
Exhibit 99.1

NASDAQ: TRAW June 2025 Corporate Presentation

Forward - looking statements 2 This presentation contains, and certain oral statements made by management from time to time may contain, “forward - looking state ments” within the meaning of the “safe harbor” provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securiti es Act”), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Such statements include actions, events, results, strategies and expectations and are often identifiable by use of t he words “believes”, “expects”, “intends”, “anticipates”, “plans”, “seeks”, “estimates”, “projects”, “may”, “will”, “could”, “might”, or “continues” or similar expressions. Forward - looking statem ents within this presentation include, but are not limited to, express or implied statements regarding the nature, strategy, opportunities and focus of Traws Pharma, Inc. (“Traws”); the de vel opment, commercial potential and potential benefits of any product candidates; anticipated clinical drug development activities, related timelines and expected milestones; anticipated int eractions with regulatory authorities, including the FDA, HREC, and other international regulatory agencies; and other statements that are not historical fact. All statements other than sta tem ents of historical fact contained in this communication are forward - looking statements. These forward - looking statements are made as of the date they were first issued, and were based on t he then - current expectations, estimates, forecasts, and projections, as well as the beliefs and assumptions of management. There can be no assurance that future developments affecti ng the company will be those that have been anticipated. Forward - looking statements are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, many of which involve factors or circumstances th at are beyond Traws’ control. Traws’ actual results could differ materially from those stated or implied in forward - looking statements due to a number of factors, including but not limit ed to (i) the uncertainties associated with Traws’ product candidates, as well as risks associated with the clinical development and regulatory approval of product candidates, includin g p otential delays in the commencement and completion of clinical trials, studies and evaluations; (ii) risks related to the inability of Traws to obtain sufficient additional capita l t o continue to advance its product candidates and operate its business; (iii) uncertainties in obtaining successful clinical results for product candidates and unexpected costs that may result therefrom; (i v) risks related to the failure to realize any value from product candidates currently being developed and anticipated to be developed in light of inherent risks and difficulties involved in suc cessfully bringing product candidates to market; (v) uncertainties in retaining key personnel, including the executive team and directors; (vi) risks that may stem from changes in the regulato ry, economic and/or political landscape, (vii) disruption and volatility in the global currency, capital, and credit markets; and (viii) risks associated with the possible failure to realize certain an ticipated benefits of Traws’ 2024 merger with Trawsfynydd Therapeutics, Inc., including with respect to future financial and operating results and the other risks and uncertainties in clu ded in Traws’ Annual Report on Form 10 - K for the year ended December 31, 2024 and Traws’ subsequent filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). Actual results and the timing of events could differ materially from those anticipated in such forward - looking statements as a result of these risks and uncertainties. You should not place undue reliance on these forward - looking statements, which are made only as of the date hereof or as of the dates indicated in the forward - looking statements. Traws expressly disclaims any obligation or u ndertaking, unless required by applicable law, to release publicly any updates or revisions to any forward - looking statements contained herein to reflect any change in its expectations with regar d thereto or any change in events, conditions or circumstances on which any such statements are