| Breakthrough Antibodies for Obesity and Cardiometabolic Diseases Corporate Presentation June 2025 |
| Certain statements in this presentation constitute "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended. Words such as "may," "might," "will," "should," "believe," "expect," "anticipate," "estimate," "continue," "predict," "forecast," "project," "plan," "intend" or similar expressions, or statements regarding intent, belief, or current expectations, are forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are based upon current estimates and includes statements regarding near term catalysts. While iBio, Inc., a Delaware corporation (including its consolidated subsidiaries, “iBio,” the “Company,” “we,” “us” or “our”) believes these forward-looking statements are reasonable, undue reliance should not be placed on any such forward-looking statements, which are based on information available to us on the date of this presentation. These forward-looking statements are subject to various risks and uncertainties, many of which are difficult to predict that could cause actual results to differ materially from current expectations and assumptions from those set forth or implied by any forward-looking statements. Important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from current expectations include, among others, the Company’s ability to obtain regulatory approvals for commercialization of its product candidates, or to comply with ongoing regulatory requirements, regulatory limitations relating to its ability to promote or commercialize its product candidates for specific indications, acceptance of its product candidates in the marketplace and the successful development, marketing or sale of products, its ability to attain license agreements, the continued maintenance and growth of its patent estate, its ability to establish and maintain collaborations, its ability to obtain or maintain the capital or grants necessary to fund its research and development activities, competition, its ability to retain its key employees or maintain its Nasdaq Stock Market listing, and the other factors discussed in the Company’s most recent Annual Report on Form 10-K and the Company’s subsequent filings with the SEC, including subsequent periodic reports on Forms 10-Q and 8-K. The information in this presentation is provided only as of today, and we undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation on account of new information, future events, or otherwise, except as required by law. Forward looking statements 2 |
| Revolution Sparked a New Era in Obesity Treatment Evolution Will Define Its Future Incretin Class Agonists Have Revolutionized Obesity Treatment >10% of American adults have taken a GLP-11 Interventional weight loss previously only achievable via surgery Attention is Shifting to Therapies That Build on That Foundation Durability of weight loss Lean mass preservation and fat-specific weight loss Improved tolerability and convenience 1. https://www.kff.org/health-costs/poll-finding/kff-health-tracking-poll-may-2024-the-publics-use-and-views-of-glp-1-drugs/ |
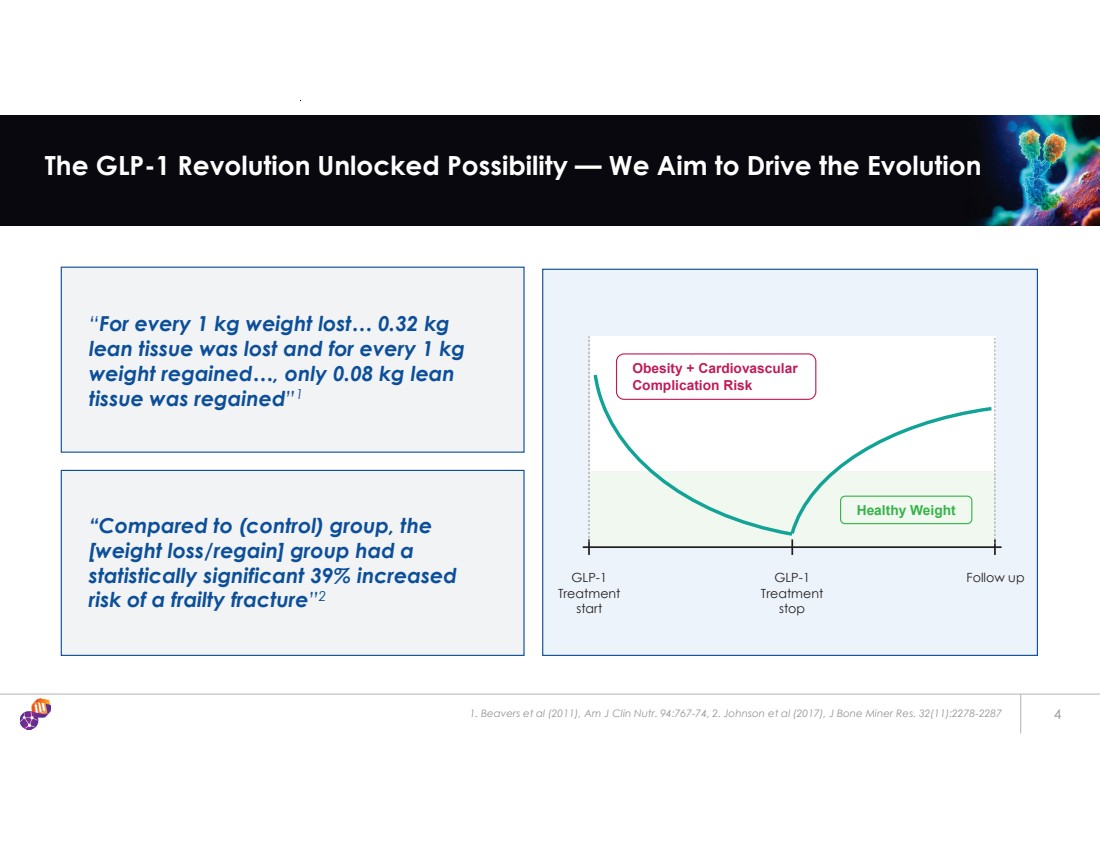
