s business and operation. The following table summarizes the components of acquired intangible asset balances.
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Software | $ | $ | ||||||
| Customer relationship | ||||||||
| Less: accumulated amortization | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Intangible assets, net | $ | $ | ||||||
Amortization expense
recognized in cost of revenues for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024 amounted to approximately $
The Company did not recognize any impairment loss on intangible assets for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and the year ended December 31, 2024.
The future amortization expense of the intangible assets for the twelve months ending June 30 of the following years is expected as follows:
| Twelve months ending June 30, | Amortization expenses | |||
| In thousands of USD | ||||
| 2026 | $ | |||
| 2027 | ||||
| 2028 | ||||
| 2029 | ||||
| 2030 | ||||
| Total | $ | |||
| 8. | Goodwill |
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Bondly HK | $ | $ | ||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, | $ | $ | ||||||
| Acquisitions (Note 15) | ||||||||
| Goodwill, net | $ | $ | ||||||
F-19
| 9. | Leases |
As of June 30, 2025, the Company had the following non-cancellable lease contract.
| Description of the lease | Lease term | |
| Office premises |
(a) Amount recognized in the consolidated balance sheet:
Operating lease right -of-use assets, net was as follows as of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024:
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Right-of-use assets | $ | $ | ||||||
| Lease liabilities, current | ||||||||
| Lease liabilities, non-current | ||||||||
| Total operating lease liabilities | $ | $ | ||||||
(b)
| For the six months ended June 30, 2025 | For the six months ended June 30, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Amortization of right-of-use assets | $ | $ | ||||||
| Interest of lease liabilities | $ | $ | ||||||
Maturity analysis of operating lease liabilities of June 30, 2025 is as follows:
| Operating lease payment | In thousands of USD | |||
| Within one year | ||||
| One to three years | ||||
| Total future minimum lease payments | $ | |||
| Less: imputed interest | ( | ) | ||
| Total | ||||
F-20
| 10. | Prepaid and other assets |
Other assets consisted of the following:
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Deposit of Haicang property | $ | $ | ||||||
| Deposits to software developer | ||||||||
| The deposits for potential acquisition | ||||||||
| Other current assets | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
On May 18, 2023, the Company (the “Buyer”)
entered into a pre-sale agreement with Xiamen Haicang District People’s Government (the “Seller”), pursuant to which
the Company agreed to purchase the Service industrial park building, located in Haicang District of Xiamen City. The buyer immediately
pays $
On May 5, 2023, the Company made the first deposit
of $$
| 11. | Related party transactions and balances |
The table below sets forth the major related parties and their relationships with the Company as of and for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024:
| Name of related parties | Relationship with the Company | |
| Mr. Ya Li |
| i) |
| As
of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Due to the related parties | ||||||||
| Ya Li | $ | $ | ||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
Balances due to Quanzhou school and Ya Li are the result of the normal business transactions stated above. The balances were all unsecured, non-interest bearing and payable on demand.
F-21
| 12. | Accrued expenses and other current liabilities |
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities consisted of the following:
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Salary payable | $ | $ | ||||||
| Investment of potential company | ||||||||
| Others | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
| 13. | Contract liabilities |
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Contract liabilities | $ | $ | ||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
Contract liability refers
to the payment received from a customer before the Company transfers the related services in advance. Contract liability primarily consists
of advanced payment received from customers for which the Company’s revenue recognition criteria have not been met. The contract
liability will be recognized as revenue once the criteria for revenue recognition have been met. The unearned revenue amounted to $
F-22
| 14. | Taxes |
| (a) | Taxes payable |
Taxes payable consisted of the following:
| As of June 30, 2025 | As of December 31, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Income tax payable | $ | $ | | |||||
| VAT payable | ||||||||
| Other tax payable | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
| (b) | Corporate Income Taxes (“CIT”) |
Cayman Islands
Under the current tax laws of Cayman Islands, the Company is not subject to tax on income or capital gain. Additionally, the Cayman Islands does not impose a withholding tax on payments of dividends to shareholders.
BVI
Under the current tax laws of BVI, the Company is not subject to tax on income or capital gain. Additionally, the BVI does not impose a withholding tax on payments of dividends to shareholders.
Hong Kong
Under the current Hong
Kong Inland Revenue Ordinance, the Company’s subsidiaries incorporated in Hong Kong are subject to
PRC
The Company’s PRC
subsidiaries are governed by the income tax laws of the PRC and the income tax expense in respect to operations in the PRC is calculated
at the applicable tax rates on the taxable income for the periods based on existing legislation, interpretations and practices in respect
thereof. Under the Enterprise Income Tax Laws of the PRC (the “EIT Laws”), domestic enterprises and Foreign Investment Enterprises
(the “FIE”) are usually subject to a unified
| i) |
| For the six months ended June 30, 2025 | For the six months ended June 30, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Provisions for current income tax | $ | $ | ||||||
| Provisions for deferred income tax | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
There are no deferred tax assets recognized or impaired for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024.