based. This communication does not purport to summarize all of the conditions, risks and oth er attributes of an investment in Traws. This presentation is for informational purposes only and shall not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy the securities of the Traws, nor shall there be any sale of any such securities in any state or jurisdiction in which such offer, solicitation, or sale would be unlawful prior to registration or qualification under the se cur ities laws of such state or jurisdiction. No offer of securities shall be made, except by means of a prospectus meeting the requirements of Section 10 of the Securities Act or an exemption therefrom.

Targeting Critical Viral Threats to Human Health 3 Potential first - in - class bird flu program , with a goal to build out the US strategic stockpile (estimated 300 million to 600 million doses 1 ) and develop as best - in - class therapy with broad label covering seasonal and bird flu Potential best - in - class COVID protease inhibitor to replace existing therapies (>$6B revenue, 2024 2 ), additionally addressing PAXLOVID® - ineligible patients, incidence of clinical rebound and treatment of Long COVID 4 5 F ocusing on small molecule antiviral drugs active against respiratory viruses with pandemic potential Experienced team, supported by recognized institutional investors, including OrbiMed and Perceptive Advisors Actively seeking development and commercialization partners for legacy oncology assets (rigosertib and narazaciclib) Source: 1. TRAW internal information. 2. Pfizer 2024 financial results here, p. 24, Merck 2024 financial results here, p5 = $ 5.7 B + $964M = >$6B

4 Antiviral drugs attack a conserved virus component that does not vary according to seasonal changes in virus Antiviral drugs are small molecules that inhibit the activity of critical viral enzymes and are used specifically to treat active infections or to prevent virus spread to close contacts of an infected person Sources: 1. TRAW information. 2. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMsb2506929 3. BIKTARVY is a registered trademark o f G ilead Science, Inc. 4. PAXLOVID® is a registered trademark of Pfizer, Inc. 5 Antiviral Drugs Represent a Significant Growth Sector for Biopharma 1 V accine use is waning dramatically due to fast development of resistance and regulatory hurdles for approvals, including new guidance restricting broad use in the absence of long - term safety studies 2 Antivirals have experienced continued blockbuster growth (2024 revenue): • BIKTARVY®: $13.4 billion 3 (Gilead: HIV, 2018 introduction) • PAXLOVID®: $5.7 billion 4 (Pfizer: COVID, 2021 introduction) Traws’ next generation antivirals are designed to maximize efficacy and safety while overcoming resistance to existing agents
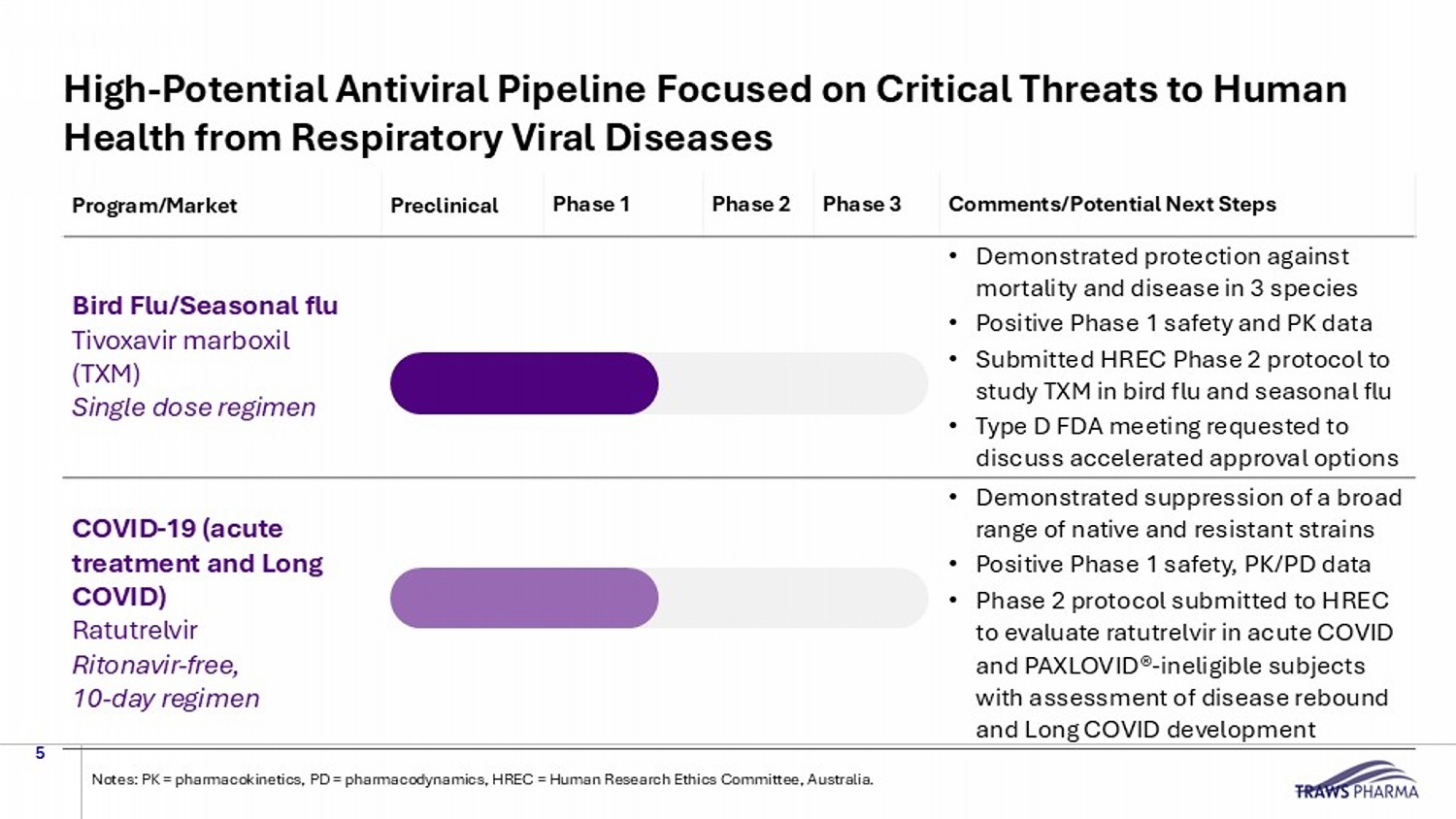
Comments/Potential Next Steps Phase 3 Phase 2 Phase 1 Preclinical Program/Market • Demonstrated protection against mortality and disease in 3 species • Positive Phase 1 safety and PK data • Submitted HREC Phase 2 protocol to study TXM in bird flu and seasonal flu • Type D FDA meeting requested to discuss accelerated approval options Bird Flu/Seasonal flu Tivoxavir marboxil (TXM) Single dose regimen • Demonstrated suppression of a broad range of native and resistant strains • Positive Phase 1 safety, PK/PD data • Phase 2 protocol submitted to HREC to evaluate ratutrelvir in acute COVID and PAXLOVID ® - ineligible subjects with assessment of disease rebound and Long COVID development COVID - 19 (acute treatment and Long COVID) Ratutrelvir Ritonavir - free, 10 - day regimen High - Potential Antiviral Pipeline Focused on Critical Threats to Human Health from Respiratory Viral Diseases 5 Notes: PK = pharmacokinetics, PD = pharmacodynamics, HREC = Human Research Ethics Committee, Australia.
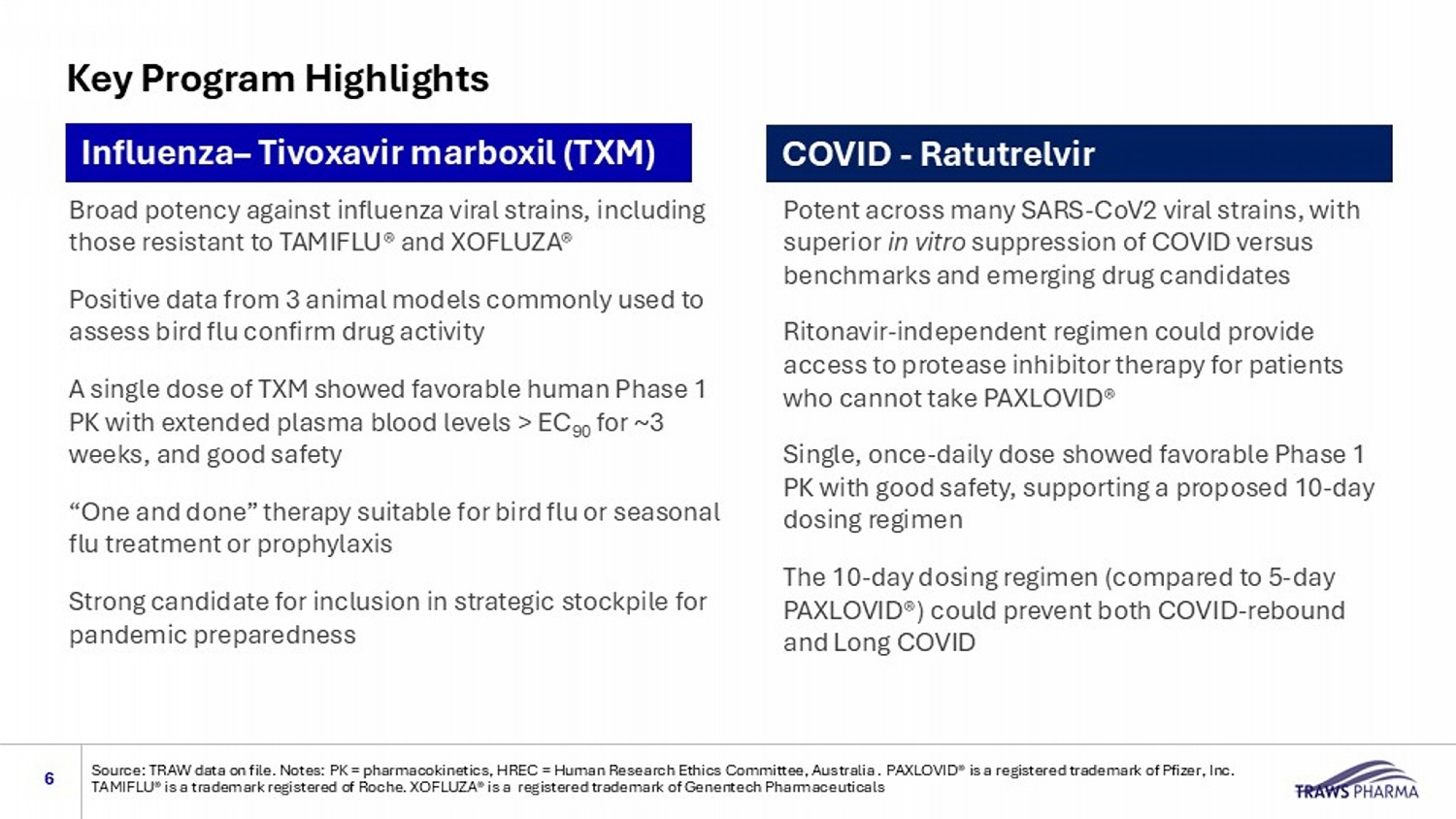