| “For every 1 kg weight lost… 0.32 kg lean tissue was lost and for every 1 kg weight regained…, only 0.08 kg lean tissue was regained”1 1. Beavers et al (2011), Am J Clin Nutr. 94:767-74, 2. Johnson et al (2017), J Bone Miner Res. 32(11):2278-2287 4 The GLP-1 Revolution Unlocked Possibility — We Aim to Drive the Evolution GLP-1 Treatment start GLP-1 Treatment stop Follow up Obesity + Cardiovascular Complication Risk “Compared to (control) group, the [weight loss/regain] group had a statistically significant 39% increased risk of a frailty fracture”2 Healthy Weight |
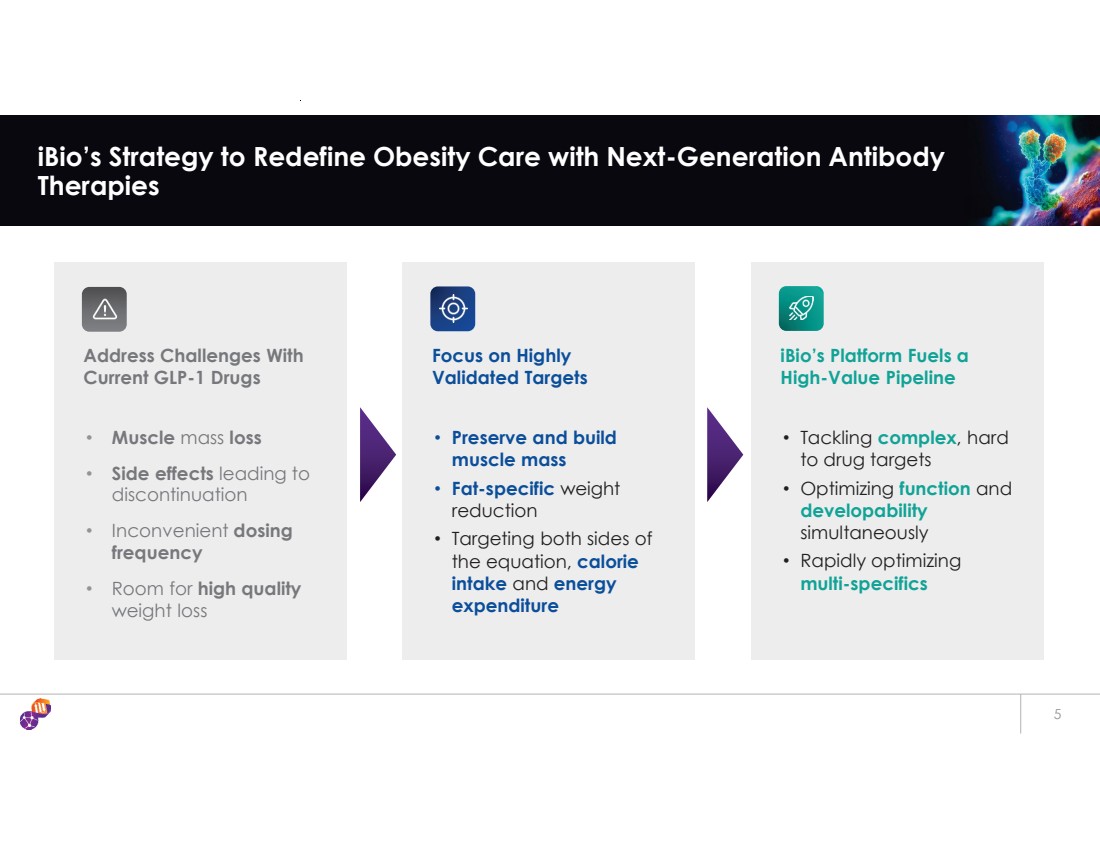
| 5 iBio’s Strategy to Redefine Obesity Care with Next-Generation Antibody Therapies Address Challenges With Current GLP-1 Drugs • Muscle mass loss • Side effects leading to discontinuation • Inconvenient dosing frequency • Room for high quality weight loss Focus on Highly Validated Targets • Preserve and build muscle mass • Fat-specific weight reduction • Targeting both sides of the equation, calorie intake and energy expenditure iBio’s Platform Fuels a High-Value Pipeline • Tackling complex, hard to drug targets • Optimizing function and developability simultaneously • Rapidly optimizing multi-specifics |
| Next Generation Antibodies for Obesity Targeting Key Gaps in Current Care Corporate Highlights Lead Programs ƒ IBIO-600: Long-acting myostatin antibody ƒ IBIO-610: First-in-class Activin E antibody Pipeline Expansion ƒ 3 early-stage high novelty programs and 2 partnered programs ƒ Discovery to development candidate in as little as 7 months ƒ AI engine delivers precisely targeted antibodies with exceptional developability Near Term Catalyst 6 IBIO-600 IND/IND equivalent filing by 1Q2026* IBIO-600 Phase 1 initiated 2Q2026* IBIO-610 IND/IND equivalent filing by end of 2026* * Financing Dependent |
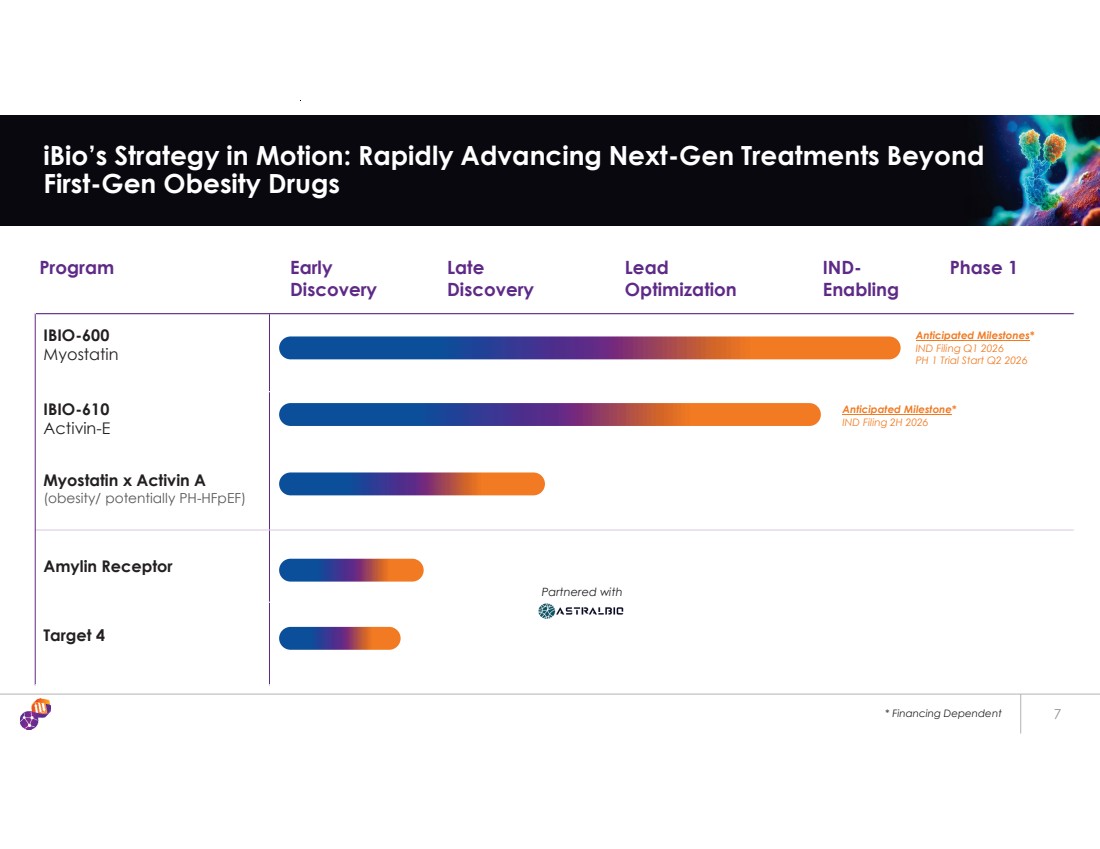
| * Financing Dependent 7 iBio’s Strategy in Motion: Rapidly Advancing Next-Gen Treatments Beyond First-Gen Obesity Drugs Program Early Discovery Late Discovery Lead Optimization IND-Enabling Phase 1 IBIO-600 Myostatin IBIO-610 Activin-E Myostatin x Activin A (obesity/ potentially PH-HFpEF) Amylin Receptor Target 4 Partnered with Anticipated Milestones* IND Filing Q1 2026 PH 1 Trial Start Q2 2026 Anticipated Milestone* IND Filing 2H 2026 |
| Transition slide – IBIO-600 Long-Acting Anti-Myostatin Antibody |
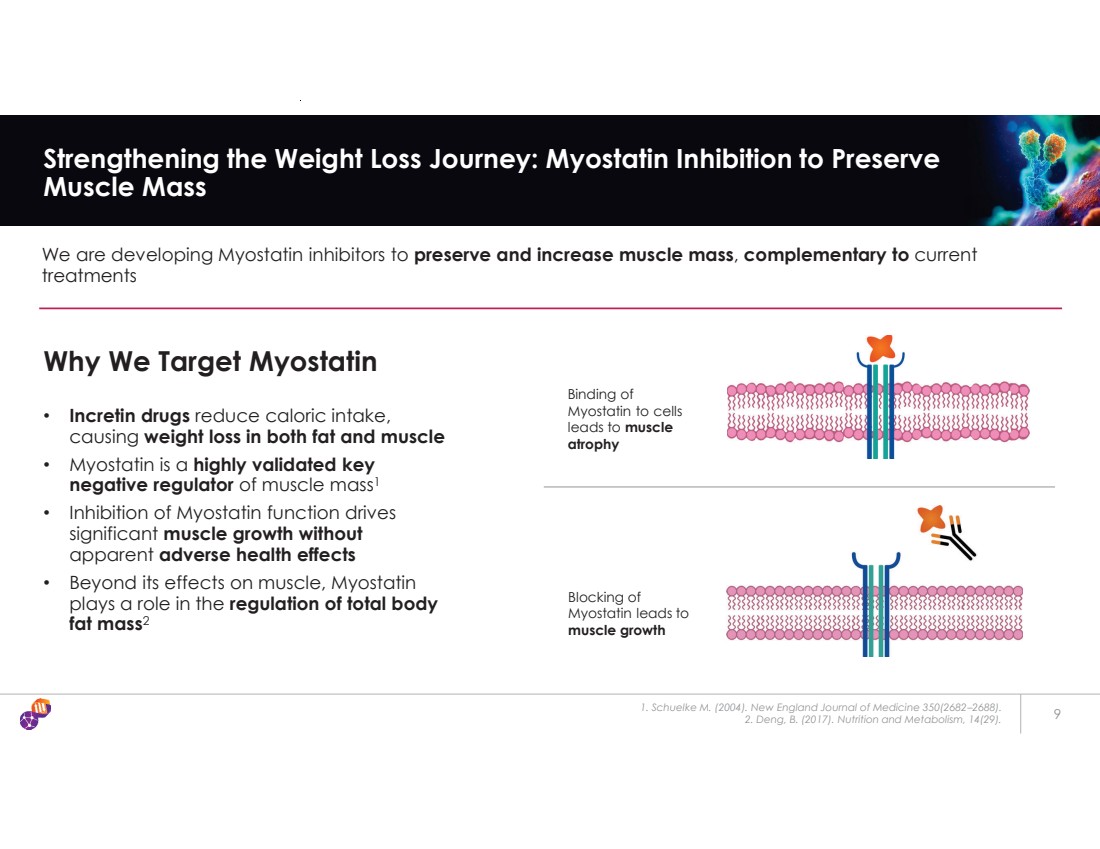
| 1. Schuelke M. (2004). New England Journal of Medicine 350(2682–2688). 2. Deng, B. (2017). Nutrition and Metabolism, 14(29). 9 Strengthening the Weight Loss Journey: Myostatin Inhibition to Preserve Muscle Mass We are developing Myostatin inhibitors to preserve and increase muscle mass, complementary to current treatments Why We Target Myostatin • Incretin drugs reduce caloric intake, causing weight loss in both fat and muscle • Myostatin is a highly validated key negative regulator of muscle mass1 • Inhibition of Myostatin function drives significant muscle growth without apparent adverse health effects • Beyond its effects on muscle, Myostatin plays a role in the regulation of total body fat mass2 Binding of Myostatin to cells leads to muscle atrophy Blocking of Myostatin leads to muscle growth |