F-23
| ii) | The following table reconciles PRC statutory rates to the Company’s effective tax rate: |
The following table reconciles the China statutory rates to the Company’s effective tax rate for the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024:
| For the six months ended June 30, 2025 | For the six months ended June 30, 2024 | |||||||
| PRC statutory income tax rate | % | % | ||||||
| Effect of different tax jurisdiction | ( | )% | ||||||
| Non-deductible expenses (1) | ( | )% | % | |||||
| Change in valuation allowance | ( | )% | ( | )% | ||||
| Effective income tax rate | % | % | ||||||
| (1) | Non-deductible expenses represented meal and entertainment fees not-deductible in PRC tax returns. |
| iii) |
| For the six months ended June 30, 2025 | For the six months ended June 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets: | In thousands of USD | |||||||
| Net accumulated loss-carry forward | $ | $ | ||||||
| Less: valuation allowance | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net deferred tax assets | $ | $ | ||||||
Movement of valuation allowance is as follows:
| For the six months ended June 30, 2025 | For the six months ended June 30, 2024 | |||||||
| In thousands of USD | ||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | $ | ||||||
| Write-off | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Change of valuation allowance | ||||||||
| Ending balance | $ | $ | ||||||
Certain subsidiaries had tax loss of approximately
$
Uncertain tax positions
The Company evaluates each uncertain tax position (including the potential application of interest and penalties) based on the technical merits, and measure the unrecognized benefits associated with the tax positions. As of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, the Company did not have any significant unrecognized uncertain tax positions. The Company did not incur interest and penalties during the six months ended June 30, 2025 and 2024.
F-24
15. Business Combination
Acquisition of Bondly HK
On July 29, 2024, the Company acquired
On February 26, 2025, the Company acquired the
remaining
The Company engaged an independent valuation firm to assist management in valuing assets acquired, liabilities assumed, intangible assets identified and contingent consideration as of the acquisition day.
The identifiable intangible assets acquired upon acquisition were proprietary technology with definite useful life. All other current assets and current liabilities carrying value approximated fair value at the time of acquisition. The fair value of the consideration was based on closing market price of the Company’s common share on the acquisition date.
According to the independent valuation report,
the purchase price was allocated to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their fair values.
| Fair value of total consideration transferred: | ||||
| Cash consideration | $ | |||
| Subtotal | $ | |||
| Recognized amounts of identifiable assets acquired and liability assumed: | ||||
| Cash | $ | |||
| Current assets other than cash | ||||
| Intangible asset – customer relationships | ||||
| Other non-current assets | ||||
| Current liabilities | ( | ) | ||
| Total identifiable net assets | $ | |||
| Fair value of non-controlling interests* | ||||
| Goodwill | $ | |||
| 16. | Share Based Compensation |
2023 Equity incentive plan
In September 2023, the Company adopted the 2023
Equity incentive plan which allows the Company to offer incentive awards to employee, directors and consultants (collectively, “the
Participants”). Under the 2023 Equity incentive plan, the Company issued
Share-based compensation expense of $
F-25
| 17. | Ordinary share |
The Company was established
as a holding company under the laws of Cayman Islands. The Company’s authorized share capital of US$
On February 6, 2023,
the Company announced the closing of its initial public offering of
On March 12, 2024, the
Company issued an aggregate of
On May 2, 2024, the Company
entered into the Securities Purchase Agreements with eight purchasers, each an unrelated third party to the Company (collectively, the
“Purchasers”). Pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreements, the Purchasers agreed to subscribe for and purchase, and the
Company agreed to issue and sell to the Purchasers, an aggregate of
On November 8, 2024,
the Company issued an aggregate of
On December 12, 2024,
the Company entered into a securities purchase agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with certain institutional investors (collectively,
the “Purchasers”). Pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreements, the Purchasers agreed to subscribe for and purchase, and
the Company agreed to issue and sell to the Purchasers, an aggregate of
On December 26, 2024,
the Company entered into a securities purchase agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with certain institutional investors (collectively,
the “Purchasers”). Pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreements, the Purchasers agreed to subscribe for and purchase, and
the Company agreed to issue and sell to the Purchasers, an aggregate of
F-26
On December 29, 2024,
the Company entered into a securities purchase agreement with certain institutional investors named thereto (the “Purchasers”).
Pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreements, the Purchasers agreed to subscribe for and purchase, and the Company agreed to issue and
sell to the Purchasers, an aggregate of
On January 28, 2025,
the Company entered into a securities purchase agreement with certain institutional investors named thereto (the “Purchasers”).
Pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreements, the Purchasers agreed to subscribe for and purchase, and the Company agreed to issue and
sell to the Purchasers, an aggregate of
On February 10, 2025, the Board approved a one-for-two-hundred (1:200) Reverse Split of the Company’s issued and unissued Class A and Class B ordinary shares.
As of June 30, 2025,
| 18. | Statutory surplus reserves |
The Company is required
to make appropriations to certain reserve funds, comprising the statutory surplus reserve and the discretionary surplus reserve, based
on after-tax net income determined in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles of the PRC (“PRC GAAP”). Appropriations
to the statutory surplus reserve are required to be at least
| 19. | Restricted assets |
The Company’s ability to pay dividends is primarily dependent on the Company receiving distributions of funds from its subsidiary. Relevant PRC statutory laws and regulations permit payments of dividends by the PRC subsidiaries only out of its retained earnings, if any, as determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. The results of operations reflected in the accompanying consolidated financial statements prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP differ from those reflected in the statutory financial statements of the PRC entities.
The PRC entities are
required to set aside at least
As a result of the foregoing restrictions, the
PRC entities are restricted in their ability to transfer their assets to the Company. Foreign exchange and other regulation in the PRC
may further restrict the PRC entities from transferring funds to the Company in the form of dividends, loans and advances. As of June
30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, amounts restricted are the paid-in-capital and statutory reserve of the PRC entities, which amounted to
$
F-27
| 20. | Risks and Concentration |
| a) | Concentration of credit risk |
Financial instruments
that potentially subject the Company to significant concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash. As of June 30, 2025 and December
31, 2024, approximately $
The Company is also exposed to risk from its accounts receivable and other receivables. These assets are subjected to credit evaluations. An allowance has been made for estimated unrecoverable amounts which have been determined by reference to past default experience and the current economic environment.
A majority of the Company’s expense transactions are denominated in RMB and a significant portion of the Company and its subsidiaries’ assets and liabilities are denominated in RMB. RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currencies. In the PRC, certain foreign exchange transactions are required by law to be transacted only by authorized financial institutions at exchange rates set by the People’s Bank of China (“PBOC”). Remittances in currencies other than RMB by the Company in China must be processed through the PBOC or other China foreign exchange regulatory bodies which require certain supporting documentation in order to affect the remittance.
The Company’s functional
currency is RMB, and its unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements are presented in U.S. dollars. The RMB appreciated by
To the extent that the Company needs to convert U.S. dollars into RMB for capital expenditures and working capital and other business purposes, appreciation of RMB against U.S. dollar would have an adverse effect on the RMB amount the Company would receive from the conversion. Conversely, if the Company decides to convert RMB into U.S. dollar for the purpose of making payments for dividends, strategic acquisition or investments or other business purposes, appreciation of U.S. dollar against RMB would have a negative effect on the U.S. dollar amount available to the Company.
| b) | Concentration of customers and suppliers |
All revenue was derived
from customers located in PRC. There are no customers from whom revenues individually represent greater than
For the six months ended
June 30, 2025, Beijing Duoying Times Culture Media Co., Ltd contributed approximately
F-28
| 21. | Commitments and contingencies |
| (a) | Capital commitments |
The Company’s capital commitment primarily relate to investing activities contracted but not yet reflected in the unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements:
| Twelve months ending June 30, | Haicang Property | |||
| In thousands of USD | ||||
| Less than one year | $ | |||
| 1-3 years | ||||
| 3-5 years | ||||
| More than 5 years | ||||
| Total | $ | |||
Other than those shown above, the Company did not have any significant commitments, long-term obligations, or guarantees as of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024.
| (b) | Contingencies |
The Company is subject to legal proceedings and regulatory actions in the ordinary course of business. The results of such proceedings cannot be predicted with certainty, but the Company does not anticipate that the final outcome arising out of any such matter will have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, cash flows or results of operations on an individual basis or in the aggregate. As of June 30, 2025 and December 31, 2024, the Company is not a party to any material legal or administrative proceedings.
| 22. | Subsequent events |
On July 9, 2025, the Company established a subsidiary in China, Xiamen Legend Technology Co., Ltd. (“Lichen Technology”), which is wholly owned by Lichen Zixun. Currently, Lichen Technology do not have operating business yet.
On September 15, 2025, the Company entered into
a certain securities purchase agreement (the “SPA”) with certain investors (the “Purchasers”), pursuant to which
the Company agreed to sell up to
In preparing these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements, the Company has evaluated events and transactions for potential recognition or disclosure through September 19, 2025, the date the unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements were available to be issued. No events require adjustment to or disclosure in the unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-29