Key Program Highlights 6 Source: TRAW data on file. Notes: PK = pharmacokinetics, HREC = Human Research Ethics Committee, Australia . PAXLOVID® is a r egi stered trademark of Pfizer, Inc. TAMIFLU® is a trademark registered of Roche. XOFLUZA® is a registered trademark of Genentech Pharmaceuticals Influenza – Tivoxavir marboxil (TXM) COVID - Ratutrelvir Broad potency against influenza viral strains, including those resistant to TAMIFLU® and XOFLUZA® Positive data from 3 animal models commonly used to assess bird flu confirm drug activity A single dose of TXM showed favorable human Phase 1 PK with extended plasma blood levels > EC 90 for ~3 weeks, and good safety “One and done” therapy suitable for bird flu or seasonal flu treatment or prophylaxis Strong candidate for inclusion in strategic stockpile for pandemic preparedness Potent across many SARS - CoV2 viral strains, with superior in vitro suppression of COVID versus benchmarks and emerging drug candidates Ritonavir - independent regimen could provide access to protease inhibitor therapy for patients who cannot take PAXLOVID® Single, once - daily dose showed favorable Phase 1 PK with good safety, supporting a proposed 10 - day dosing regimen The 10 - day dosing regimen (compared to 5 - day PAXLOVID® ) could prevent both COVID - rebound and Long COVID
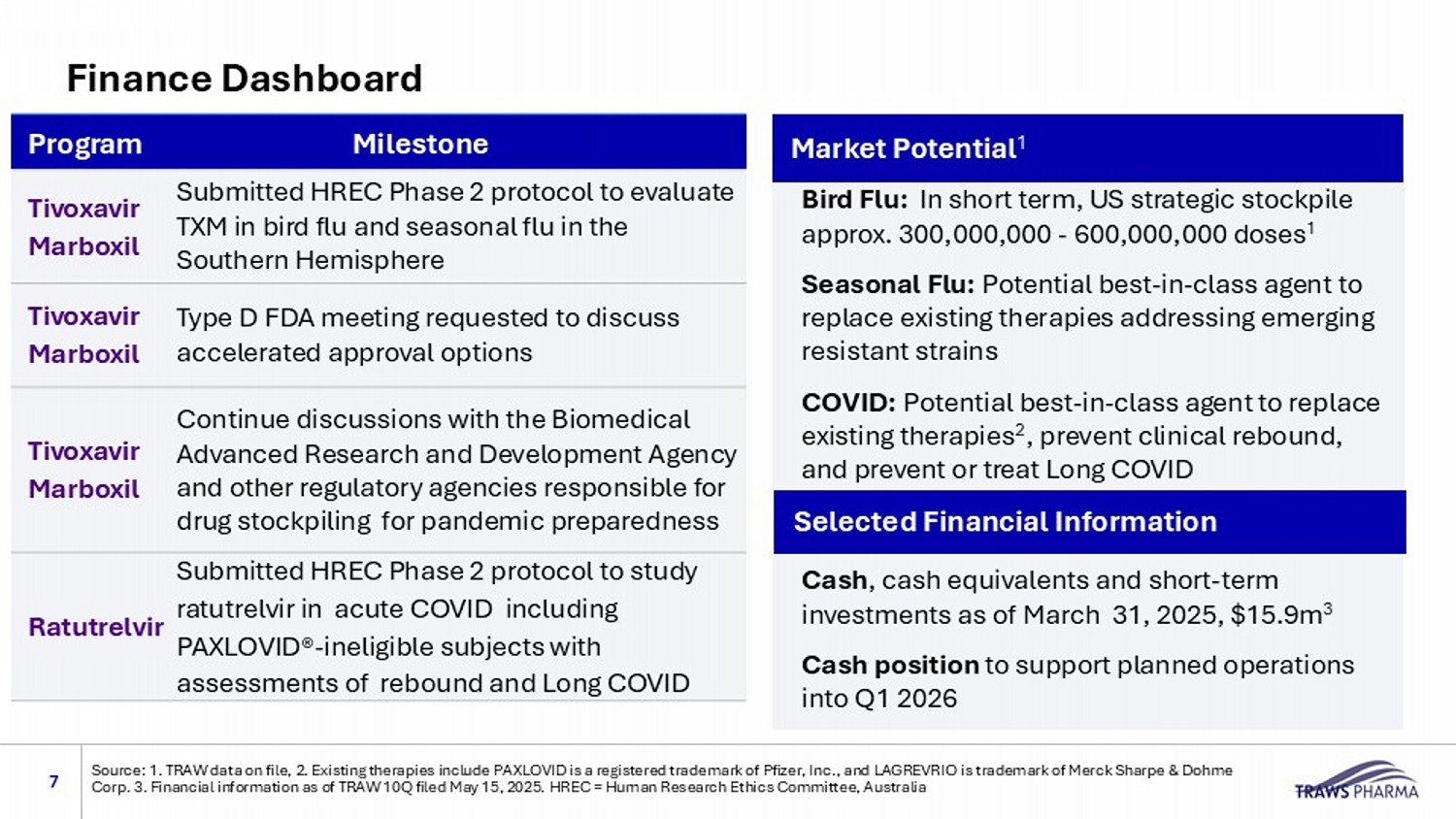
Bird Flu: In short term, US strategic stockpile approx. 300,000,000 - 600,000,000 doses 1 Seasonal Flu: Potential best - in - class agent to replace existing therapies addressing emerging resistant strains COVID: Potential b est - in - class agent to replace existing therapies 2 , prevent clinical rebound, and prevent or treat Long COVID Cash , cash equivalents and short - term investments as of March 31, 2025, $15.9m 3 Cash position to support planned operations into Q1 2026 Selected Financial Information Milestone Program Submitted HREC Phase 2 protocol to evaluate TXM in bird flu and seasonal flu in the Southern Hemisphere Tivoxavir Marboxil Type D FDA meeting requested to discuss accelerated approval options Tivoxavir Marboxil Continue discussions with the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Agency and other regulatory agencies responsible for drug stockpiling for pandemic preparedness Tivoxavir Marboxil Submitted HREC Phase 2 protocol to study ratutrelvir in acute COVID including PAXLOVID® - ineligible subjects with assessments of rebound and Long COVID Ratutrelvir Finance Dashboard Source: 1. TRAW data on file, 2. Existing therapies include PAXLOVID is a registered trademark of Pfizer, Inc., and LAGREVRIO is trademark of Merck Sharpe & Dohme Corp. 3. Financial information as of TRAW 10Q filed May 15, 2025. HREC = Human Research Ethics Committee, Australia Market Potential 1 7

Strong Team with Track Record of Executing and Creating Value Robert R. Redfield, MD Chief Medical Officer C. David Pauza, PhD Chief Science Officer Nora Brennan Interim Chief Financial Officer Board of Directors Nikolay Savchuk, PhD Chief Operating Officer, Director Chairman Jack E. Stover Interim CEO, Director Iain D. Dukes, MA D Phil COO, Director Nikolay Savchuk, PhD Special Advisor, Director Werner Cautreels, PhD Director Trafford Clarke Director Teresa Shoemaker 8 Iain D. Dukes, MA, D Phil Interim CEO, Director
Bird Flu Tivoxavir marboxil (TXM, TRX100) A single - dose investigational, CAP - dependent endonuclease inhibitor for treatment or prevention of H5N1 bird flu 9

Influenza is a Critical Threat To Human Health Today High pandemic potential with no currently approved treatments 10 Major and increasing agricultural impact of bird flu No bird flu therapies approved today 4 5 High historical human mortality from bird flu, with human pandemic potential 1 L imited cross protection provided by current seasonal flu vaccines Inadequate potency of current antiviral agents for bird flu Source: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/cumulative - number - of - confirmed - human - cases - for - avian - influenza - a(h5n1) - reported - to - who -- 2003 - 2025 -- 19 - march - 2025

Tivoxavir Marboxil (TXM): Value Proposition for Bird Flu 11 Differentiating features of TXM, a potent oral antiviral drug candidate A single dose reduced disease and prevented death in 3 preclinical animal models used commonly in flu drug development, with large reductions in lun g virus levels and lung pathology A singl e dose maintained plasma levels above the EC 90 for approximately 3 weeks in Phase 1 human studies 4 5 Broadly effective against bird flu strains including “Texas dairy worker strain”, demonstrated through in vivo studies Large safety window enables use of higher TXM doses, if needed, to treat future emergent resistant strains