| 10 IBIO-600: A Differentiated Long Acting Anti-Myostatin Program Potential best-in-class PK based on allometric scaling and dosing regimen suggests 2-4x improved PK over competitors Improved Pharmacokinetics Dual myostatin and GDF11 blockade has potential for improved lean mass preservation and fat mass reduction Dual Mechanism Optimized for high expression and stability to enable efficient manufacturing process Enhanced Manufacturability High formulation concentration to lower injection volume Coformulation Optionality Convenience Administration as infrequent as twice a year |
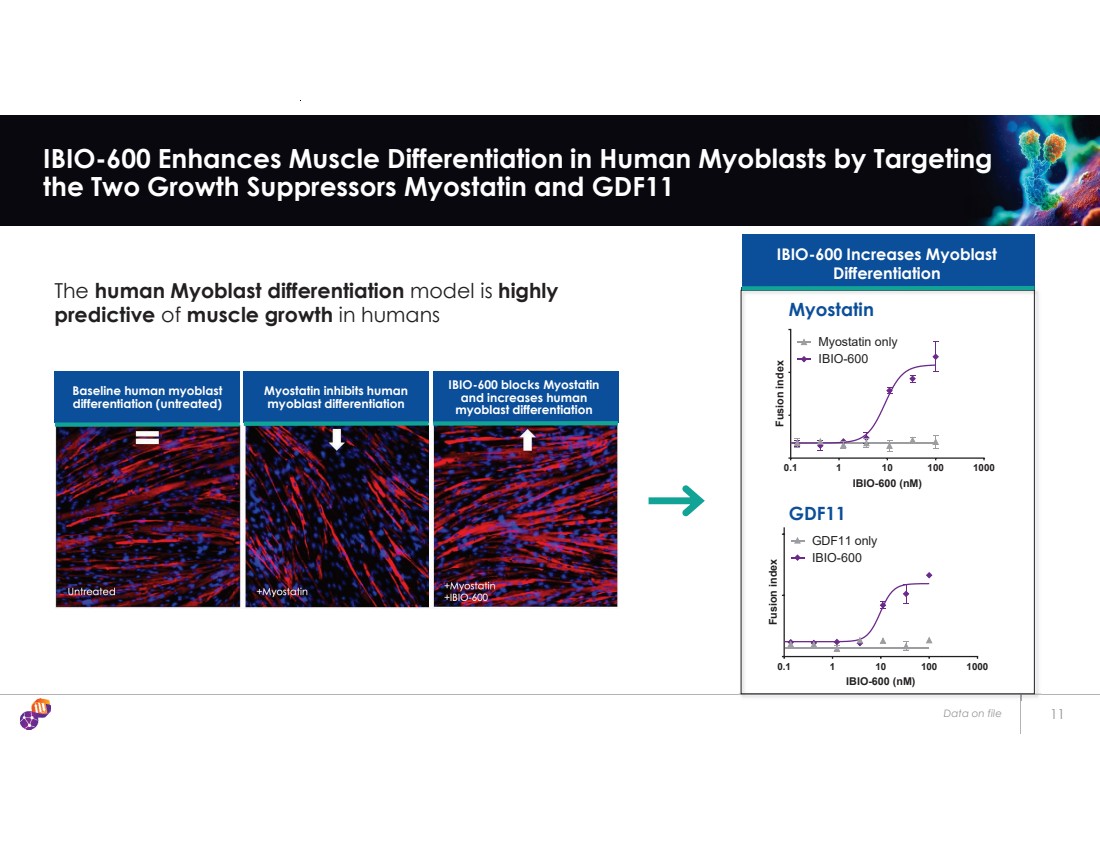
| Data on file 11 IBIO-600 Enhances Muscle Differentiation in Human Myoblasts by Targeting the Two Growth Suppressors Myostatin and GDF11 IBIO-600 Increases Myoblast Differentiation Baseline human myoblast differentiation (untreated) Myostatin inhibits human myoblast differentiation IBIO-600 blocks Myostatin and increases human myoblast differentiation The human Myoblast differentiation model is highly predictive of muscle growth in humans 0.1 1 10 100 1000 IBIO-600 (nM) Fusion index Myostatin only IBIO-600 0.1 1 10 100 1000 IBIO-600 (nM) Fusion index GDF11 only IBIO-600 Myostatin GDF11 |
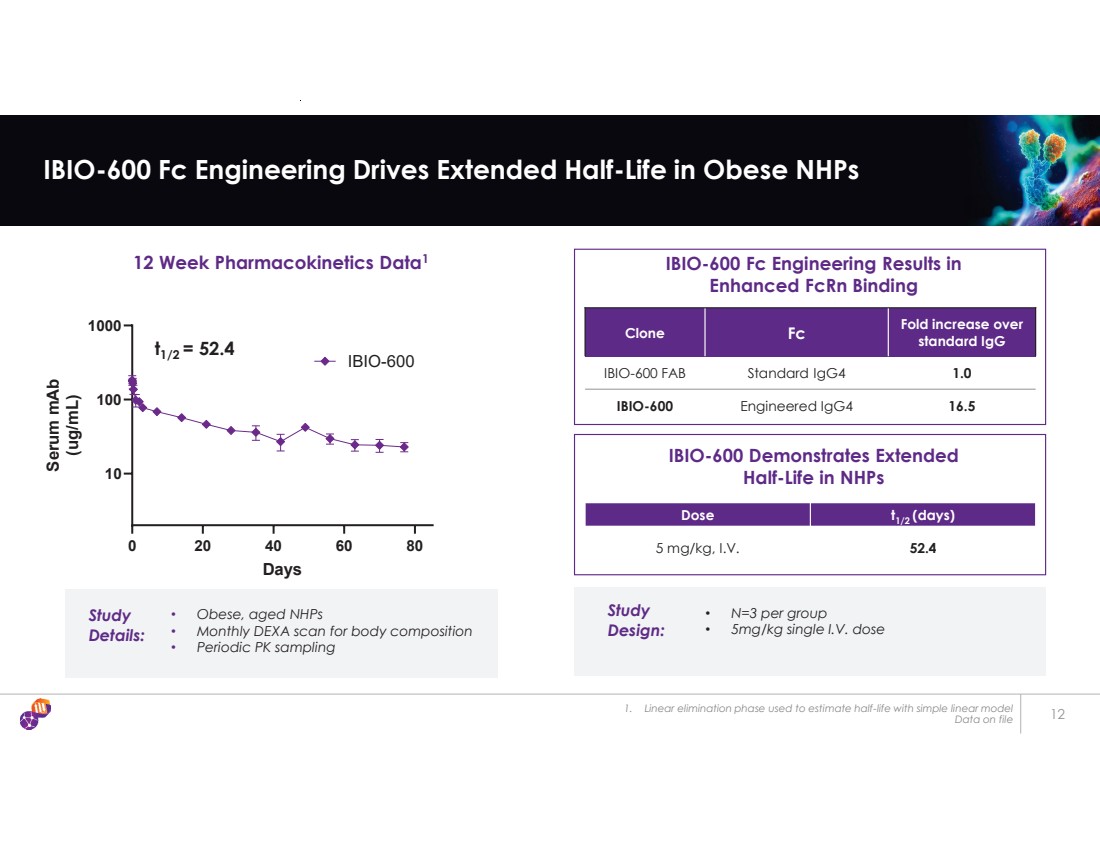
| 1. Linear elimination phase used to estimate half-life with simple linear model Data on file 12 IBIO-600 Fc Engineering Drives Extended Half-Life in Obese NHPs Dose t1/2 (days) 5 mg/kg, I.V. 52.4 IBIO-600 Fc Engineering Results in Enhanced FcRn Binding Clone Fc Fold increase over standard IgG IBIO-600 FAB Standard IgG4 1.0 IBIO-600 Engineered IgG4 16.5 IBIO-600 Demonstrates Extended Half-Life in NHPs 12 Week Pharmacokinetics Data1 0 20 40 60 80 10 100 1000 Days Serum mAb (ug/mL) IBIO-600 Study Details: • Obese, aged NHPs • Monthly DEXA scan for body composition • Periodic PK sampling Study Design: • N=3 per group • 5mg/kg single I.V. dose t1/2 = 52.4 |
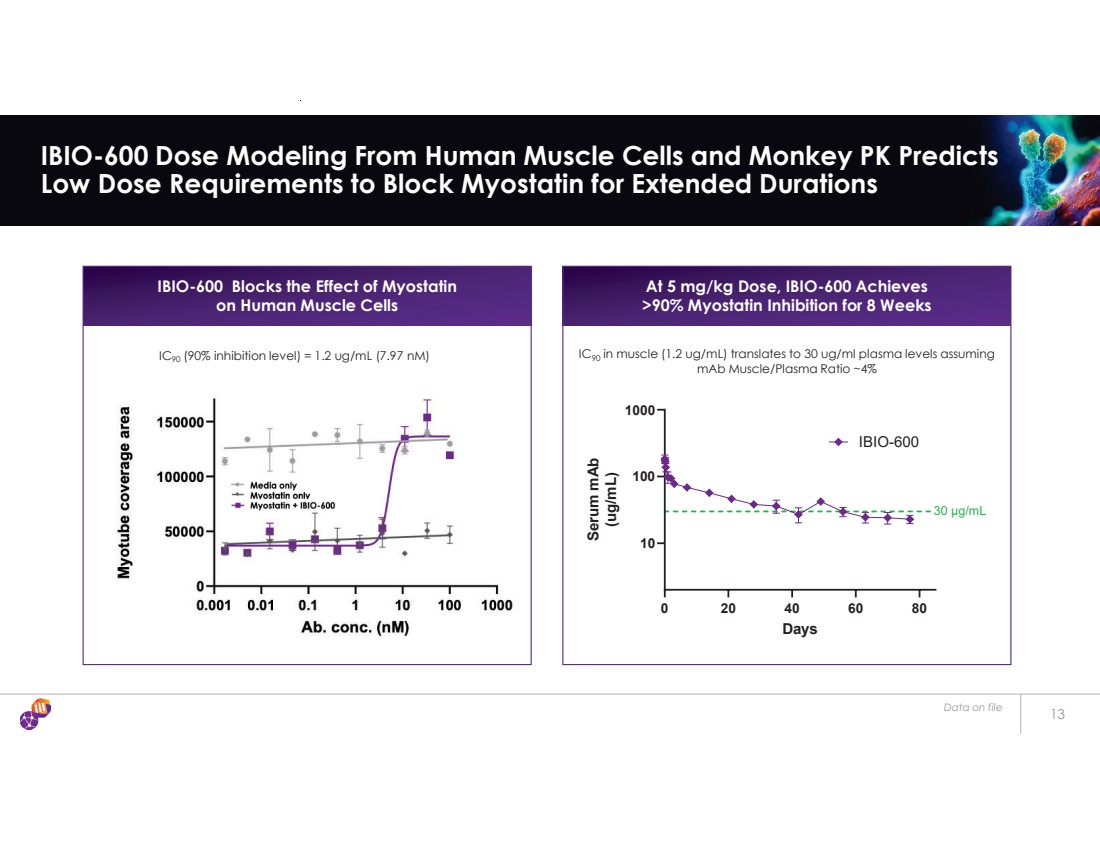
| 13 IBIO-600 Dose Modeling From Human Muscle Cells and Monkey PK Predicts Low Dose Requirements to Block Myostatin for Extended Durations IBIO-600 Blocks the Effect of Myostatin on Human Muscle Cells IC90 (90% inhibition level) = 1.2 ug/mL (7.97 nM) 0 20 40 60 80 10 100 1000 Days Serum mAb (ug/mL) IBIO-600 30 μg/mL At 5 mg/kg Dose, IBIO-600 Achieves >90% Myostatin Inhibition for 8 Weeks IC90 in muscle (1.2 ug/mL) translates to 30 ug/ml plasma levels assuming mAb Muscle/Plasma Ratio ~4% Data on file |
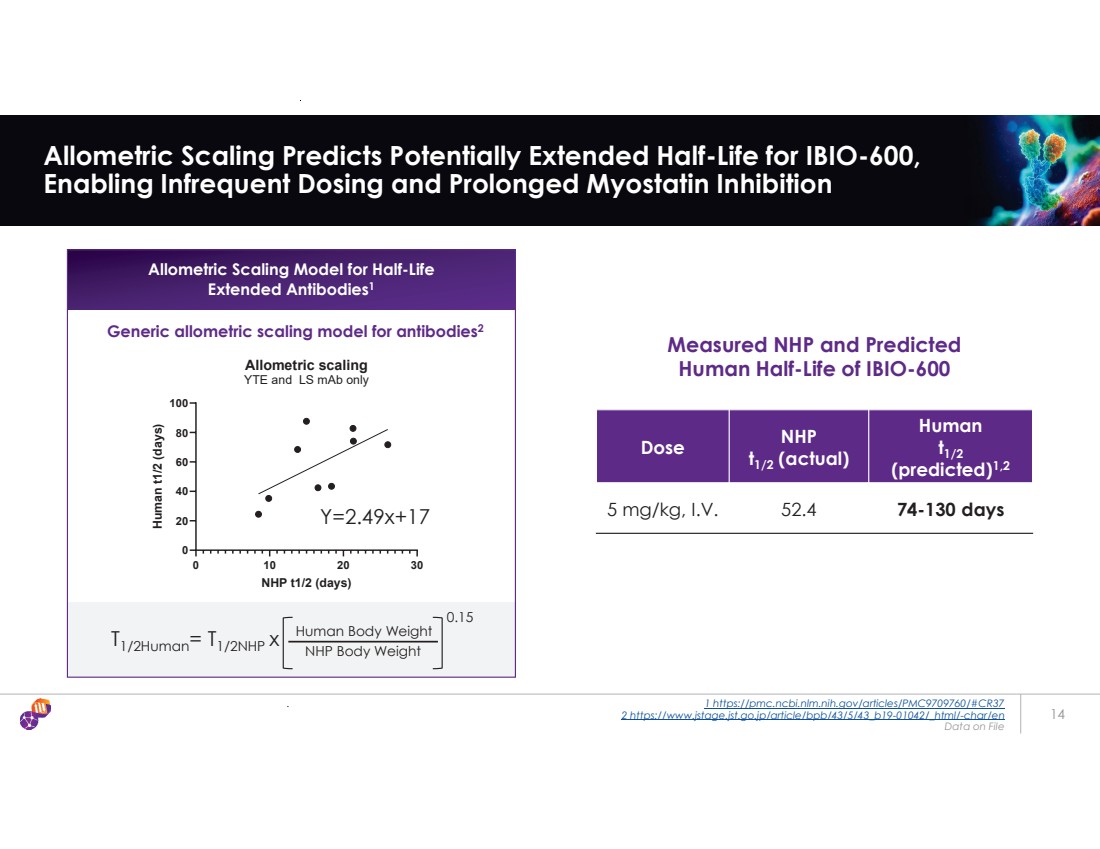
| . 1 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9709760/#CR37 2 https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bpb/43/5/43_b19-01042/_html/-char/en Data on File 14 Allometric Scaling Predicts Potentially Extended Half-Life for IBIO-600, Enabling Infrequent Dosing and Prolonged Myostatin Inhibition Y=2.49x+17 0 10 20 30 0 20 40 60 80 100 Allometric scaling YTE and LS mAb only NHP t1/2 (days) Human t1/2 (days) Dose NHP t1/2 (actual) Human t1/2 (predicted)1,2 5 mg/kg, I.V. 52.4 74-130 days Measured NHP and Predicted Human Half-Life of IBIO-600 Allometric Scaling Model for Half-Life Extended Antibodies1 Generic allometric scaling model for antibodies2 T1/2Human= T1/2NHP x Human Body Weight NHP Body Weight 0.15 |
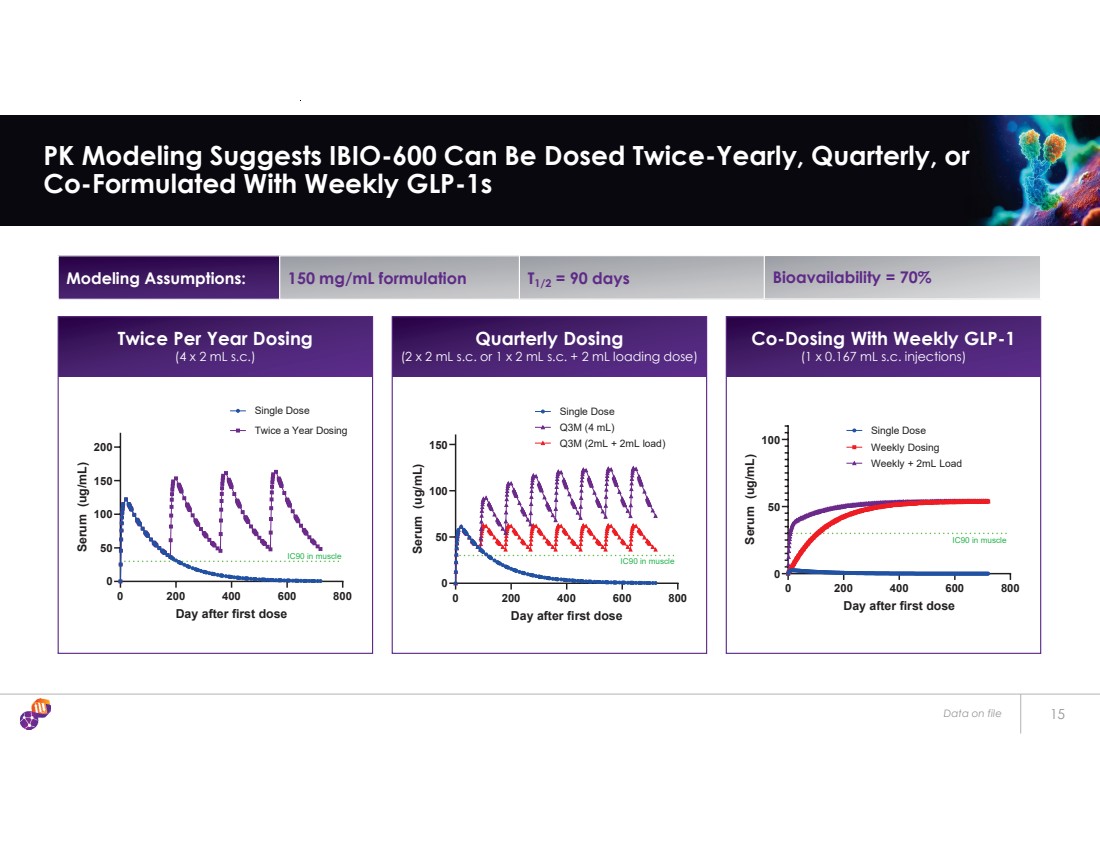
| Data on file 15 PK Modeling Suggests IBIO-600 Can Be Dosed Twice-Yearly, Quarterly, or Co-Formulated With Weekly GLP-1s Twice Per Year Dosing (4 x 2 mL s.c.) 0 200 400 600 800 0 50 100 150 200 Day after first dose Serum (ug/mL) Single Dose Twice a Year Dosing IC90 in muscle 0 200 400 600 800 0 50 100 Day after first dose Serum (ug/mL) Single Dose Weekly Dosing IC90 in muscle Weekly + 2mL Load Modeling Assumptions: 150 mg/mL formulation T1/2 = 90 days Bioavailability = 70% Quarterly Dosing (2 x 2 mL s.c. or 1 x 2 mL s.c. + 2 mL loading dose) 0 200 400 600 800 0 50 100 150 Day after first dose Serum (ug/mL) Single Dose Q3M (4 mL) IC90 in muscle Q3M (2mL + 2mL load) Co-Dosing With Weekly GLP-1 (1 x 0.167 mL s.c. injections) |
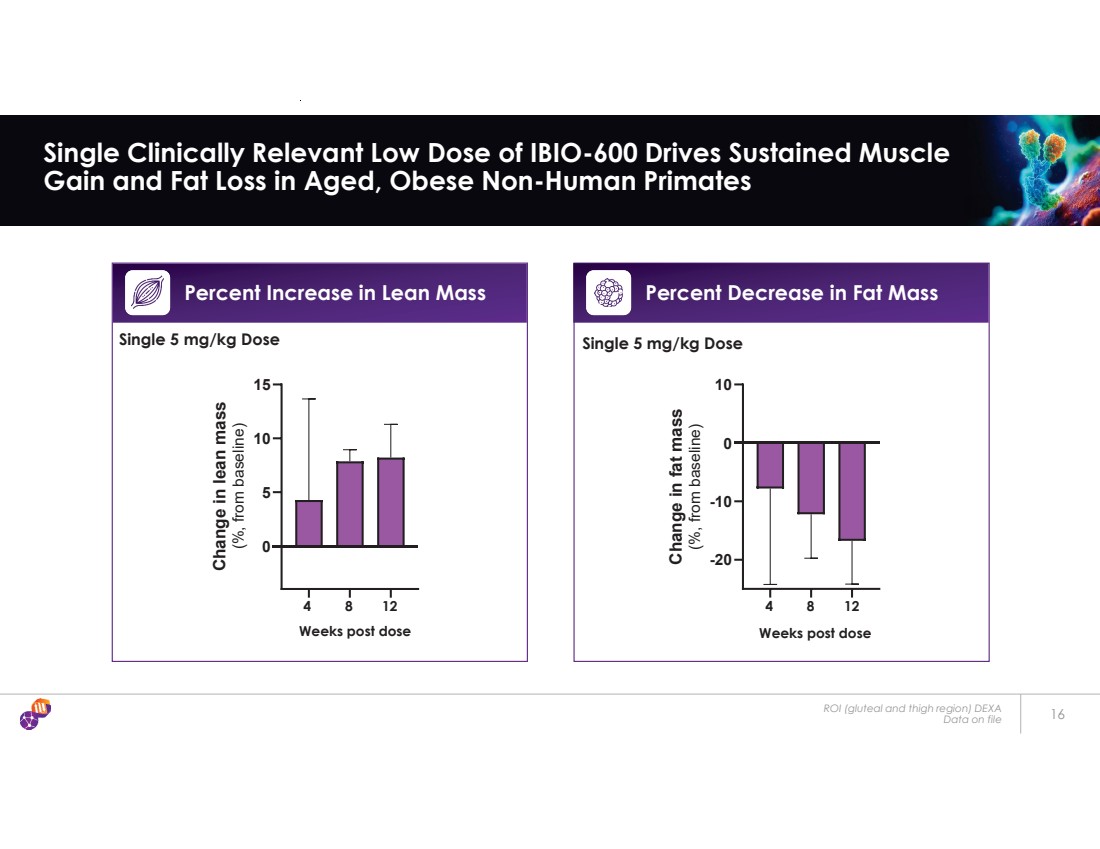
| ROI (gluteal and thigh region) DEXA Data on file 16 Single Clinically Relevant Low Dose of IBIO-600 Drives Sustained Muscle Gain and Fat Loss in Aged, Obese Non-Human Primates Percent Increase in Lean Mass Weeks post dose 0 5 10 15 Change in lean mass (%, from baseline) 4 8 12 -20 -10 0 10 Change in fat mass (%, from baseline) 4 8 12 Weeks post dose Percent Decrease in Fat Mass Single 5 mg/kg Dose Single 5 mg/kg Dose |
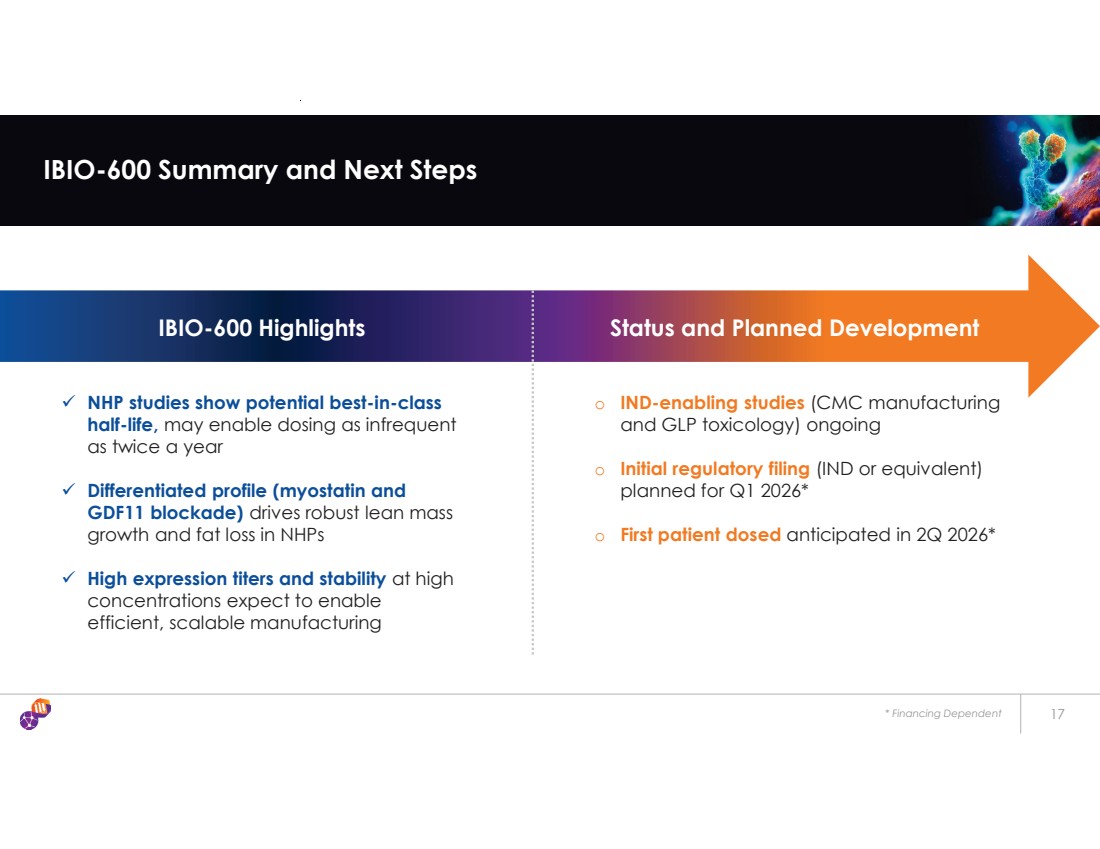
| * Financing Dependent 17 IBIO-600 Summary and Next Steps 9 NHP studies show potential best-in-class half-life, may enable dosing as infrequent as twice a year 9 Differentiated profile (myostatin and GDF11 blockade) drives robust lean mass growth and fat loss in NHPs 9 High expression titers and stability at high concentrations expect to enable efficient, scalable manufacturing IBIO-600 Highlights o IND-enabling studies (CMC manufacturing and GLP toxicology) ongoing o Initial regulatory filing (IND or equivalent) planned for Q1 2026* o First patient dosed anticipated in 2Q 2026* Status and Planned Development |
| IBIO-610 Anti-Activin E Antibody |
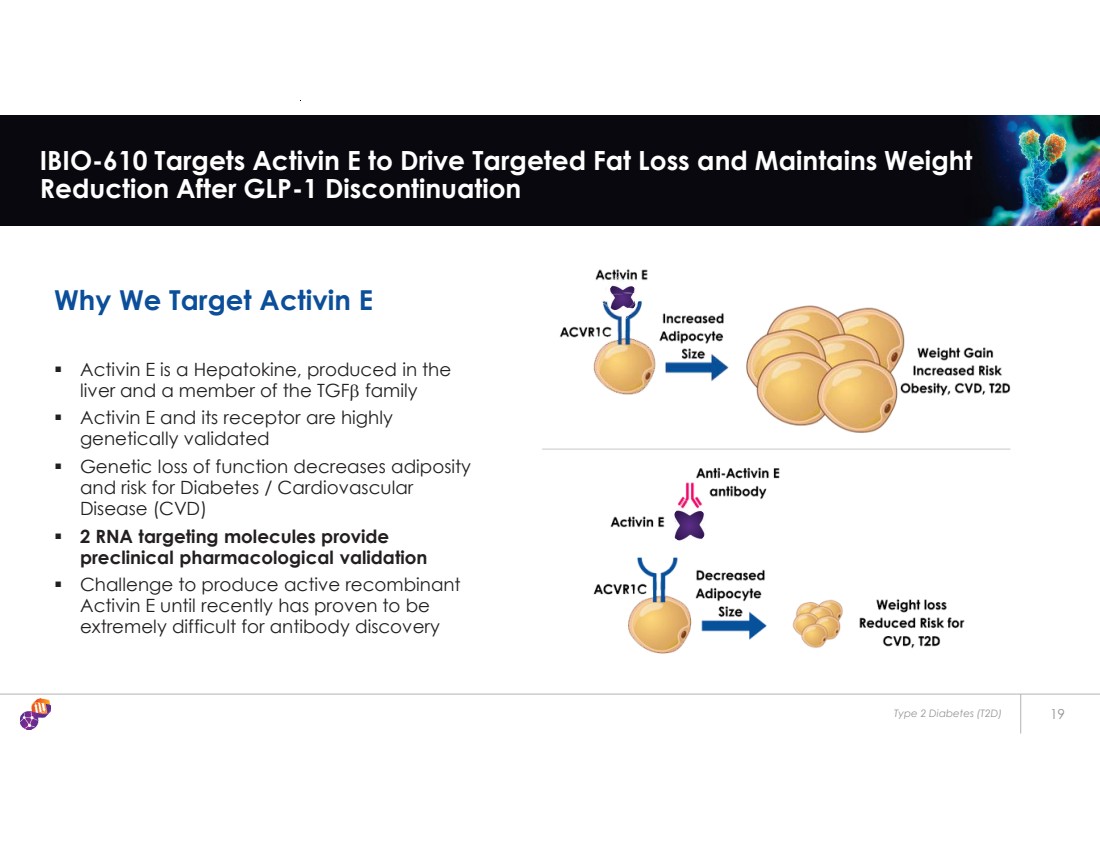
| Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) 19 IBIO-610 Targets Activin E to Drive Targeted Fat Loss and Maintains Weight Reduction After GLP-1 Discontinuation Why We Target Activin E ƒ Activin E is a Hepatokine, produced in the liver and a member of the TGF E family ƒ Activin E and its receptor are highly genetically validated ƒ Genetic loss of function decreases adiposity and risk for Diabetes / Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) ƒ 2 RNA targeting molecules provide preclinical pharmacological validation ƒ Challenge to produce active recombinant Activin E until recently has proven to be extremely difficult for antibody discovery |
| 20 IBIO-610 Breaks New Ground as the Known First-in-Class Antibody Targeting Activin E Antagonist antibody offers potential for greater Activin E inhibition than siRNA-based knockdown approaches Class-Leading Pathway Targeting Pre-clinical studies demonstrate weight loss with no impact on lean mass Dual Mechanism Synergistic weight loss with appetite reducing drugs like GLP-1 or Amylin Synergistic to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Stand-alone weight loss intervention and weight loss maintenance post GLP-1 or Amylin treatment Weight Lowering and Maintenance Therapy |