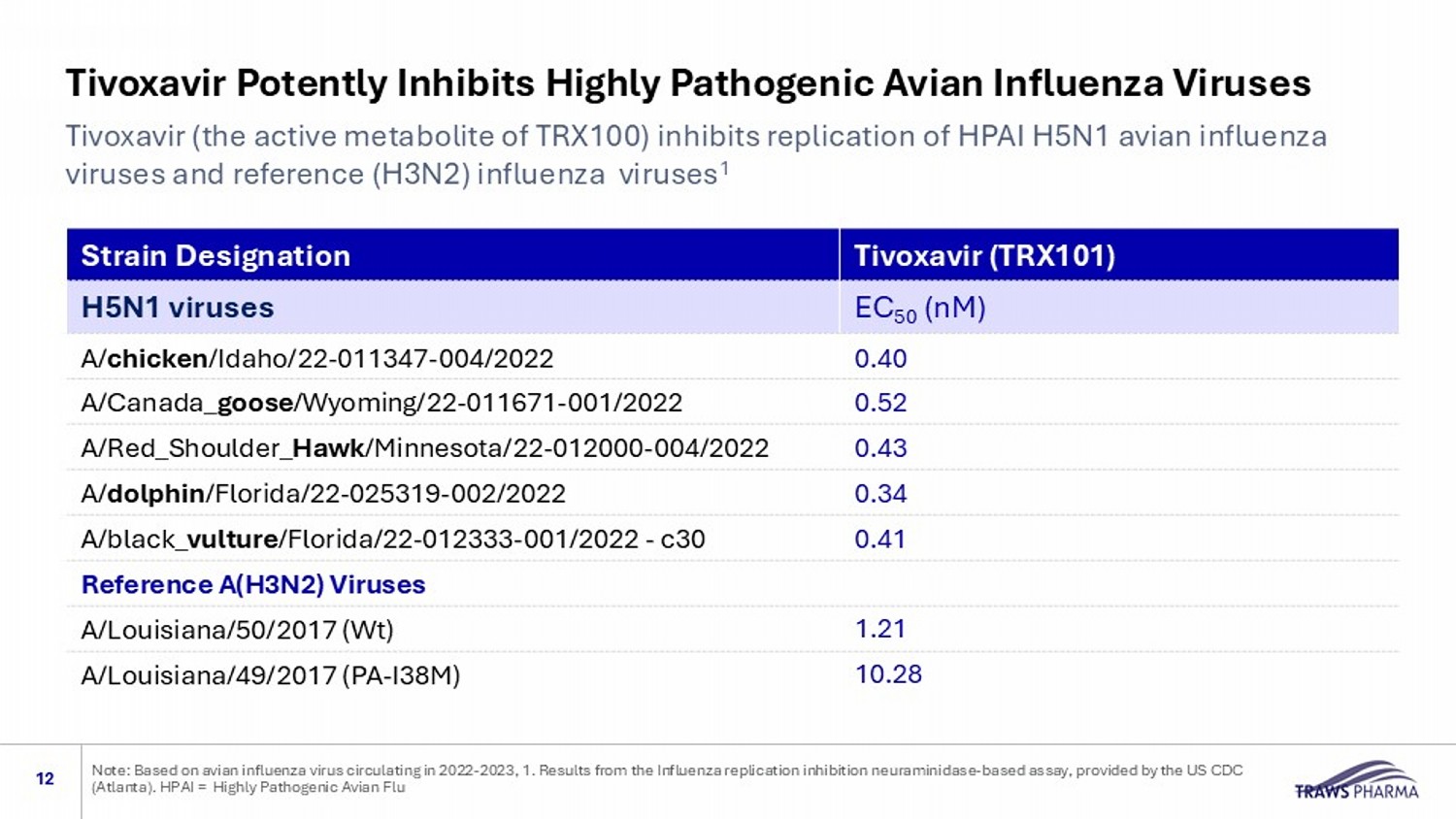
Tivoxavir Potently Inhibits Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses 12 Tivoxavir (the active metabolite of TRX100) inhibits replication of HPAI H5N1 avian influenza viruses and reference (H3N2) influenza viruses 1 Note: Based on avian influenza virus circulating in 2022 - 2023, 1. Results from the Influenza replication inhibition neuraminidas e - based assay, provided by the US CDC (Atlanta). HPAI = Highly Pathogenic Avian Flu Tivoxavir (TRX101) Strain Designation EC 50 (nM) H5N1 viruses 0.40 A/ chicken /Idaho/22 - 011347 - 004/2022 0.52 A/Canada_ goose /Wyoming/22 - 011671 - 001/2022 0.43 A/Red_Shoulder_ Hawk /Minnesota/22 - 012000 - 004/2022 0.34 A/ dolphin /Florida/22 - 025319 - 002/2022 0.41 A/black_ vulture /Florida/22 - 012333 - 001/2022 - c30 Reference A(H3N2) Viruses 1.21 A/Louisiana/50/2017 (Wt) 10.28 A/Louisiana/49/2017 (PA - I38M)
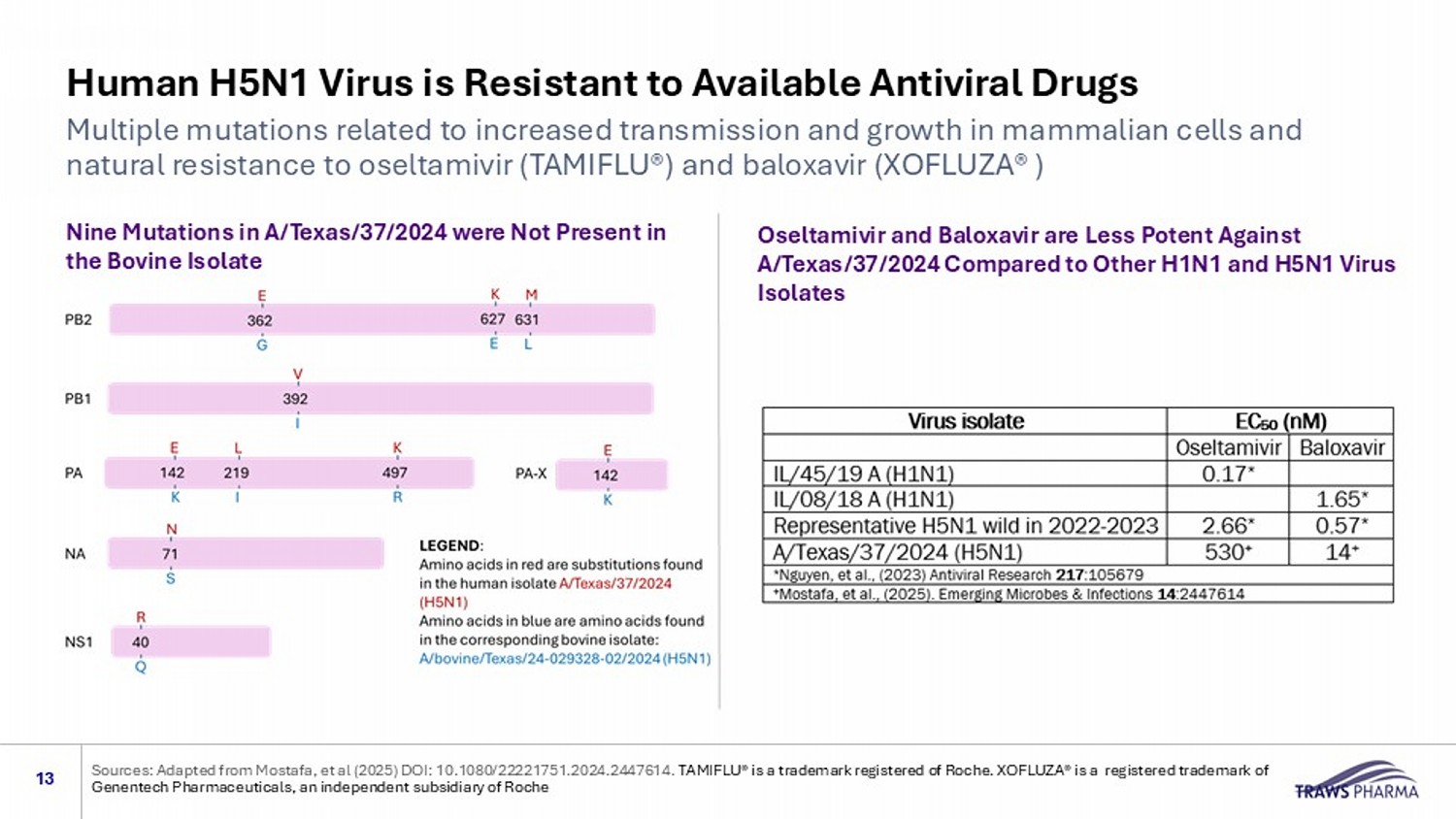
Human H5N1 Virus is Resistant to Available Antiviral Drugs Multiple mutations related to increased transmission and growth in mammalian cells and natural resistance to oseltamivir (TAMIFLU®) and baloxavir (XOFLUZA® ) 13 Nine Mutations in A/Texas/37/2024 were Not Present in the Bovine Isolate Oseltamivir and Baloxavir are Less Potent Against A/Texas/37/2024 Compared to Other H1N1 and H5N1 Virus Isolates Sources: Adapted from Mostafa, et al (2025) DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2447614. TAMIFLU® is a trademark registered of Roche. XOFLUZA® is a registered trademark of Genentech Pharmaceuticals, an independent subsidiary of Roche
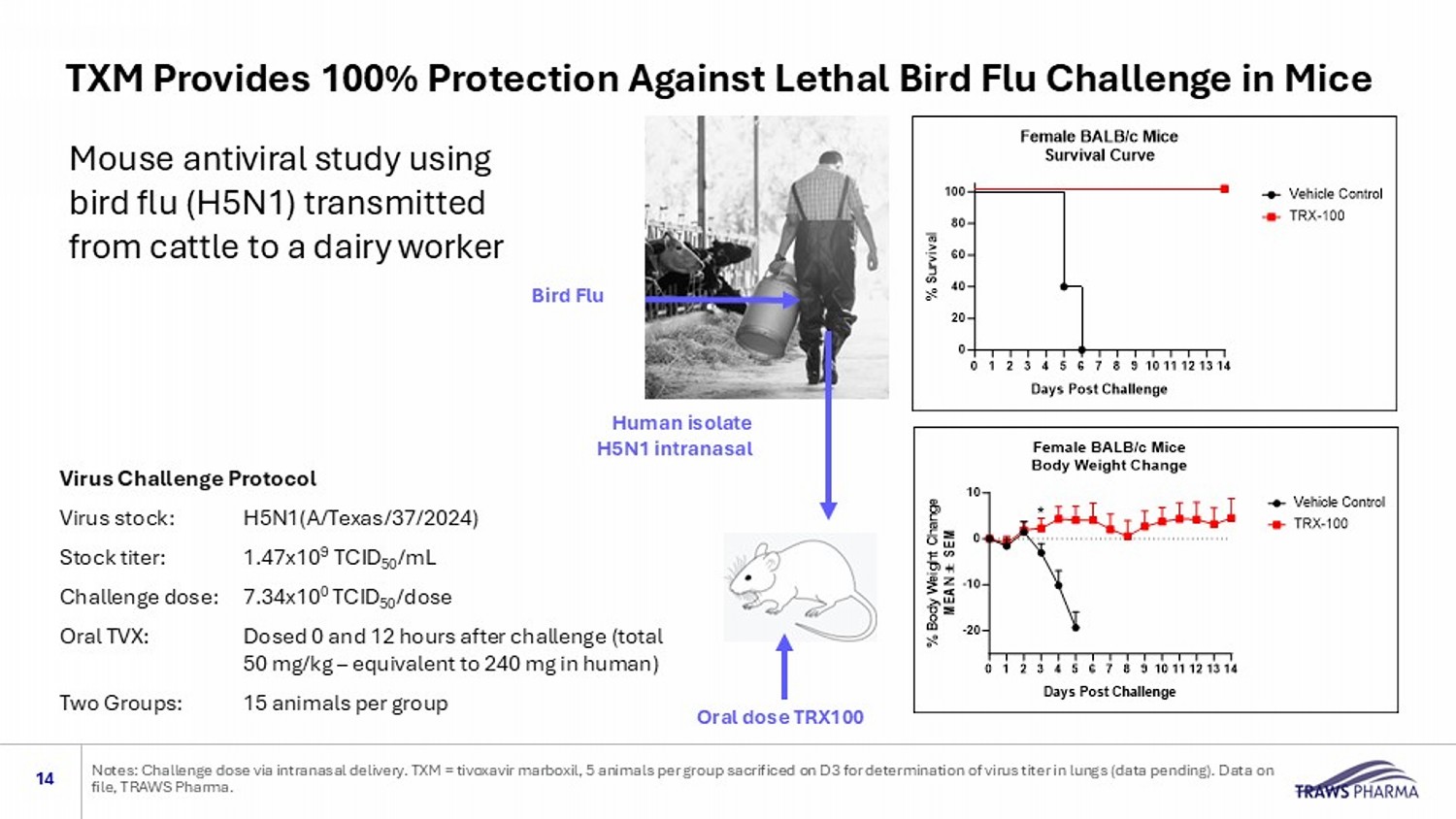
Mouse antiviral study using bird flu (H5N1) transmitted from cattle to a dairy worker 14 Notes: Challenge dose via intranasal delivery. TXM = tivoxavir marboxil, 5 animals per group sacrificed on D3 for determinati on of virus titer in lungs (data pending). Data on file, TRAWS Pharma. Virus Challenge Protocol Virus stock: H5N1(A/Texas/37/2024) Stock titer: 1.47x10 9 TCID 50 /mL Challenge dose: 7.34x10 0 TCID 50 /dose Oral TVX: Dosed 0 and 12 hours after challenge (total 50 mg/kg – equivalent to 240 mg in human) Two Groups: 15 animals per group Bird Flu Human isolate H5N1 intranasal Oral dose TRX100 TXM Provides 100% Protection Against Lethal Bird Flu Challenge in Mice
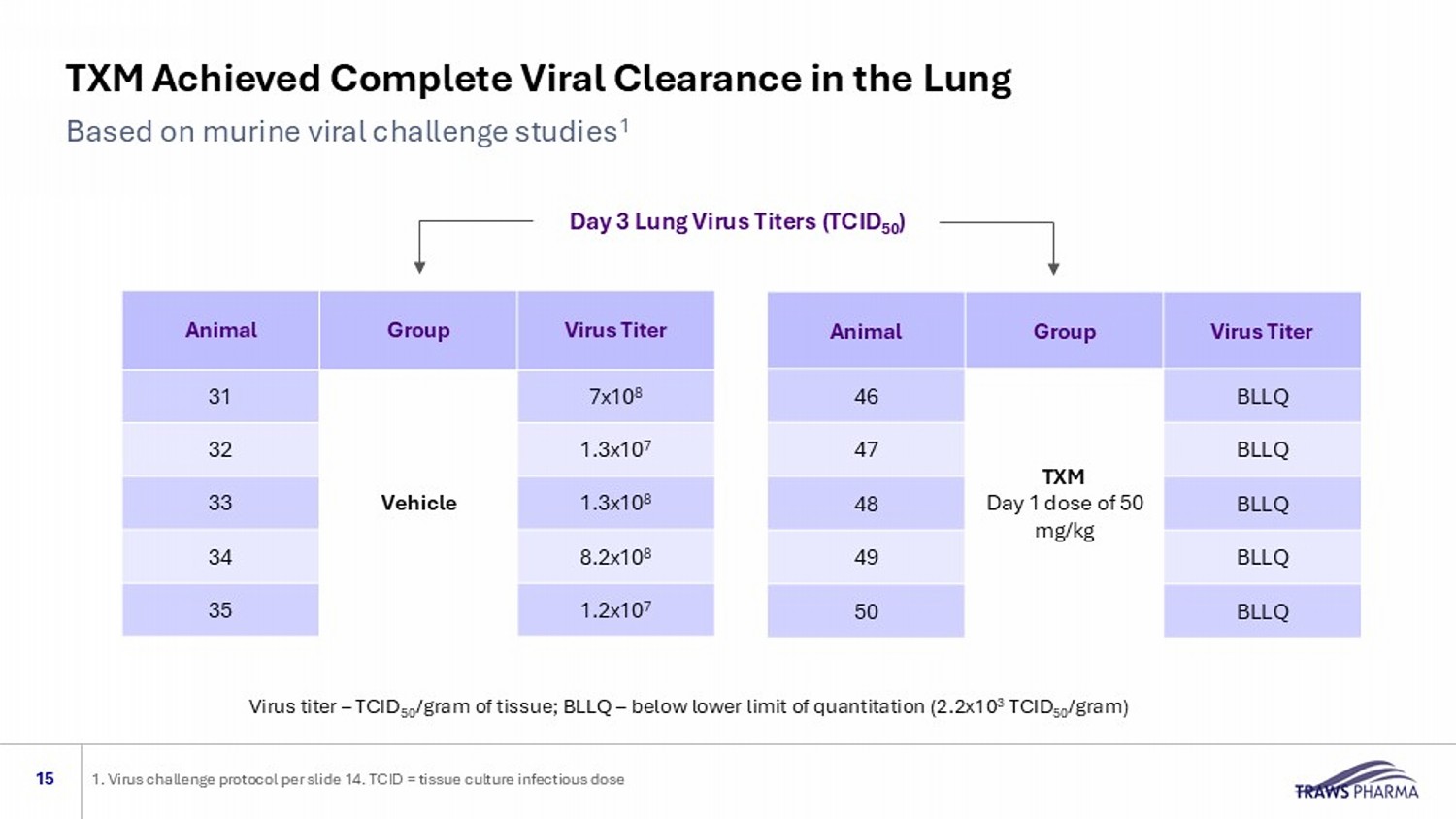
15 1. Virus challenge protocol per slide 14. TCID = tissue culture infectious dose Virus Titer Group Animal 7x10 8 Vehicle 31 1.3x10 7 32 1.3x10 8 33 8.2x10 8 34 1.2x10 7 35 Virus Titer Group Animal BLLQ TXM Day 1 dose of 50 mg/kg 46 BLLQ 47 BLLQ 48 BLLQ 49 BLLQ 50 Virus titer – TCID 50 /gram of tissue; BLLQ – below lower limit of quantitation (2.2x10 3 TCID 50 /gram) Day 3 Lung Virus Titers (TCID 50 ) TXM Achieved Complete Viral Clearance in the Lung Based on murine viral challenge studies 1
Virus Challenge Study in Ferrets: Key Data to Support Clinical and Regulatory Strategy for TXM in Bird Flu 16 Note: TRAW data on file. intranasal challenge/inoculation. Virus challenge stock: A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); 4 animals per group sa crificed at three days after viral inoculation for lung virus burden determinations Oral treatment: 8 hours after virus inoculation Doses: 120 mg human equivalent 240 mg in human equivalent Two Groups: 10 Animals per group (5F/5M), 13 - 15 weeks of age Treated and control Endpoints: Survival, changes in body weight, virus burden in lung and nasal tissues Topline Data: Substantial improvements in disease progression observed after a single dose of TXM • Lethal challenge showed that TXM increased the proportion of surviving animals • Lowered the viral burden in lungs and nasal tissues • Delayed and reduced body weight loss Promising topline data in ferret model using virus isolated from a dairy worker. Viral inoculum: 1X10 3 TCID 50 of A/Texas/37/2024 H5N1 via intranasal instillation Ferret model
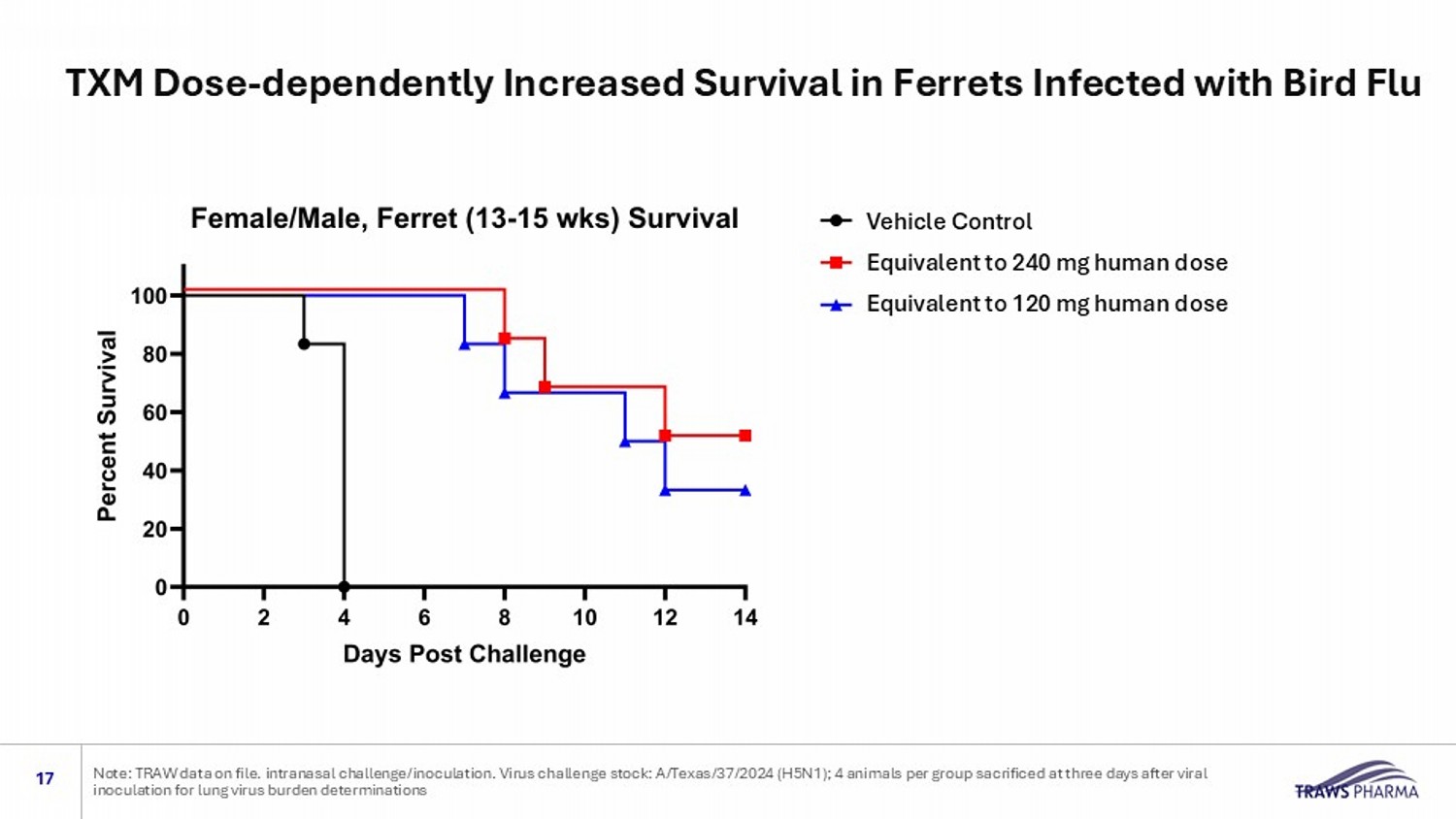