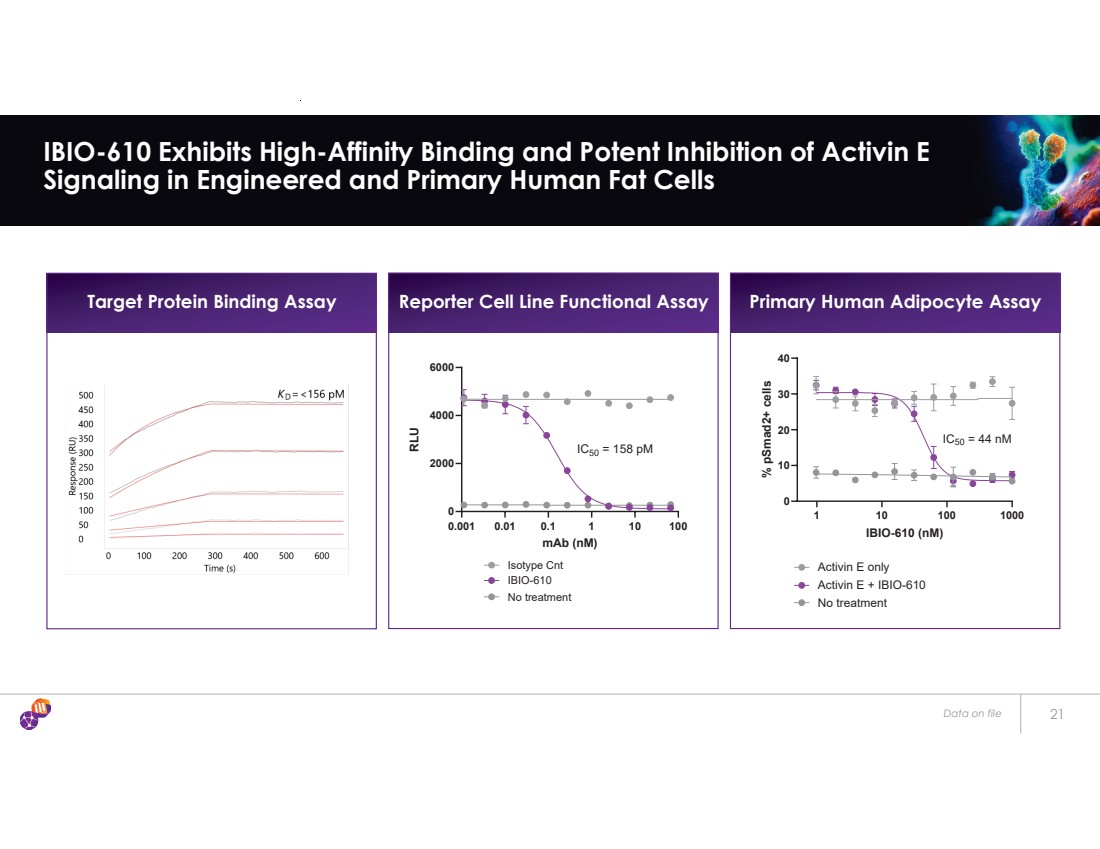
| Target Protein Binding Assay Reporter Cell Line Functional Assay Primary Human Adipocyte Assay Data on file 21 IBIO-610 Exhibits High-Affinity Binding and Potent Inhibition of Activin E Signaling in Engineered and Primary Human Fat Cells 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 0 2000 4000 6000 mAb (nM) RLU Isotype Cnt IBIO-610 No treatment IC50 = 158 pM 1 10 100 1000 0 10 20 30 40 IBIO-610 (nM) % pSmad2+ cells No treatment Activin E only Activin E + IBIO-610 IC50 = 44 nM |
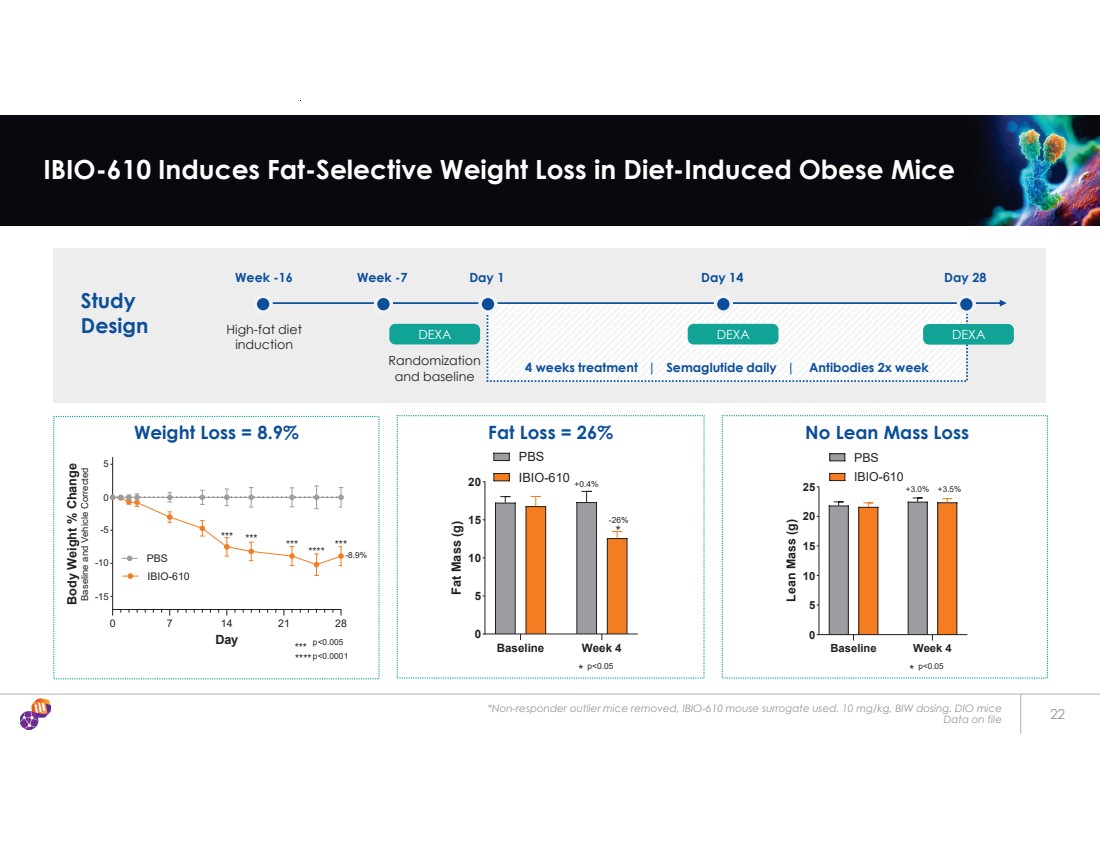
| *Non-responder outlier mice removed, IBIO-610 mouse surrogate used. 10 mg/kg, BIW dosing. DIO mice Data on file 22 IBIO-610 Induces Fat-Selective Weight Loss in Diet-Induced Obese Mice 0 7 14 21 28 -15 -10 -5 0 5 Day Body Weight % Change Baseline and Vehicle Corrected PBS IBIO-610 -8.9% *** *** *** *** **** p<0.0001 p<0.005 *** **** Baseline Week 4 0 5 10 15 20 Fat Mass (g) * p<0.05 * +0.4% -26% PBS IBIO-610 Weight Loss = 8.9% Fat Loss = 26% No Lean Mass Loss Baseline Week 4 0 5 10 15 20 25 Lean Mass (g) * p<0.05 +3.0% +3.5% PBS IBIO-610 Study Design Week -16 High-fat diet induction Week -7 DEXA Day 1 DEXA Day 14 DEXA Day 28 Randomization and baseline 4 weeks treatment | Semaglutide daily | Antibodies 2x week |
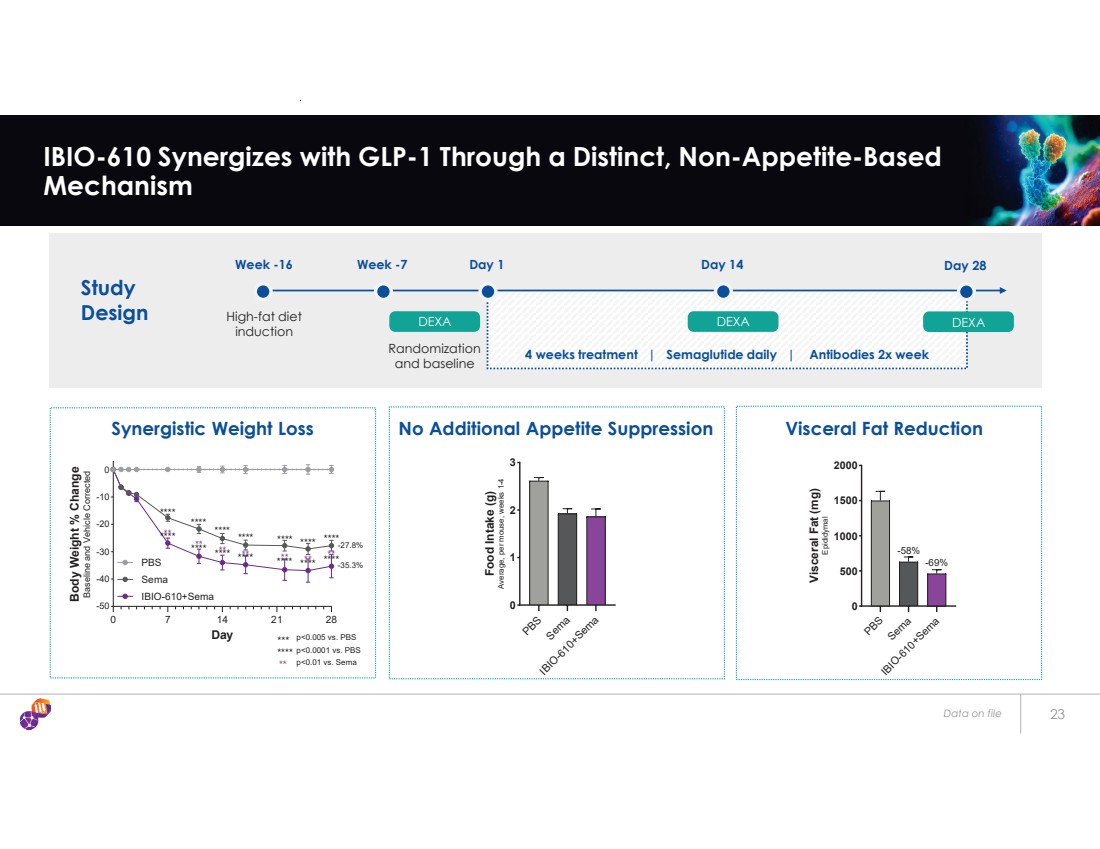
| Data on file 23 IBIO-610 Synergizes with GLP-1 Through a Distinct, Non-Appetite-Based Mechanism Synergistic Weight Loss No Additional Appetite Suppression Visceral Fat Reduction Study Design Week -16 High-fat diet induction Week -7 DEXA Day 1 DEXA Day 14 DEXA Day 28 Randomization and baseline 4 weeks treatment | Semaglutide daily | Antibodies 2x week 0 7 14 21 28 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 Day Body Weight % Change Baseline and Vehicle Corrected PBS Sema IBIO-610+Sema -27.8% -35.3% p<0.0001 vs. PBS p<0.005 vs. PBS p<0.01 vs. Sema **** *** ** **** ** **** ** **** **** ** **** ** **** ** ** **** ** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** PBS Sema IBIO-610+Sema 0 1 2 3 Food Intake (g) Average, per mouse, weeks 1-4 PBS Sema IBIO-610+Sema 0 500 1000 1500 2000 Visceral Fat (mg) Epididymal -58% -69% |
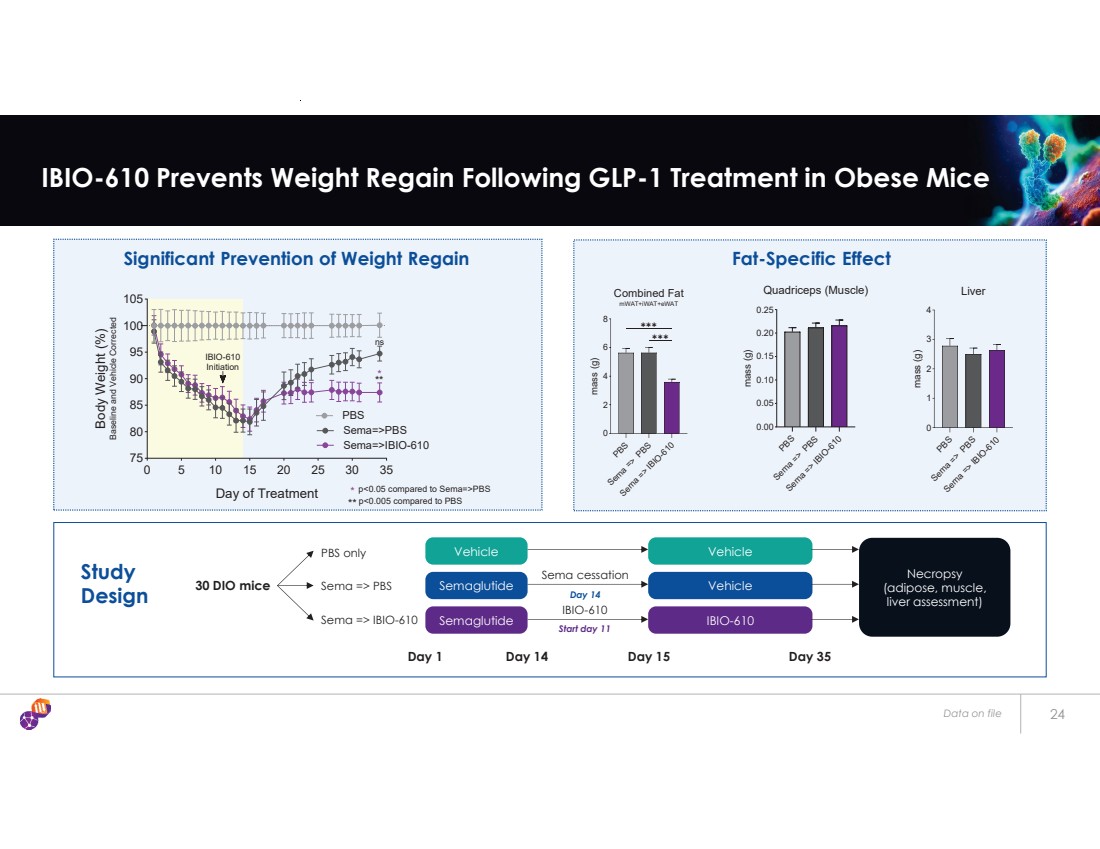
| Data on file 24 IBIO-610 Prevents Weight Regain Following GLP-1 Treatment in Obese Mice Significant Prevention of Weight Regain Fat-Specific Effect Study Design 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 Day of Treatment Body Weight (%) Baseline and Vehicle Corrected PBS Sema=>PBS Sema=>IBIO-610 IBIO-610 Initiation ns ** * ** * p<0.05 compared to Sema=>PBS p<0.005 compared to PBS PBS Sema => PBS Sema => IBIO-610 0 2 4 6 8 Combined Fat mWAT+iWAT+eWAT mass (g) ✱✱✱ ✱✱✱ PBS Sema => PBS Sema => IBIO-610 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 Quadriceps (Muscle) mass (g) PBS Sema => PBS Sema => IBIO-610 0 1 2 3 4 Liver mass (g) Vehicle Semaglutide Semaglutide 30 DIO mice PBS only Sema => PBS Sema => IBIO-610 Day 1 Sema cessation Day 14 IBIO-610 Start day 11 Day 14 Vehicle Vehicle IBIO-610 Day 15 Day 35 Necropsy (adipose, muscle, liver assessment) |
| 25 The Next Wave of iBio Innovation Early Pre-Clinical Programs |
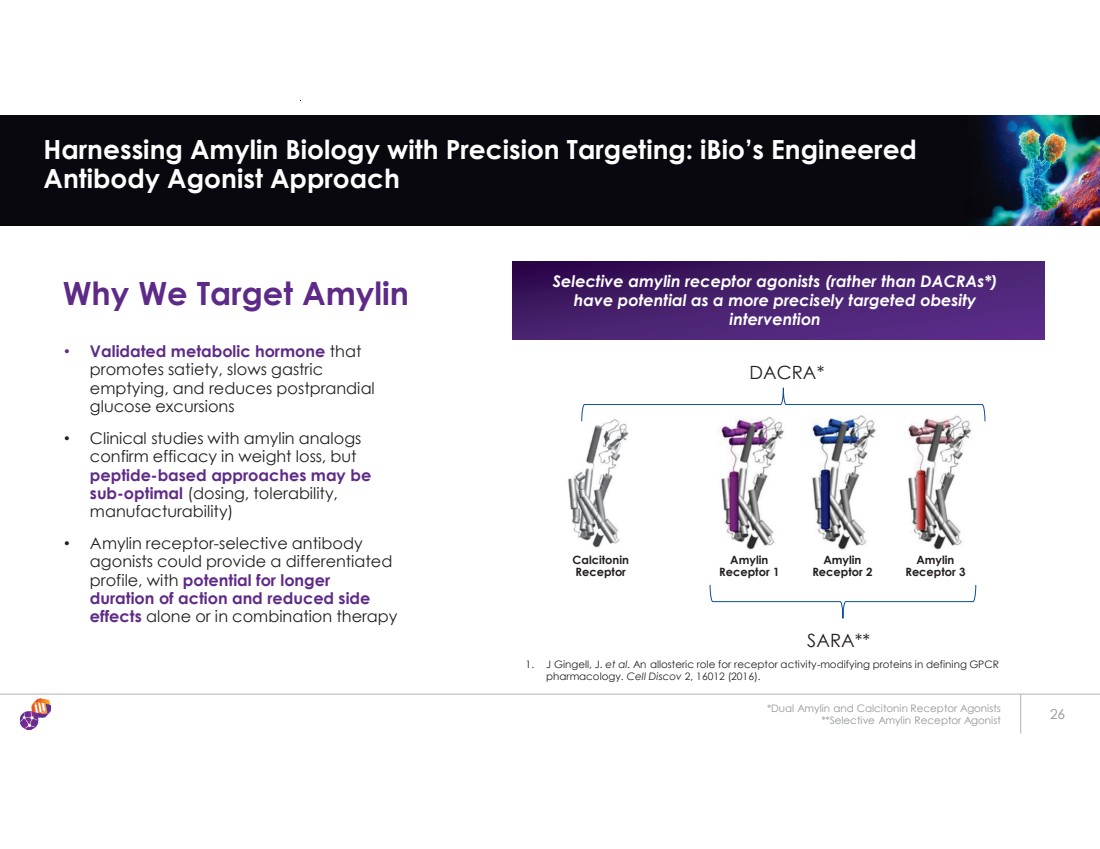
| *Dual Amylin and Calcitonin Receptor Agonists **Selective Amylin Receptor Agonist 26 Harnessing Amylin Biology with Precision Targeting: iBio’s Engineered Antibody Agonist Approach Why We Target Amylin Selective amylin receptor agonists (rather than DACRAs*) have potential as a more precisely targeted obesity intervention • Validated metabolic hormone that promotes satiety, slows gastric emptying, and reduces postprandial glucose excursions • Clinical studies with amylin analogs confirm efficacy in weight loss, but peptide-based approaches may be sub-optimal (dosing, tolerability, manufacturability) • Amylin receptor-selective antibody agonists could provide a differentiated profile, with potential for longer duration of action and reduced side effects alone or in combination therapy Calcitonin Receptor Amylin Receptor 1 Amylin Receptor 2 Amylin Receptor 3 DACRA* 1. J Gingell, J. et al. An allosteric role for receptor activity-modifying proteins in defining GPCR pharmacology. Cell Discov 2, 16012 (2016). SARA** |
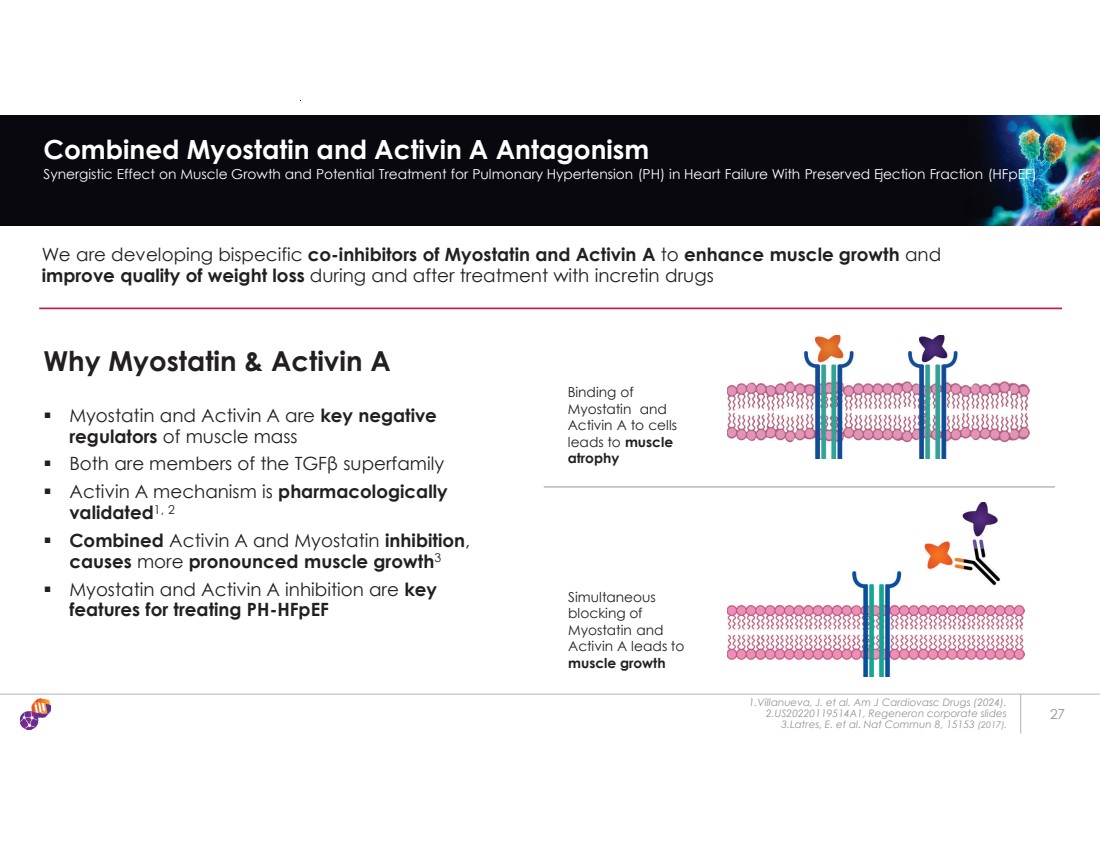
| 27 Combined Myostatin and Activin A Antagonism Synergistic Effect on Muscle Growth and Potential Treatment for Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) We are developing bispecific co-inhibitors of Myostatin and Activin A to enhance muscle growth and improve quality of weight loss during and after treatment with incretin drugs Why Myostatin & Activin A ƒ Myostatin and Activin A are key negative regulators of muscle mass ƒ Both are members of the TGF β superfamily ƒ Activin A mechanism is pharmacologically validated1, 2 ƒ Combined Activin A and Myostatin inhibition, causes more pronounced muscle growth3 ƒ Myostatin and Activin A inhibition are key features for treating PH-HFpEF 1.Villanueva, J. et al. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs (2024). 2.US20220119514A1, Regeneron corporate slides 3.Latres, E. et al. Nat Commun 8, 15153 (2017). Binding of Myostatin and Activin A to cells leads to muscle atrophy Simultaneous blocking of Myostatin and Activin A leads to muscle growth |
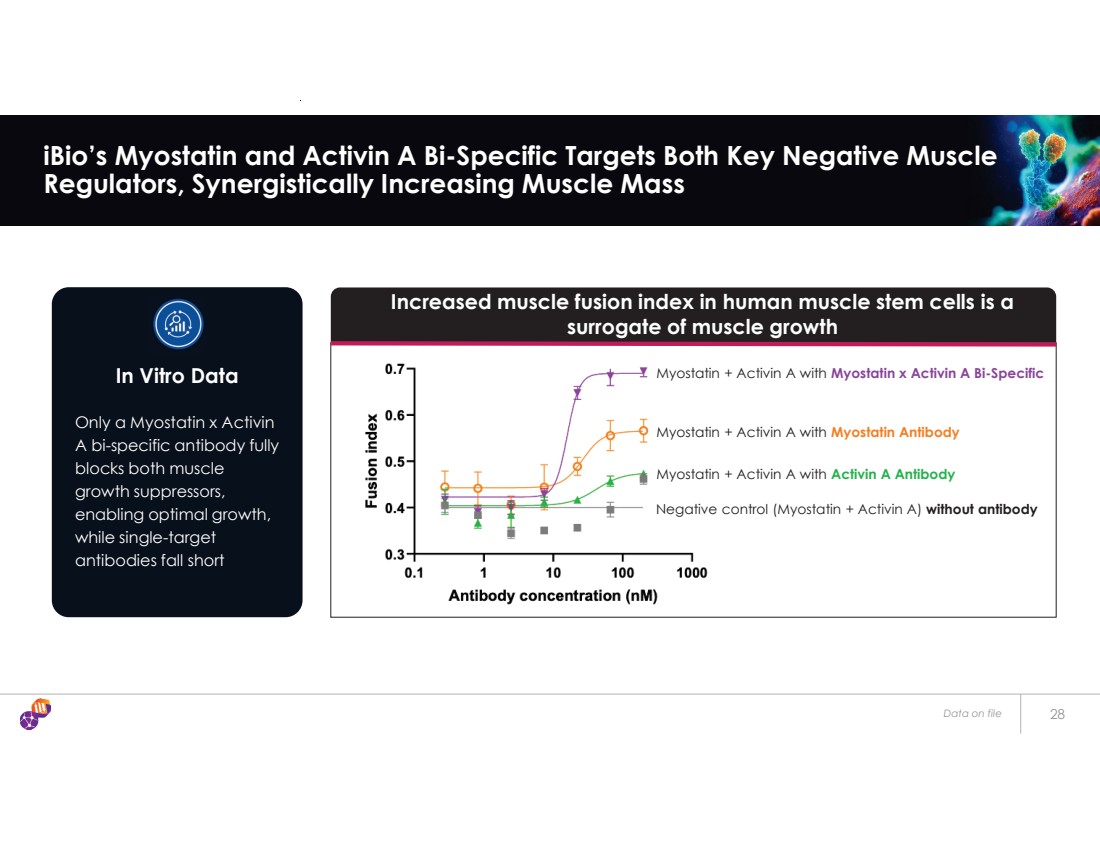
| Data on file 28 iBio’s Myostatin and Activin A Bi-Specific Targets Both Key Negative Muscle Regulators, Synergistically Increasing Muscle Mass Increased muscle fusion index in human muscle stem cells is a surrogate of muscle growth Negative control (Myostatin + Activin A) without antibody Myostatin + Activin A with Activin A Antibody Myostatin + Activin A with Myostatin Antibody Myostatin + Activin A with Myostatin x Activin A Bi-Specific Only a Myostatin x Activin A bi-specific antibody fully blocks both muscle growth suppressors, enabling optimal growth, while single-target antibodies fall short In Vitro Data |
| 29 Technology Stack |
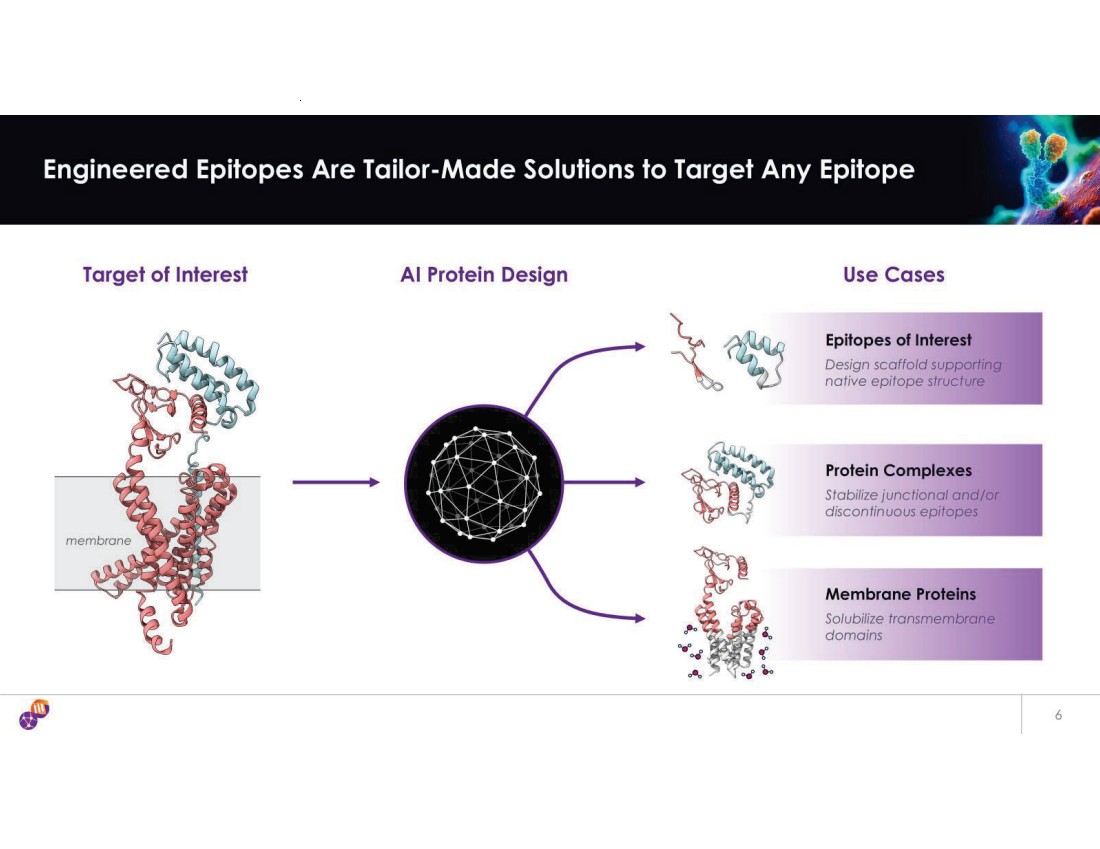