Vehicle Control Equivalent to 240 mg human dose Equivalent to 120 mg human dose TXM Dose - dependently Increased Survival in Ferrets Infected with Bird Flu 17 Note: TRAW data on file. intranasal challenge/inoculation. Virus challenge stock: A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); 4 animals per group sa crificed at three days after viral inoculation for lung virus burden determinations
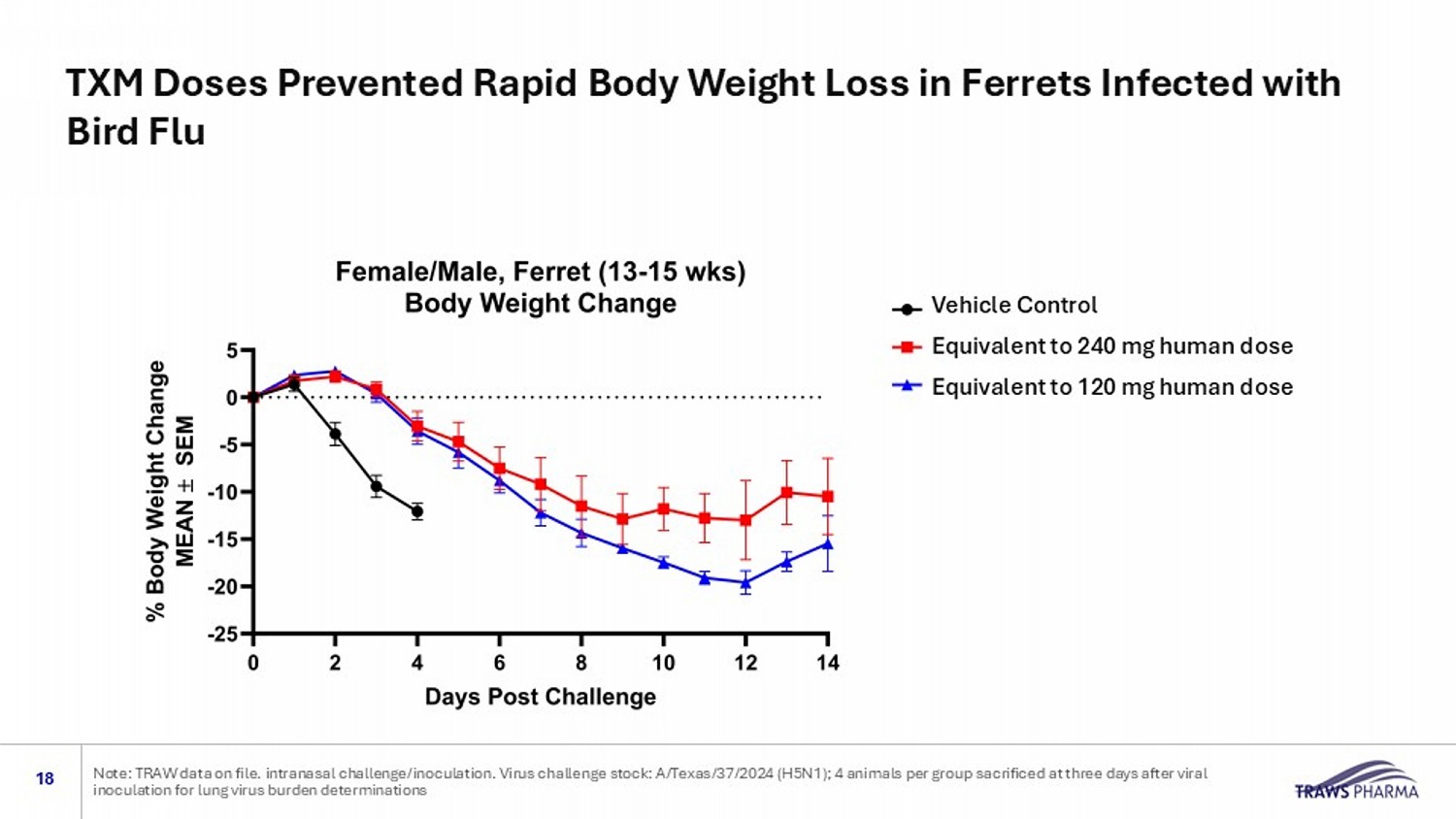
Vehicle Control High dose (equivalent to 240 mg human dose Low dose (equivalent to 120 mg human dose) Vehicle Control Equivalent to 240 mg human dose Equivalent to 120 mg human dose TXM Doses Prevented Rapid Body Weight Loss in Ferrets Infected with Bird Flu 18 Note: TRAW data on file. intranasal challenge/inoculation. Virus challenge stock: A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); 4 animals per group sa crificed at three days after viral inoculation for lung virus burden determinations
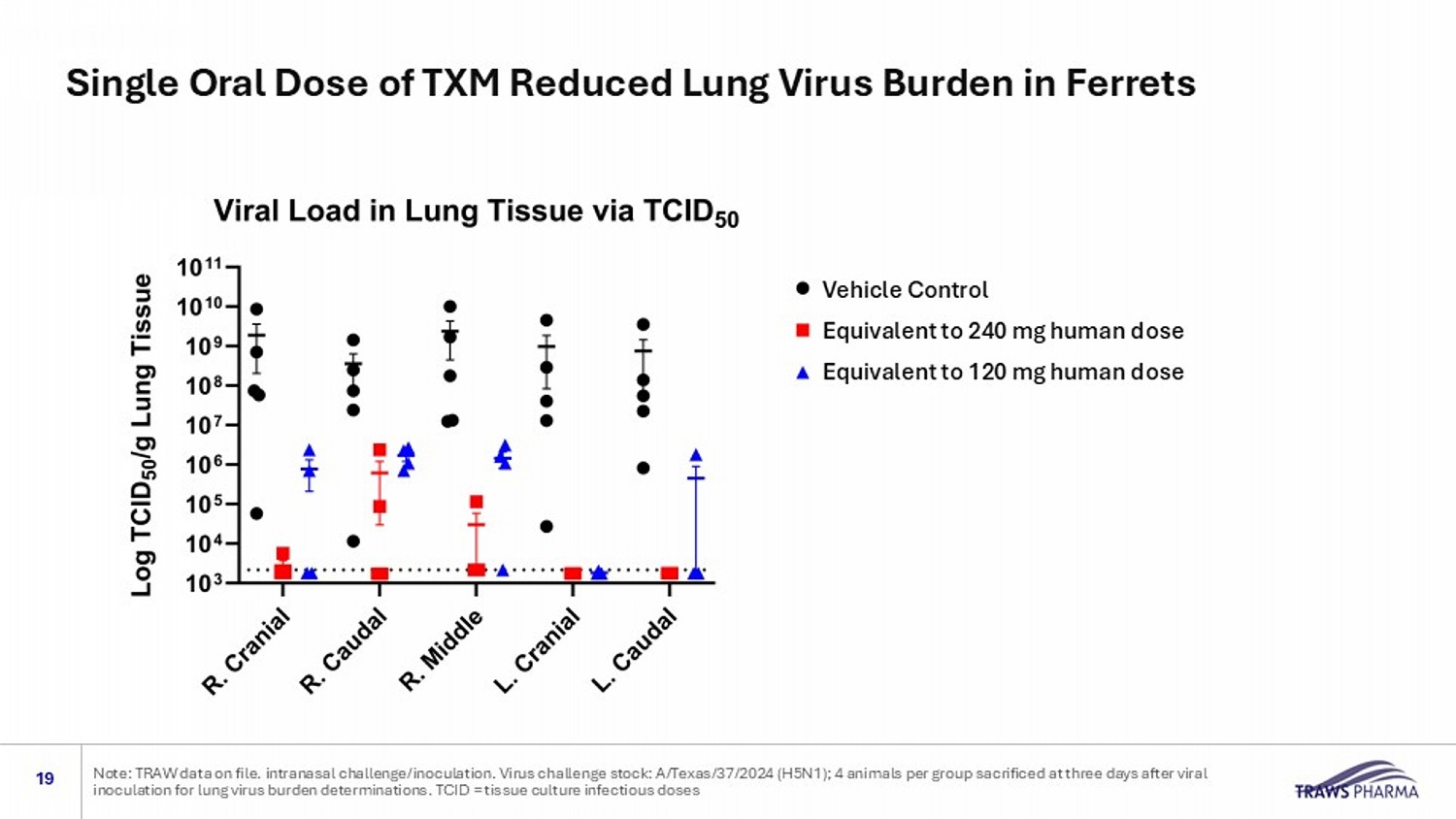
Vehicle Control Equivalent to 240 mg human dose Equivalent to 120 mg human dose Single Oral Dose of TXM Reduced Lung Virus Burden in Ferrets 19 Note: TRAW data on file. intranasal challenge/inoculation. Virus challenge stock: A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); 4 animals per group sa crificed at three days after viral inoculation for lung virus burden determinations. TCID = tissue culture infectious doses
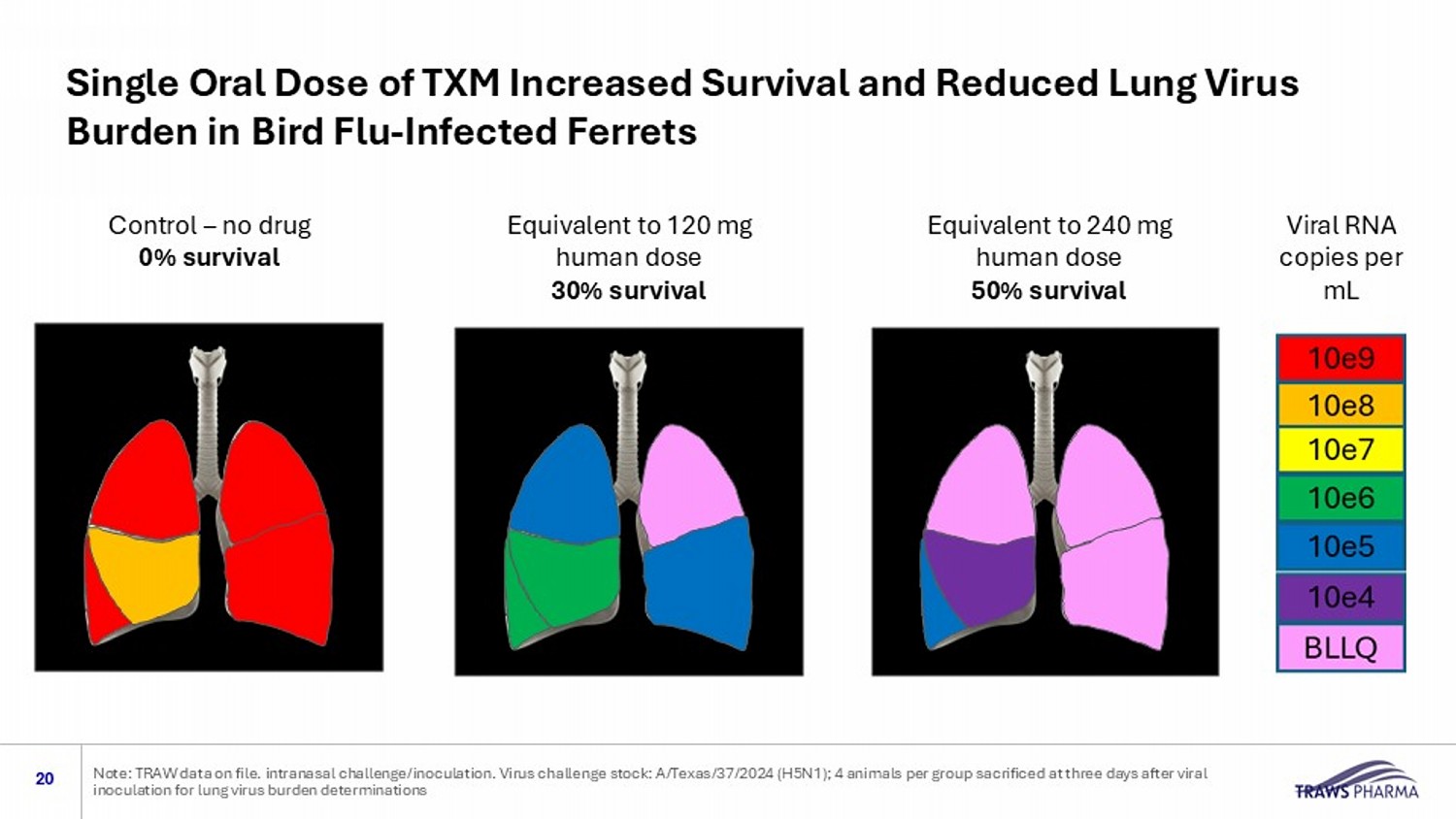
Control – no drug 0% survival Equivalent to 240 mg human dose 50% survival Equivalent to 120 mg human dose 30% survival Viral RNA copies per mL Single Oral Dose of TXM Increased Survival and Reduced Lung Virus Burden in Bird Flu - Infected Ferrets 20 Note: TRAW data on file. intranasal challenge/inoculation. Virus challenge stock: A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); 4 animals per group sa crificed at three days after viral inoculation for lung virus burden determinations
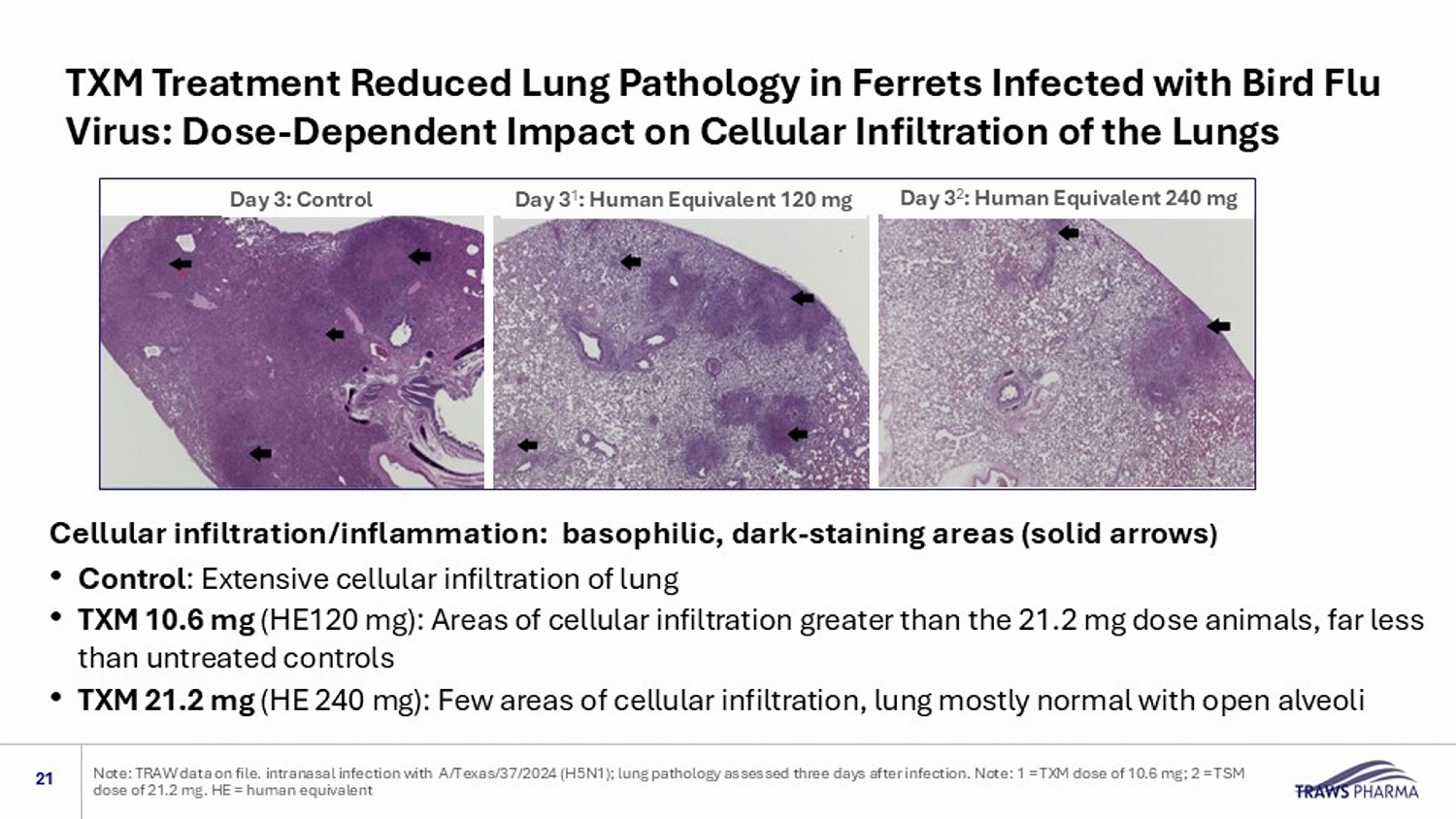
TXM Treatment Reduced Lung Pathology in Ferrets Infected with Bird Flu Virus: Dose - Dependent Impact on Cellular Infiltration of the Lungs 21 Note: TRAW data on file. intranasal infection with A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); lung pathology assessed three days after infectio n. Note: 1 = TXM dose of 10.6 mg; 2 = TSM dose of 21.2 mg. HE = human equivalent Day 3: Control Day 3 2 : Human Equivalent 240 mg Day 3 1 : Human Equivalent 120 mg Cellular infiltration/inflammation: basophilic, dark - staining areas (solid arrows ) • Control : Extensive cellular infiltration of lung • TXM 10.6 mg (HE120 mg): Areas of cellular infiltration greater than the 21.2 mg dose animals, far less than untreated controls • TXM 21.2 mg (HE 240 mg): Few areas of cellular infiltration, lung mostly normal with open alveoli
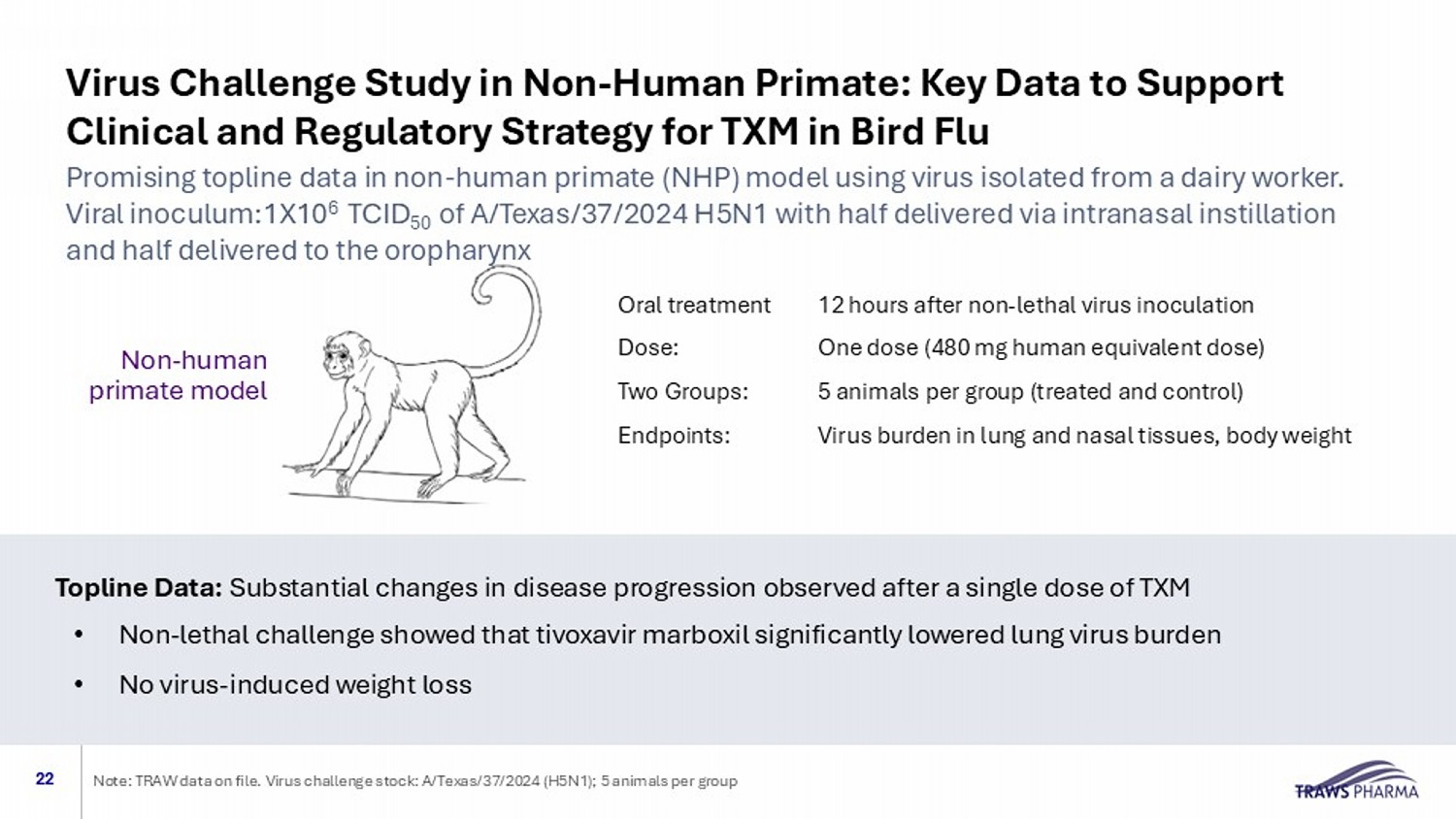
Virus Challenge Study in Non - Human Primate: Key Data to Support Clinical and Regulatory Strategy for TXM in Bird Flu 22 Oral treatment 12 hours after non - lethal virus inoculation Dose: One dose (480 mg human equivalent dose) Two Groups: 5 animals per group (treated and control) Endpoints: Virus burden in lung and nasal tissues, body weight Non - human primate model Topline Data: Substantial changes in disease progression observed after a single dose of TXM • Non - lethal challenge showed that tivoxavir marboxil significantly lowered lung virus burden • No virus - induced weight loss Promising topline data in non - human primate (NHP) model using virus isolated from a dairy worker. Viral inoculum:1X10 6 TCID 50 of A/Texas/37/2024 H5N1 with half delivered via intranasal instillation and half delivered to the oropharynx Note: TRAW data on file. Virus challenge stock: A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); 5 animals per group
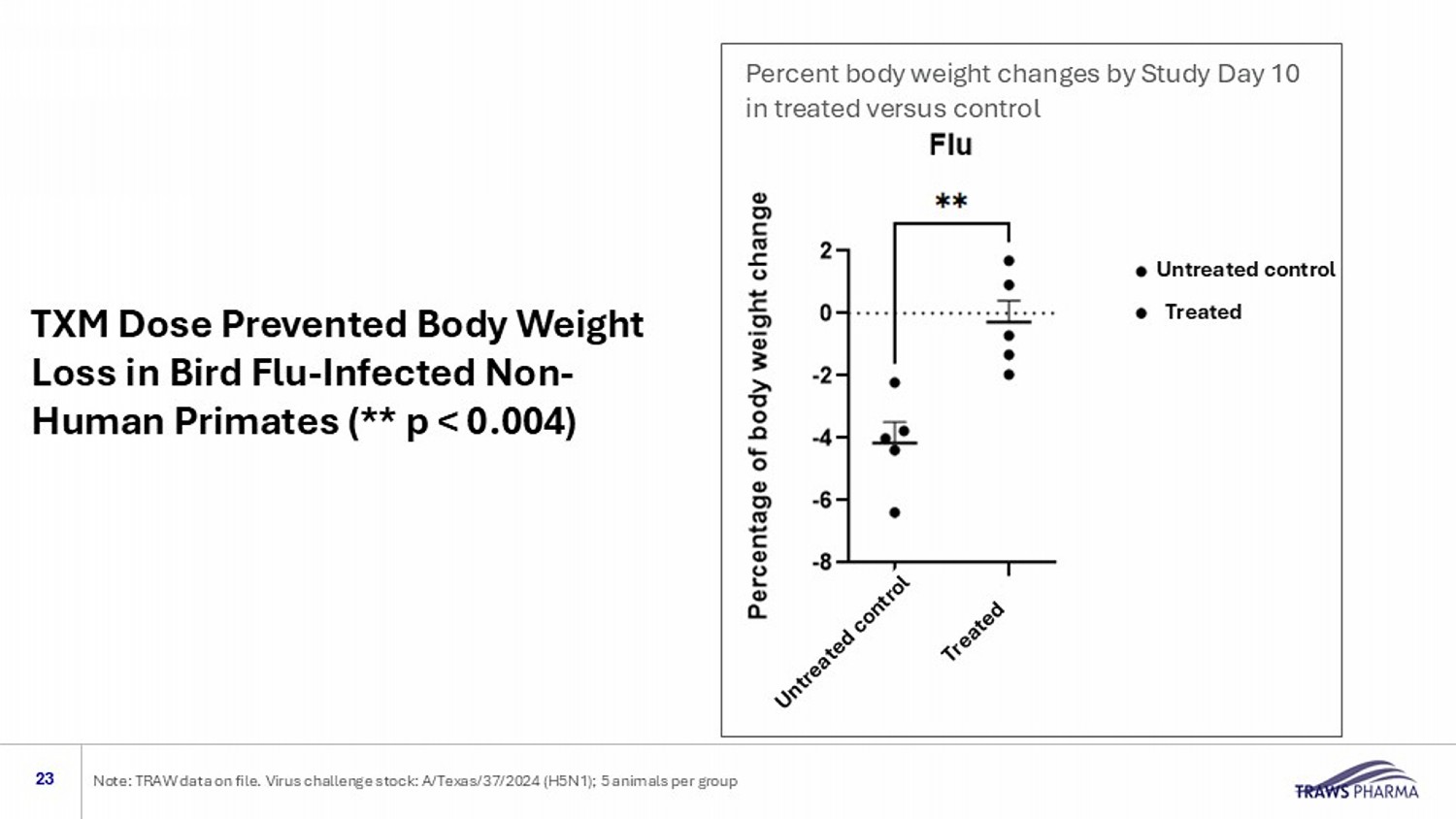
Percent body weight changes by Study Day 10 in treated versus control TXM Dose Prevented Body Weight Loss in Bird Flu - Infected Non - Human Primates (** p < 0.004) 23 Note: TRAW data on file. Virus challenge stock: A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); 5 animals per group Treated Untreated control
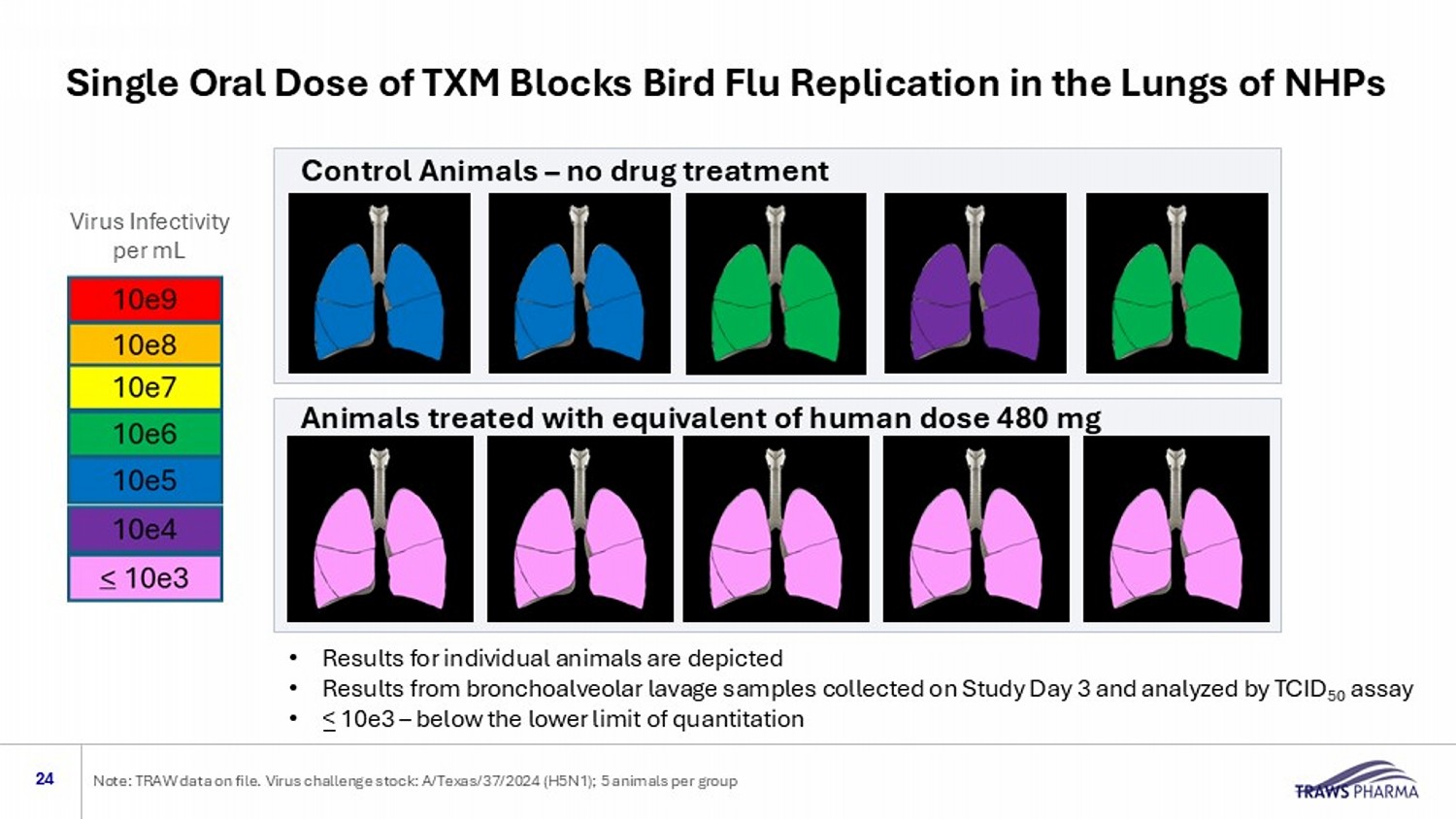