| Any Epitope on Any Drug Target AI Epitope Engineering and Antibody Optimization Engines unlock challenging target classes • Multi-layer technology platform addresses multiple challenges in Ab discovery • Patented Epitope Steering technology • Single-step Ab StableHu x Mammalian Display • Masked (ShieldTx®) Antibodies • T-cell engager panel (EngageTx gag e T x ) iBio’s Discovery Engine iBio’s Proprietary AI Technology Platform We use our Tech Stack to generate new IP against hard-to-drug targets – from idea to Development Candidate in 7 months • Selectively targets functional epitopes • Epitopes with complex modes of action • Unlocks novel target classes • Accelerates discovery of Ab against validated targets AI-guided precision hits that are epitope class agnostic • Gen AI creates mammalian display libraries with phage-like diversity • Single-shot multidimensional lead optimization • Compatible with multi-specific antibody formats • Antibody format agnostic Generative AI meets mammalian display: Ab optimization in 3 weeks 30 |
| Any Epitope on Any Drug Target AI Epitope Engineering and Antibody Optimization Engines unlock challenging target classes • Multi-layer technology platform addresses multiple challenges in Ab discovery • Patented Epitope Steering technology • Single-step Ab StableHu x Mammalian Display • Masked (ShieldTx) Antibodies • T-cell engager panel (EngageTx) iBio’s Discovery Engine iBio’s Proprietary AI Technology Platform We use our Tech Stack to generate new IP against hard-to-drug targets – from idea to Development Candidate in 7 months • Selectively targets functional epitopes • Epitopes with complex modes of action • Unlocks novel target classes • Accelerates discovery of Ab against validated targets AI-guided precision hits that are epitope class agnostic • Gen AI creates mammalian display libraries with phage-like diversity • Single-shot multidimensional lead optimization • Compatible with multi-specific antibody formats • Antibody format agnostic Generative AI meets mammalian display: Ab optimization in 3 weeks 31 |
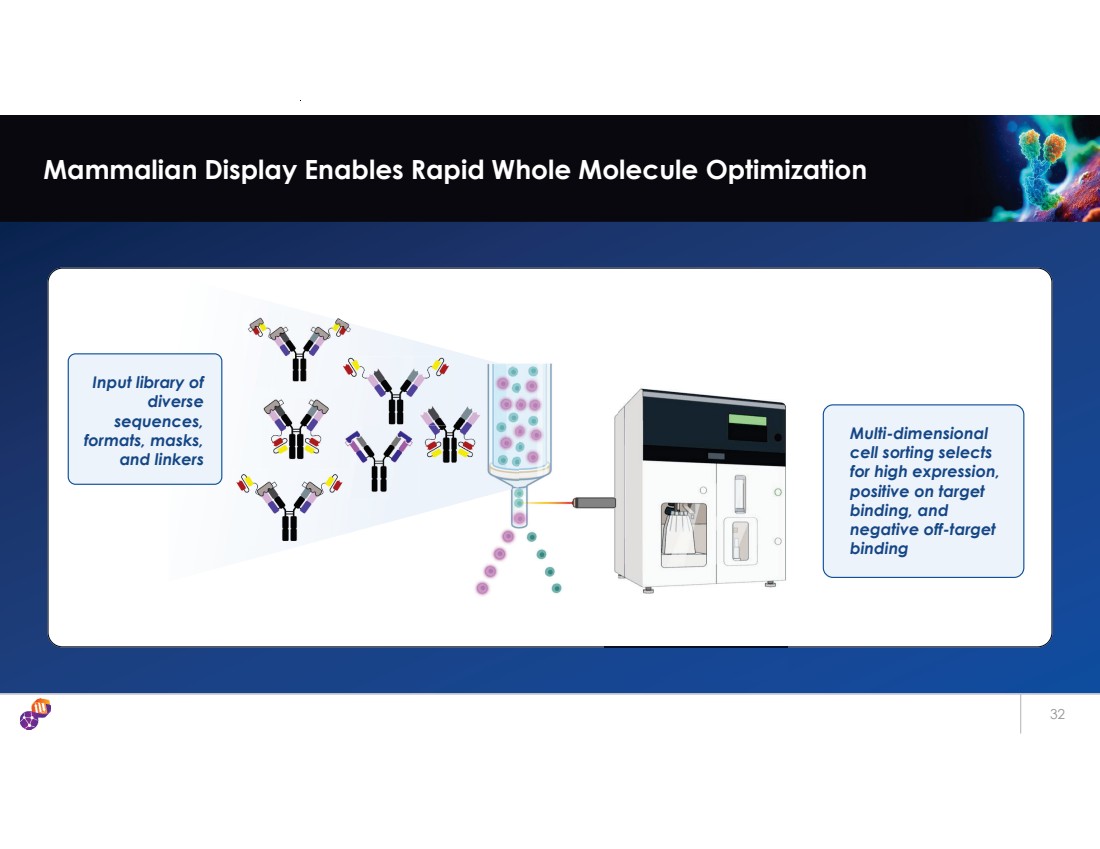
| 32 Mammalian Display Enables Rapid Whole Molecule Optimization Input library of diverse sequences, formats, masks, and linkers Multi-dimensional cell sorting selects for high expression, positive on target binding, and negative off-target binding |
| Corporate Summary |
| 34 A Leadership Team with Deep Industry Experience Deep expertise in cardiometabolic disorders Marc Banjak CLO Martin Brenner, DVM, Ph.D. CEO & CSO Kristi Sarno Senior VP BD Felipe Duran CFO |
| Executive Summary Corporate Highlights Differentiated Pipeline Solving for the Challenges of today’s GLP1’s ¾ Quality weight loss (IBIO-600, IBIO-610) ¾ Developability (IBIO-600, IBIO-610) Patented AI-Driven Discovery Tech Stack ¾ Rapidly advance a highly developable pre-clinical pipeline ¾ Solve hard-to-drug problems Financial Highlights ¾ $10.5M in cash and restricted cash and cash equivalents as of May 1, 2025 ¾ ~16.22M shares outstanding as of June 13, 2025 35 |
| Appendix |
| 37 Pre-Clinical Immuno-Oncology Pipeline |