Control Animals – no drug treatment • Results for individual animals are depicted • Results from bronchoalveolar lavage samples collected on Study Day 3 and analyzed by TCID 50 assay • < 10e3 – below the lower limit of quantitation Animals treated with equivalent of human dose 480 mg Virus Infectivity per mL Single Oral Dose of TXM Blocks Bird Flu Replication in the Lungs of NHPs 24 Note: TRAW data on file. Virus challenge stock: A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); 5 animals per group
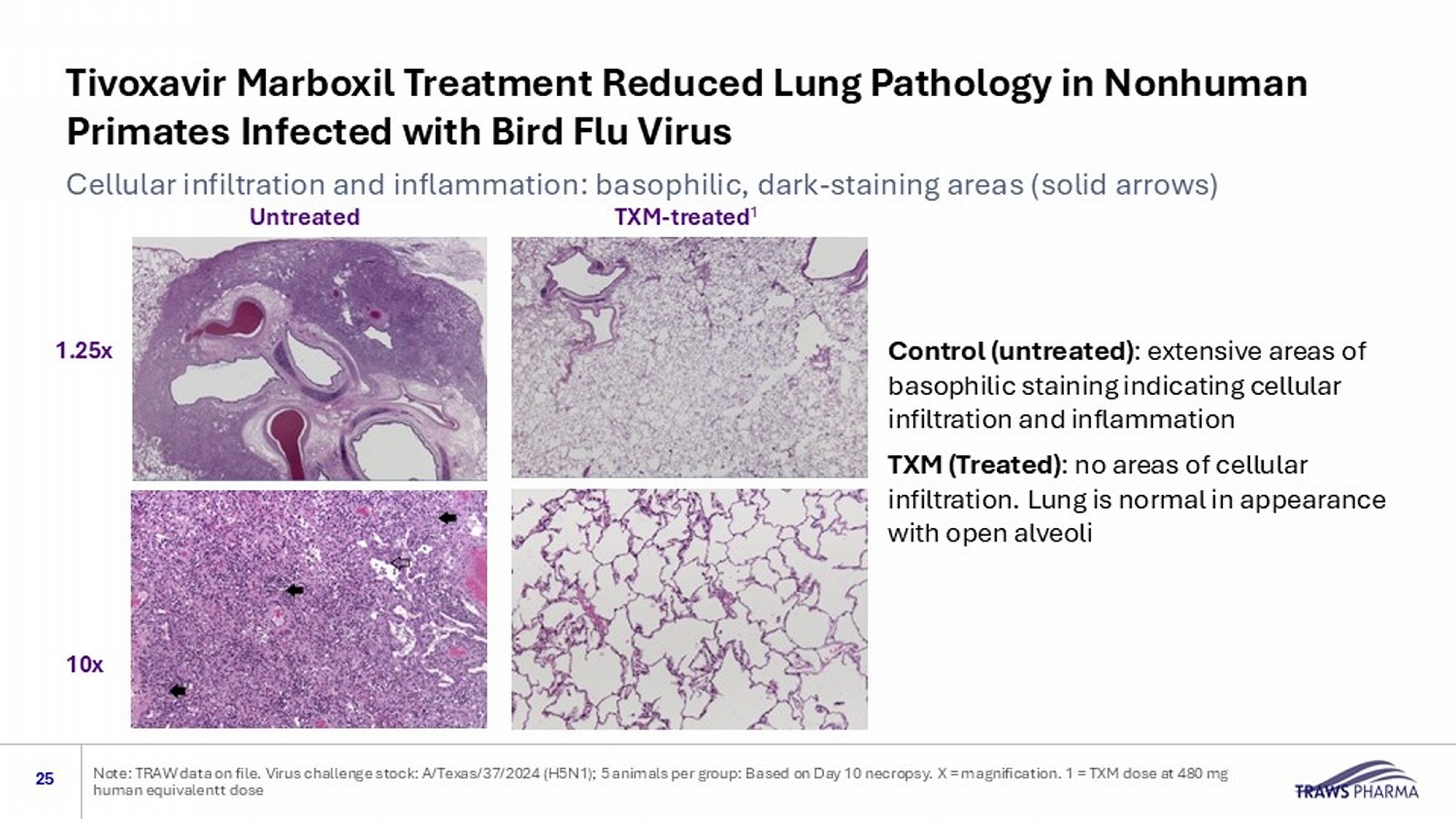
Tivoxavir Marboxil Treatment Reduced Lung Pathology in Nonhuman Primates Infected with Bird Flu Virus 25 Note: TRAW data on file. Virus challenge stock: A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); 5 animals per group: Based on Day 10 necropsy. X = ma gni fication. 1 = TXM dose at 480 mg human equivalent t dose Cellular infiltration and inflammation: basophilic, dark - staining areas (solid arrows) Untreated TXM - treated 1 Control (untreated) : extensive areas of basophilic staining indicating cellular infiltration and inflammation TXM (Treated) : no areas of cellular infiltration. Lung is normal in appearance with open alveoli 1.25x 10x
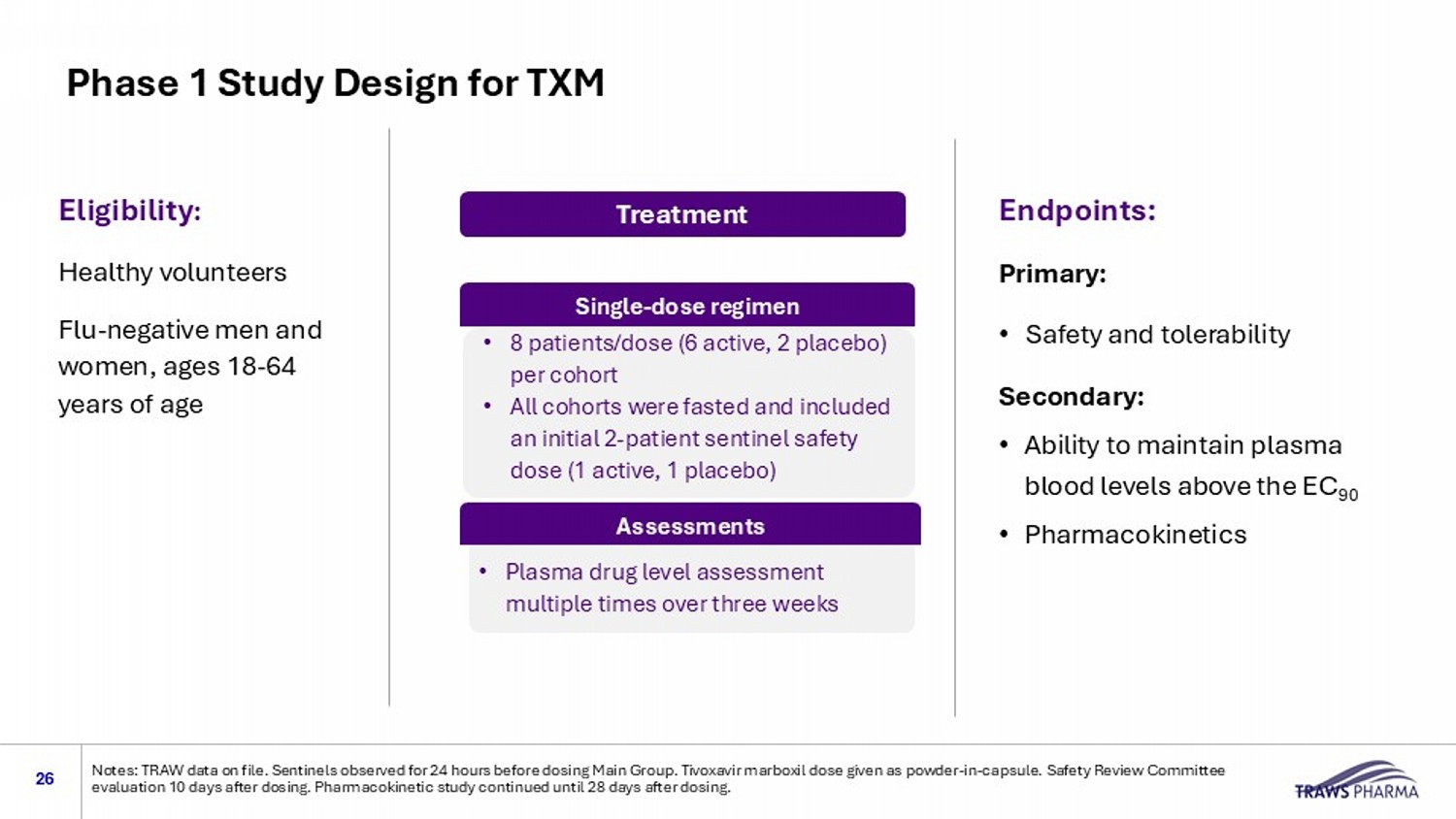
Phase 1 Study Design for TXM 26 Notes: TRAW data on file. Sentinels observed for 24 hours before dosing Main Group. Tivoxavir marboxil dose given as powder - in - c apsule. Safety Review Committee evaluation 10 days after dosing. Pharmacokinetic study continued until 28 days after dosing. Eligibility : Healthy volunteers Flu - negative men and women, ages 18 - 64 years of age Endpoints: Primary: • Safety and tolerability Secondary: • Ability to maintain plasma blood levels above the EC 90 • Pharmacokinetics Treatment 80 mg,120 mg, 240 mg, 480 mg doses • 8 patients/dose (6 active, 2 placebo) per cohort • All cohorts were fasted and included an initial 2 - patient sentinel safety dose (1 active, 1 placebo) Single - dose regimen Assessments • Plasma drug level assessment multiple times over three weeks
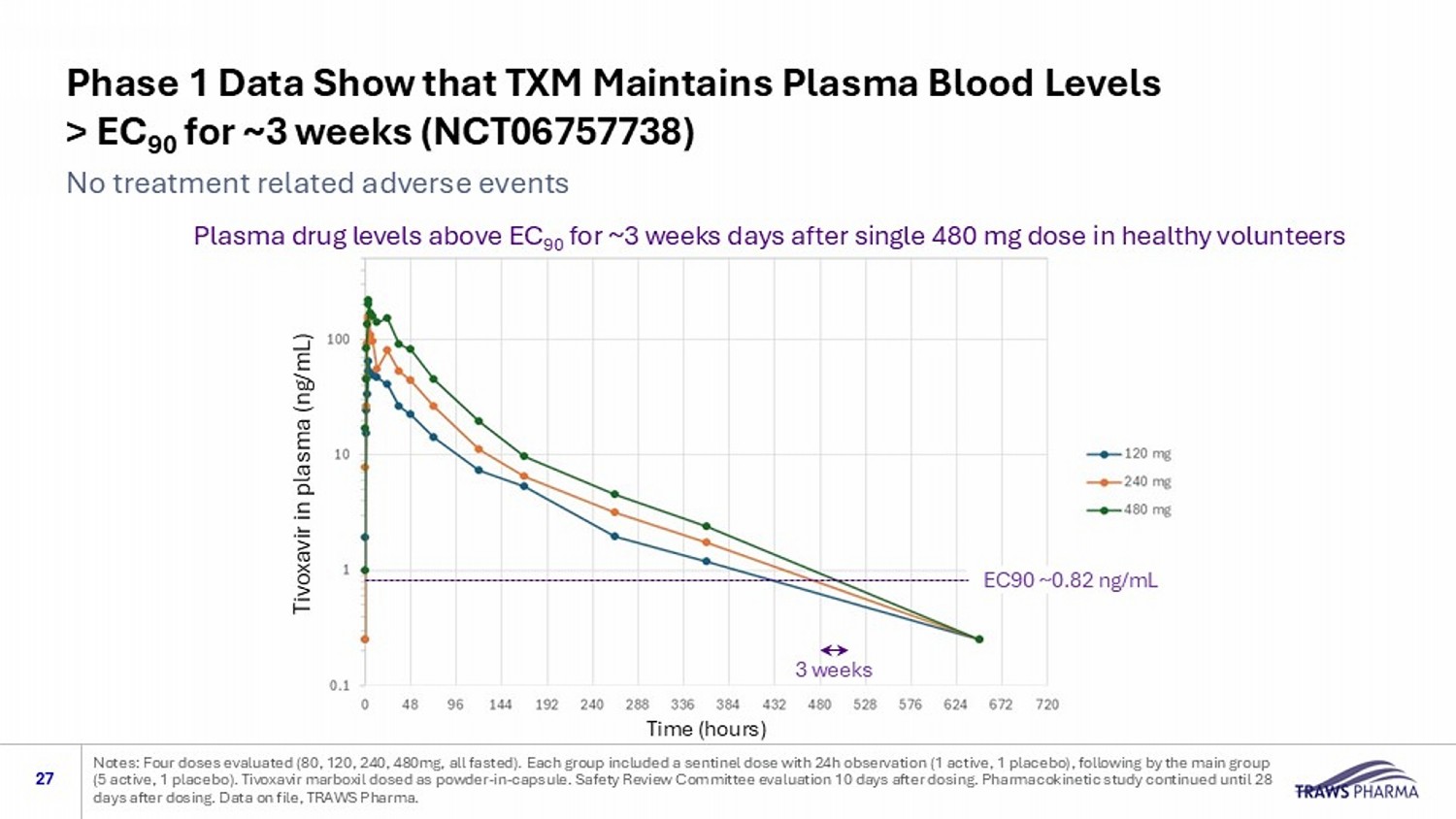
Phase 1 Data Show that TXM Maintains Plasma Blood Levels > EC 90 for ~3 weeks (NCT06757738) 27 No treatment related adverse events Notes: Four doses evaluated (80, 120, 240, 480mg, all fasted). Each group included a sentinel dose with 24h observation (1 ac tiv e, 1 placebo), following by the main group (5 active, 1 placebo). Tivoxavir marboxil dosed as powder - in - capsule. Safety Review Committee evaluation 10 days after dosing. P harmacokinetic study continued until 28 days after dosing. Data on file, TRAWS Pharma. Tivoxavir in plasma (ng/mL) Plasma drug levels above EC 90 for ~3 weeks days after single 480 mg dose in healthy volunteers Time (hours) EC90 ~0.82 ng/mL 3 weeks
Continuing Dialog with FDA to Support Seasonal/Bird Flu Strategy 28 Note: CFR314.600 thru 314.650 , October 2015 , https://www.fda.gov/media/88625/download Regulatory strategy focused on the Animal Rule to accelerate development, with plans for a combined dose - ranging efficacy/safety study in seasonal and bird flu infected patients ▪ Animal Rule intended to provide a path to approval in situations when human clinical studies would be unethical or impractical ▪ Allows FDA to rely on adequate and well - controlled animal efficacy studies to support approval of a drug ▪ Demonstration of human safety is a requirement ▪ Submitted HREC Phase 2 protocol to evaluate TXM in bird flu and seasonal flu ▪ Submitted Type D FDA meeting request to discuss accelerated approval options
Sources: 1. CFR314.600 thru 314.650, October 2015, https://www.fda.gov/media/88625/download. 2 . Traws information 3. b ird flu case fatality rate: WHO information : https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default - source/wpro --- documents/emergency/surveillance/avian - influenza/ai_20250131.pdf. TXM Could Be a Fit for the “Animal Rule” 1,2 Human challenge studies of bird flu are not possible • Virus evolved to a more virulent strain (dairy worker, mild symptoms) • History of A/H5N1 virus strains with up to 50% case fatality rate 3 • Virus can be 100% fatal in 3 - 5 days in animals (mice, ferrets, NHP) 2 • Placebo - controlled trials would be unethical and not feasible • Preclinical studies used commonly accepted flu models (mice, ferrets and non - human primates) • Positive Phase 1 safety/dosing escalation data (healthy volunteers) includes dose levels that were protective in animal studies • Maintained plasma levels above the EC 90 for more than 3 weeks, with good overall safety Requires Adequate and Well - Controlled Animal Studies Exceptional Pathogenic Potential Human Safety and Pharmacokinetics are Required 29
Seasonal Influenza Tivoxavir marboxil (TXM, TRX100) Potency against seasonal influenza, including drug resistant strains 30

Influenza is a Critical Threat To Human Health Today 1 31 Seasonal variation necessitates continual development of vaccines, and vaccines provide incomplete protection and have limited utilization Antiviral drugs attack highly conserved targets that are not subject to seasonal variation 5 Influenz a continues to be a major cause of mortality and burden on the healthcare system Antiviral drugs have a critical role in reducing morbidity and mortality from influenza Antiviral drugs are only used when influenza is present in an infected person or a risk to family and close contacts Sources: 1. Traws information

Influenza Continues to be a Critical Threat to Human Health 32 Notes: CDC information
33 COVID - 19 Ratutrelvir (TRX01) Investigational Main protease (Mpro) inhibitor Ritonavir - independent,10 - day, single pill, once - daily dosing regimen
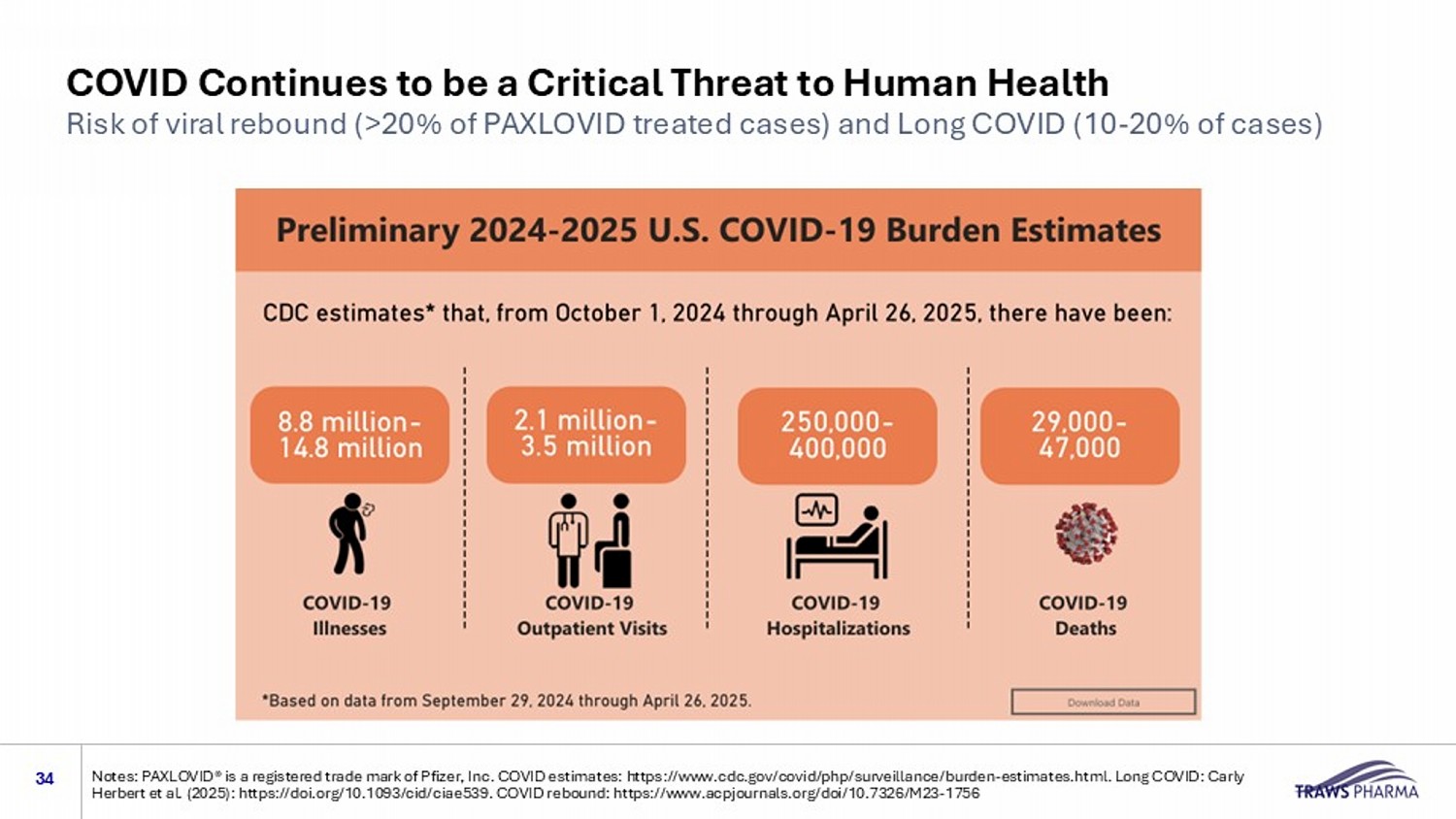
COVID Continues to be a Critical Threat to Human Health Risk of viral rebound (>20% of PAXLOVID treated cases) and Long COVID (10 - 20% of cases) 34 Notes: PAXLOVID® is a registered trade mark of Pfizer, Inc. COVID estimates: https://www.cdc.gov/covid/php/surveillance/burde n - e stimates.html. Long COVID: Carly Herbert et al. (2025): https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciae539. COVID rebound: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23 - 1756
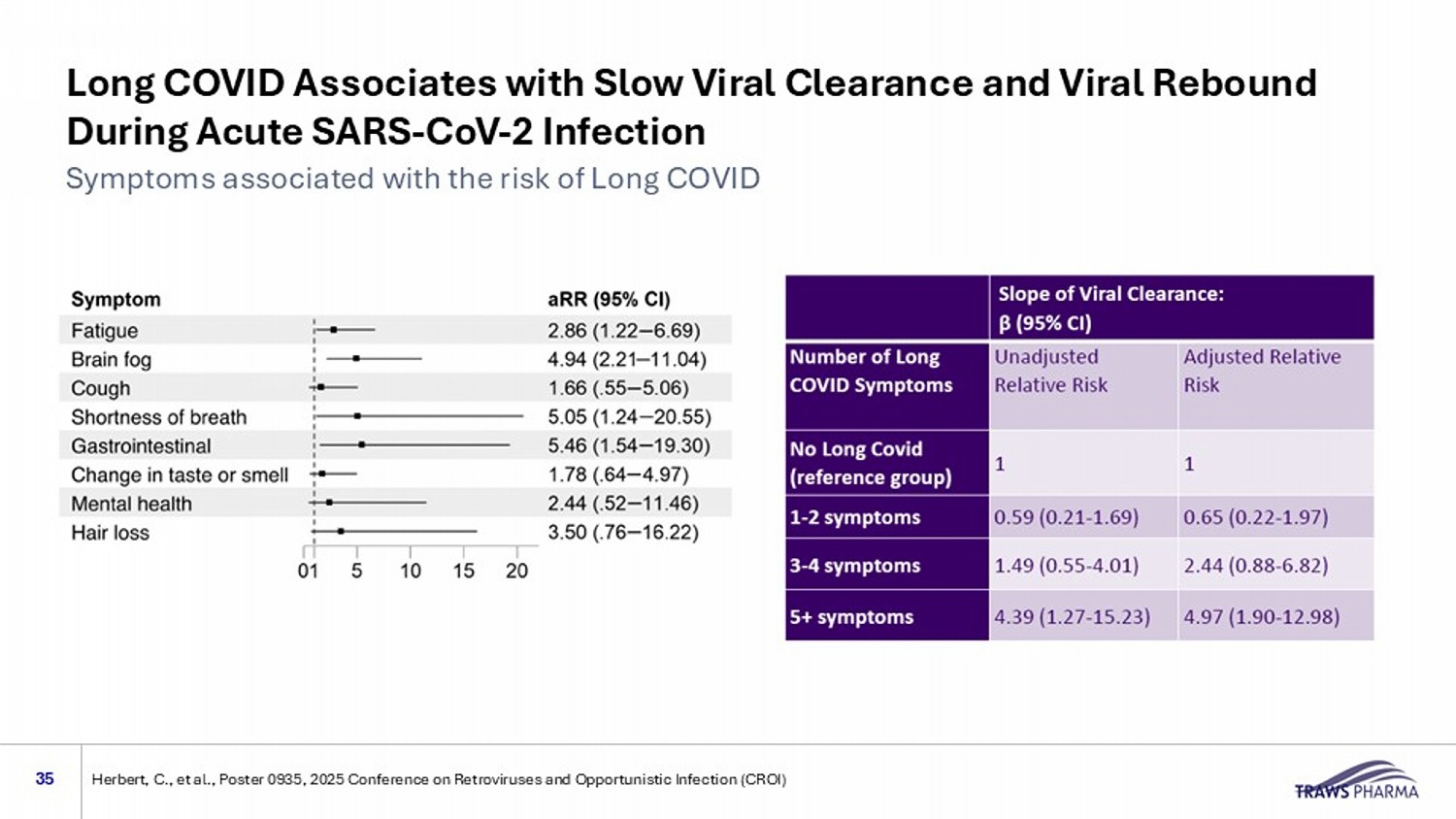
Long COVID Associates with Slow Viral Clearance and Viral Rebound During Acute SARS - CoV - 2 Infection 35 Symptoms associated with the risk of Long COVID Herbert, C., et al., Poster 0935, 2025 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infection (CROI)

Why Improving COVID Therapy Matters Significant cause of human disease and mortality in vulnerable populations 1 36 Increasing clinical and economic burden of Long COVID Current approved antiviral, PAXLOVID®, is contra - indicated in vulnerable populations, including the elderly and the immunocompromised, due to ritonavir - based drug - drug interactions The drop in vaccine use, regulatory hurdles slowing vaccine approval, and poor match of vaccines with current variants increases the spread and potential for disease Approved PAXLOVID® label limited to 5 - days, which may be insufficient. Sources and Notes: 1. Traws information, 2. Carly Herbert et al. (2025) Clinical Infectious Diseases. https://doi.org/10.109 3/c id/ciae539. PAXLOVID® is a registered trademark of Pfizer, Inc COVID is now established as a long - term public health challenge with an increasing burden of people suffering from Post - Acute Sequelae of COVID (PASC, aka Long COVID) 2
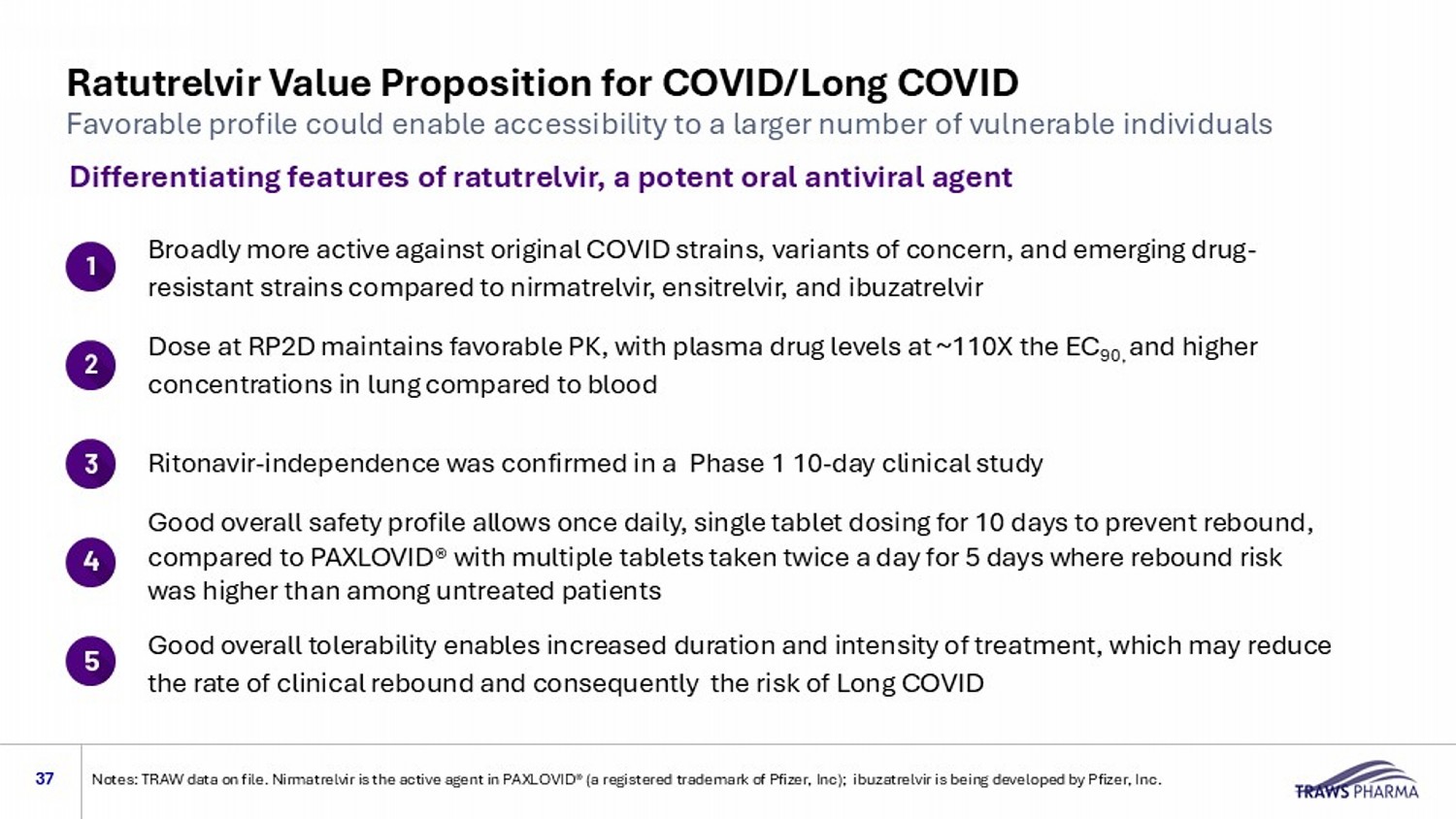
Ratutrelvir Value Proposition for COVID/Long COVID 37 Differentiating features of ratutrelvir, a potent oral antiviral agent Dose at RP2D maintains favorable PK, with plasma drug levels at ~110X the EC 9 0, and higher concentrations in lung compared to blood Broadly more active against original COVID strains, variants of concern, and emerging drug - resistant strains compared to nirmatrelvir, ensitrelvir, and ibuzatrelvir Ritonavir - independence was confirmed in a Phase 1 10 - day clinical study Good overall tolerability enables increased duration and intensity of treatment, which may reduce the rate of clinical rebound and consequently the risk of Long COVID Good overall safety profile allows once daily, single tablet dosing for 10 days to prevent rebound, compared to PAXLOVID® with multiple tablets taken twice a day for 5 days where rebound risk was higher than among untreated patients Favorable profile could enable accessibility to a larger number of vulnerable individuals Notes: TRAW data on file. Nirmatrelvir is the active agent in PAXLOVID® (a registered trademark of Pfizer, Inc); ibuzatrelvi r i s being developed by Pfizer, Inc.
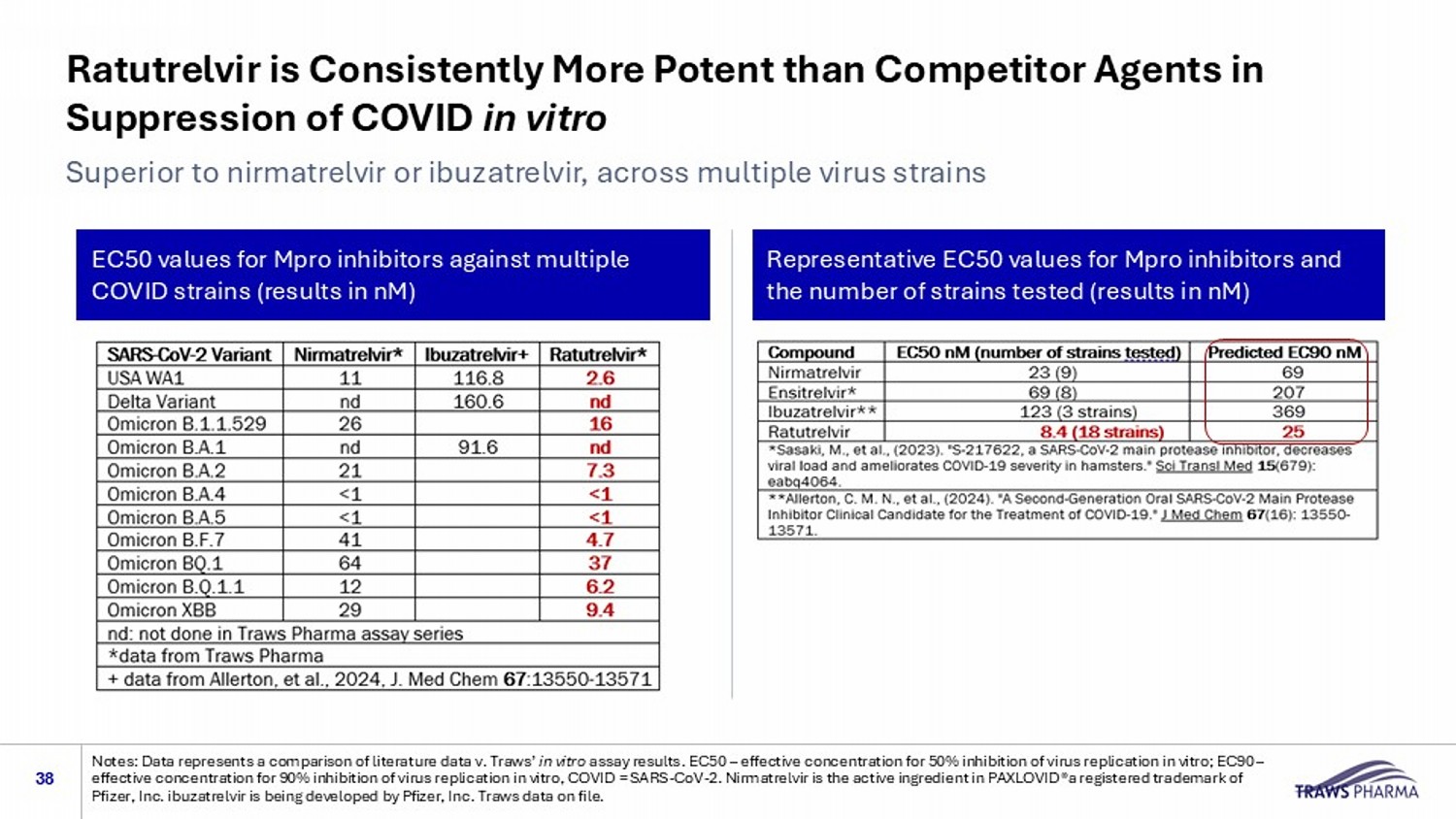
Ratutrelvir is Consistently More Potent than Competitor Agents in Suppression of COVID in vitro 38 Superior to nirmatrelvir or ibuzatrelvir, across multiple virus strains Notes: Data represents a comparison of literature data v. Traws’ in vitro assay results. EC50 – effective concentration for 50% inhibition of virus replication in vitro; EC90 – effective concentration for 90% inhibition of virus replication in vitro, COVID = SARS - CoV - 2. Nirmatrelvir is the active ingredi ent in PAXLOVID®a registered trademark of Pfizer, Inc. ibuzatrelvir is being developed by Pfizer, Inc. Traws data on file. EC50 values for Mpro inhibitors against multiple COVID strains (results in nM) Representative EC50 values for Mpro inhibitors and the number of strains tested (results in nM)
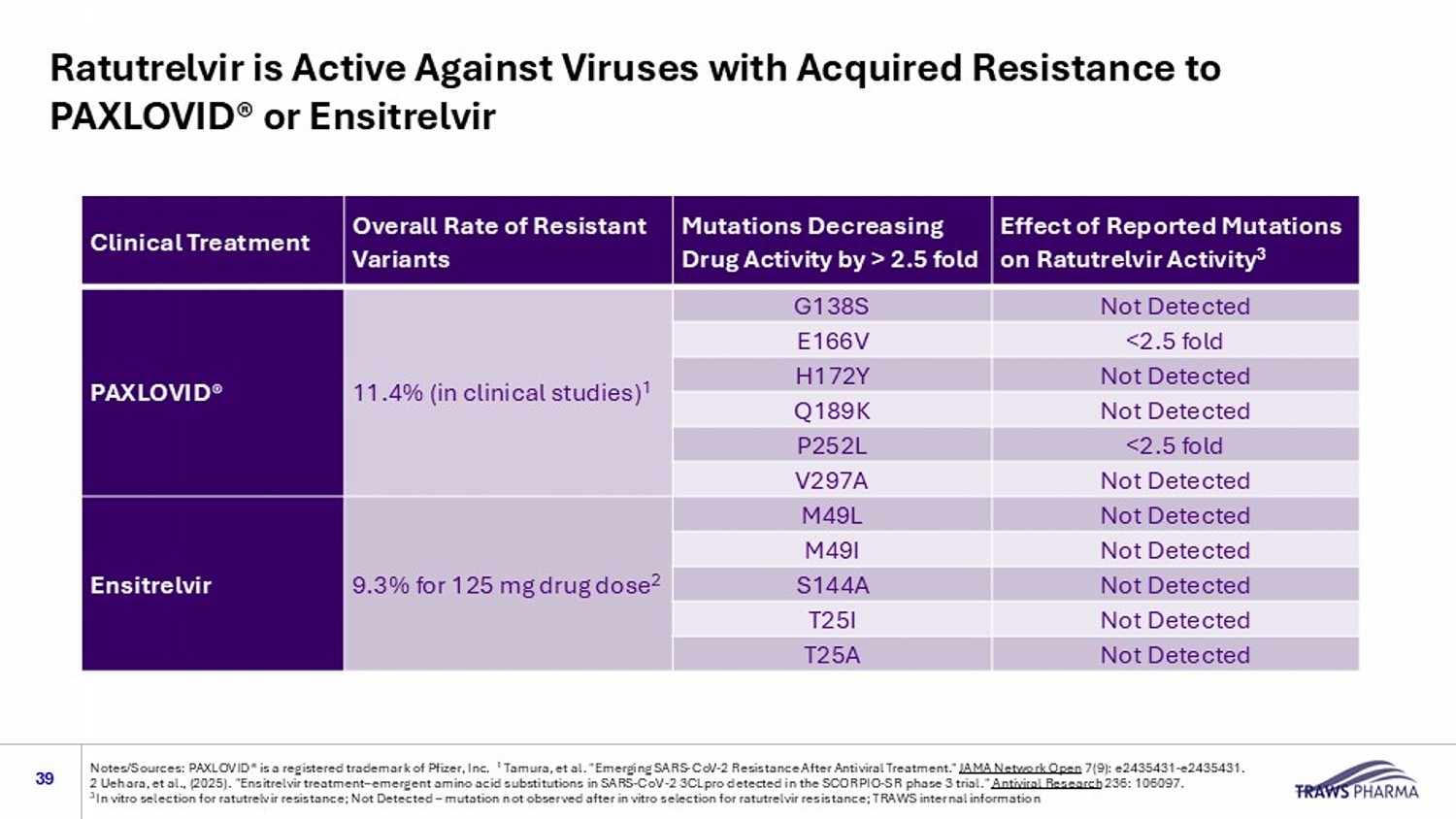
Ratutrelvir is Active Against Viruses with Acquired Resistance to PAXLOVID® or Ensitrelvir 39 Notes/Sources: PAXLOVID® is a registered trademark of Pfizer, Inc. 1 Tamura, et al. "Emerging SARS - CoV - 2 Resistance After Antiviral Treatment." JAMA Network Open 7(9): e2435431 - e2435431. 2 Uehara, et al., (2025). "Ensitrelvir treatment – emergent amino acid substitutions in SARS - CoV - 2 3CLpro detected in the SCORPIO - S R phase 3 trial." Antiviral Research 236: 106097. 3 In vitro selection for ratutrelvir resistance; Not Detected – mutation not observed after in vitro selection for ratutrelvir res istance; TRAWS internal information Effect of Reported Mutations on Ratutrelvir Activity 3 Mutations Decreasing Drug Activity by > 2.5 fold Overall Rate of Resistant Variants Clinical Treatment Not Detected G138S 11.4% (in clinical studies) 1 PAXLOVID® <2.5 fold E166V Not Detected H172Y Not Detected Q189K <2.5 fold P252L Not Detected V297A Not Detected M49L 9.3% for 125 mg drug dose 2 Ensitrelvir Not Detected M49I Not Detected S144A Not Detected T25I Not Detected T25A
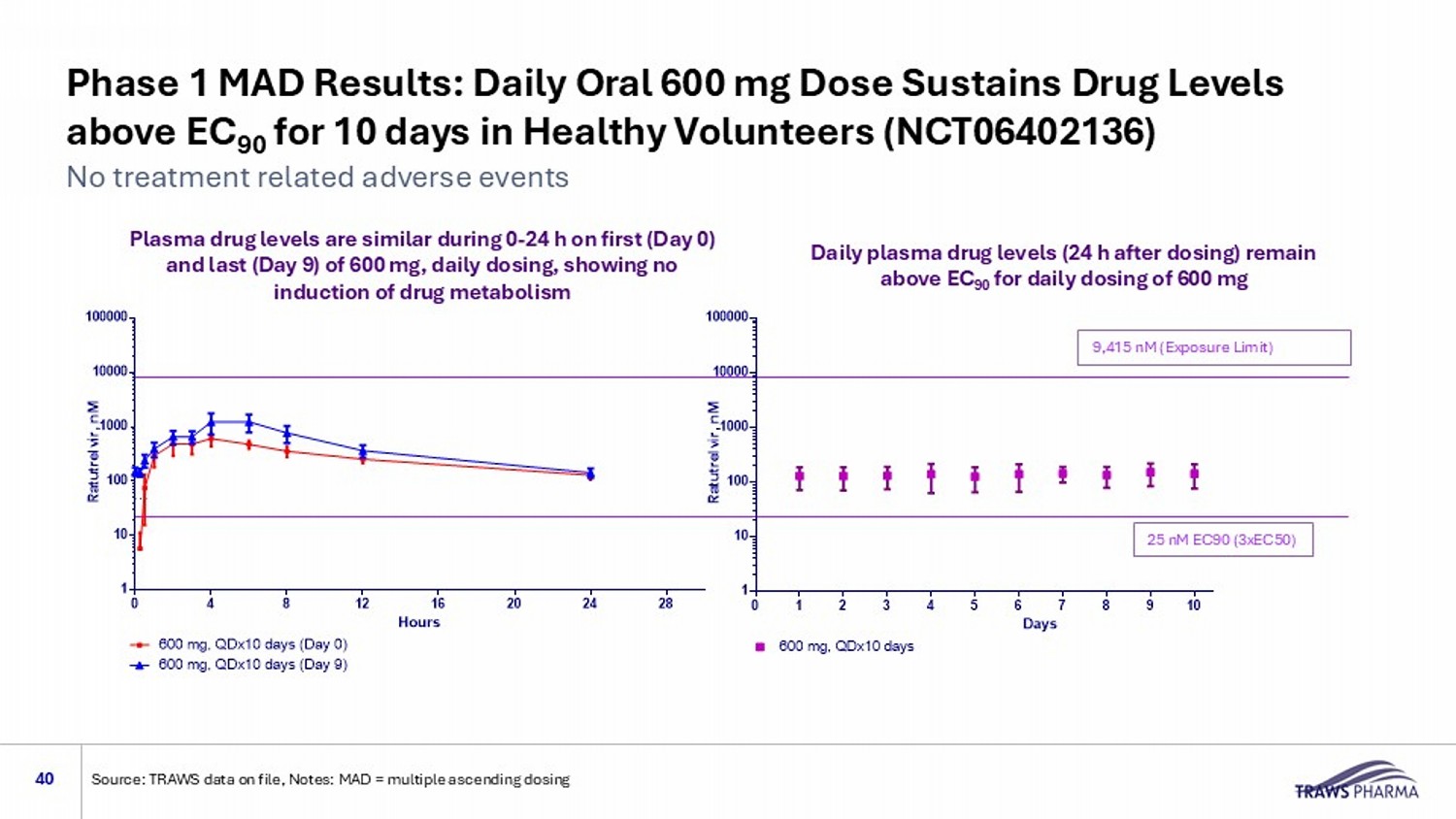
Phase 1 MAD Results: Daily Oral 600 mg Dose Sustains Drug Levels above EC 90 for 10 days in Healthy Volunteers (NCT06402136) 40 No treatment related adverse events Source: TRAWS data on file, Notes: MAD = multiple ascending dosing 9,415 nM (Exposure Limit) 25 nM EC90 (3xEC50) Multiple Ascending Doses in human trough concentrations 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 1 10 100 1000 10000 100000 Days R a t u t r e l v i r , n M 48 nM 600 mg, QDx10 days Multiple Ascending Doses in human 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 1 10 100 1000 10000 100000 Hours R a t u t r e l v i r , n M 48 nM 600 mg, QDx10 days (Day 0) 600 mg, QDx10 days (Day 9) Plasma drug levels are similar during 0 - 24 h on first (Day 0) and last (Day 9) of 600 mg, daily dosing, showing no induction of drug metabolism Daily plasma drug levels (24 h after dosing) remain above EC 90 for daily dosing of 600 mg
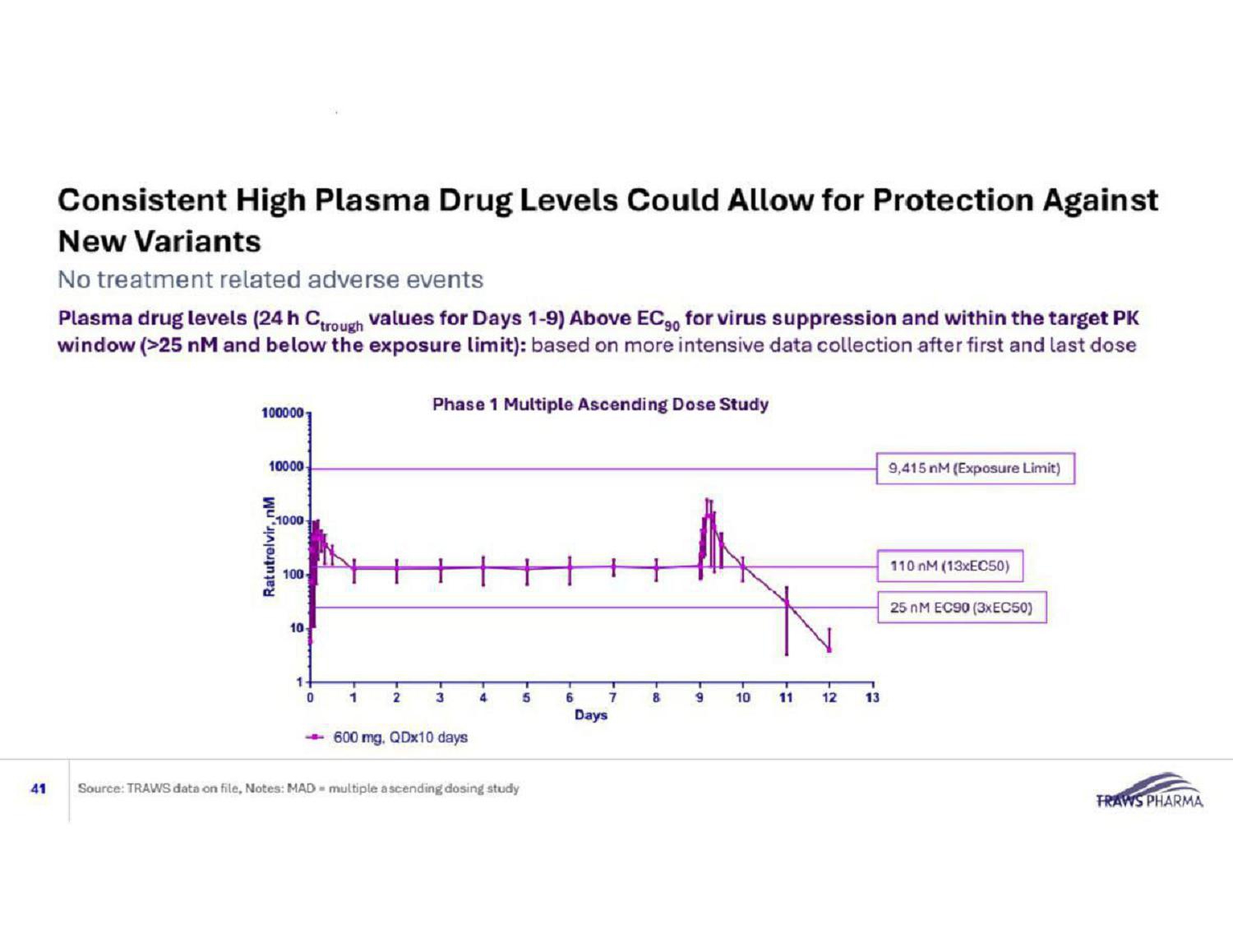
Consistent High Plasma Drug Levels Could Allow for Protection Against New Variants 41 No treatment related adverse events Source: TRAWS data on file, Notes: MAD = multiple ascending dosing study 9,415 nM (Exposure Limit) 25 nM EC90 (3xEC50) 110 nM (13xEC50) Plasma drug l evels (24 h C trough values for Days 1 - 9) Above EC 90 for virus suppression and within the target PK window (>25 nM and below the exposure limit): based on more intensive data collection after first and last dose Phase 1 Multiple Ascending Dose Study

42 Ratutrelvir has Successfully Completed Phase 1 Studies Phase 1 safety and dose escalation studies : have demonstrated excellent overall safety and tolerability and defined a target dose Next steps : submitted HREC Phase 2 protocol to evaluate ratutrelvir in acute COVID and PAXLOVID® - ineligible subjects with assessment of COVID rebound and Long COVID development Note: TRAW data on file. PAXLOVID® is a registered trademark of Pfizer, Inc.

Targeting Critical Viral Threats to Human Health 43 Potential first - in - class bird flu program , with a goal to build out the US strategic stockpile (estimated 300 million to 600 million doses 1 ) and develop as best - in - class therapy with broad label covering seasonal and bird flu Potential best - in - class COVID protease inhibitor to replace existing therapies (>$6B revenue, 2024 2 ), additionally addressing PAXLOVID® - ineligible patients, incidence of clinical rebound and treatment of Long COVID 4 5 F ocusing on small molecule antiviral drugs active against respiratory viruses with pandemic potential Experienced team, supported by recognized institutional investors, including OrbiMed and Perceptive Advisors Actively seeking development and commercialization partners for legacy oncology assets (rigosertib and narazaciclib) Source: 1. TRAW internal information. 2. Pfizer 2024 financial results here, p. 24, Merck 2024 financial results here, p5 = $ 5.7 B + $964M = >$6B

Thank You! www.trawspharma.com