| *Tumor Micro Environment 38 Beyond Cardiometabolic – Driving Value Within Our Oncology Pipeline Program MoA Potential Indications Early Discovery Late Discovery Lead Optimization IND-Enabling Highlights IBIO-101 Treg depletion, IL-2 sparing Solid tumors, orphan indications Synergistic efficacy with checkpoint inhibitors CCR8 Tumor-infiltrating Treg depletion Solid tumors Highly selective vs. closely related GPCRs Trop-2 x CD3 Tumor-protease activated T cell engager Solid tumors ShieldTx technology enables masking; delivery as pro-drug activated in TME* MUC16 x CD3 Tumor-protease activated T cell engager Ovarian and pancreatic cancer Binds membrane-proximal epitope, distinct from Regeneron MUC16xCD3 EGFRvIII ADCC- enhanced Fc Glioblastoma Highly selective for EGFRvIII over EGFR Latent TGF β Protein Complex Stabilization Solid tumors Innovative mechanism of action locking protein complex in inactive form ShieldTx EngageTx ShieldTx EngageTx |
| 39 Technology Stack |
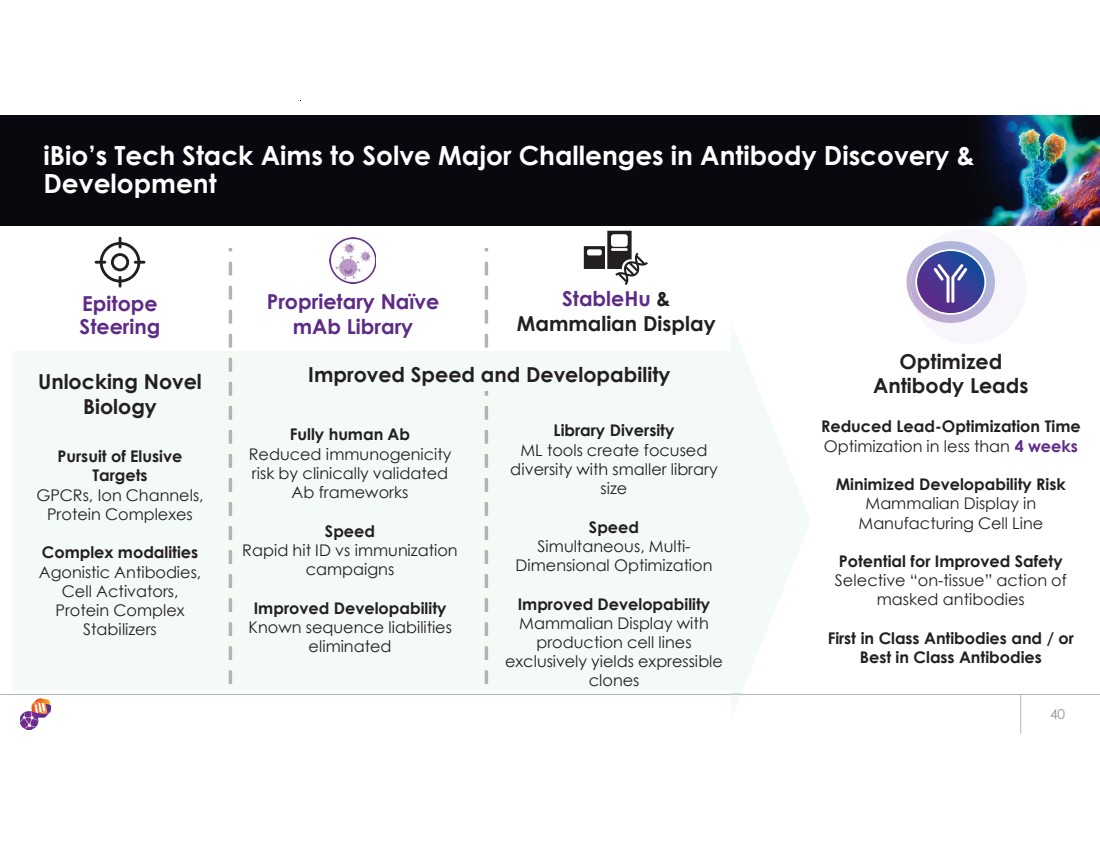
| 40 iBio’s Tech Stack Aims to Solve Major Challenges in Antibody Discovery & Development Epitope Steering StableHu & Mammalian Display Unlocking Novel Biology Reduced Lead-Optimization Time Optimization in less than 4 weeks Minimized Developability Risk Mammalian Display in Manufacturing Cell Line Potential for Improved Safety Selective “on-tissue” action of masked antibodies First in Class Antibodies and / or Best in Class Antibodies Pursuit of Elusive Targets GPCRs, Ion Channels, Protein Complexes Complex modalities Agonistic Antibodies, Cell Activators, Protein Complex Stabilizers Fully human Ab Reduced immunogenicity risk by clinically validated Ab frameworks Speed Rapid hit ID vs immunization campaigns Improved Developability Known sequence liabilities eliminated Optimized Antibody Leads Proprietary Naïve mAb Library Library Diversity ML tools create focused diversity with smaller library size Speed Simultaneous, Multi-Dimensional Optimization Improved Developability Mammalian Display with production cell lines exclusively yields expressible clones Improved Speed and Developability |
| 41 iBio’s Tech Stack Addresses Immuno-oncology Discovery and Development Challenges ShieldTx 2nd Gen T-cell Engager Panel Finely tuned T-cell engagement Adjustable T-cell engagement to fit any tumor target engager Improved safety prediction Cyno cross reactivity allows for better preclinical safety assessment Improved Safety Profile Tissue selective action through “smart”, conditionally activated, antibodies Sequence Diversity Increased humanness and broad CD3 activity for optimized pairing with antigen arms Hu-Cyno Cross Reactivity Risk reduction via cyno monkey toxicity study compatibility Range of Cytokine Release Tailored cytokine release for expanded therapeutic window Enhanced Efficacy and Safety of I/O Antibody Leads EngageTx Greater Safety With Tissue Specificity Seamlessly Integrated Ab Masking Engineered epitopes serve dual purpose for raising and masking of Abs Flexibility in Candidate Selection Simultaneous co-optimization of Ab, mask and linker provides maximized flexibility in candidate selection |
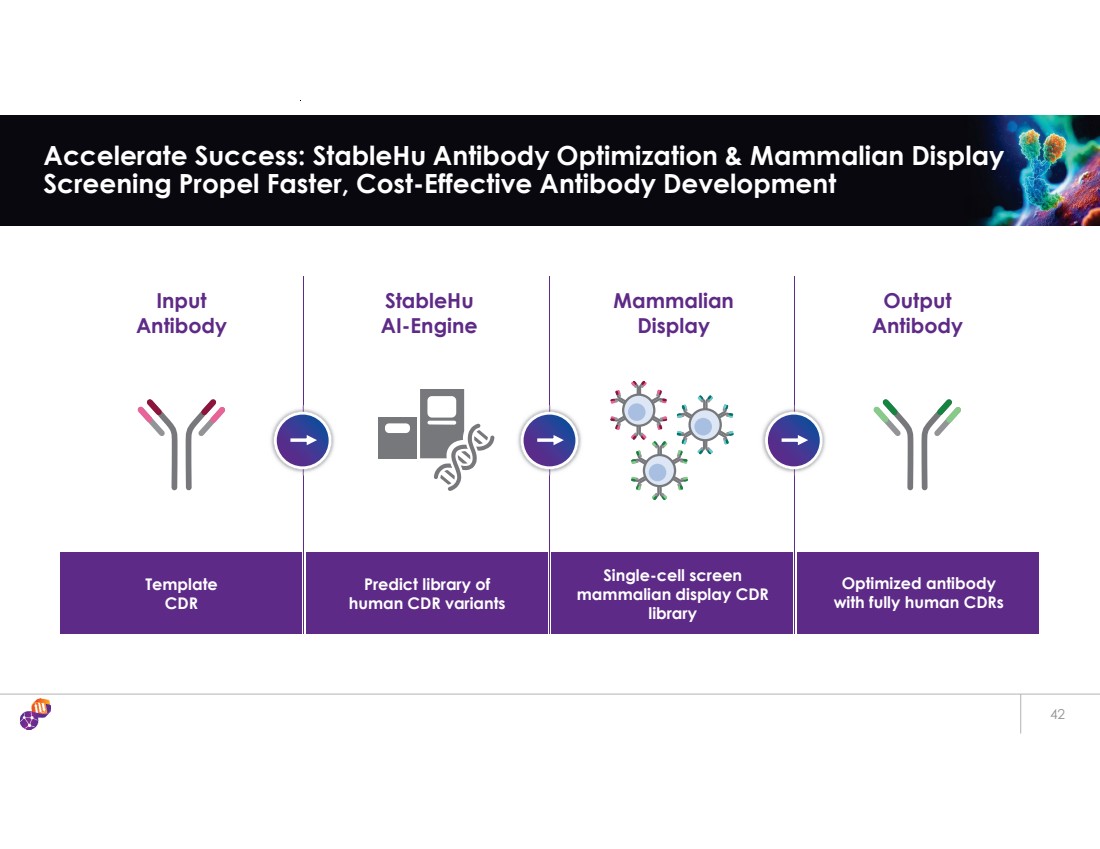
| Input Antibody StableHu AI-Engine Mammalian Display Output Antibody Template CDR Predict library of human CDR variants Single-cell screen mammalian display CDR library Optimized antibody with fully human CDRs 42 Accelerate Success: StableHu Antibody Optimization & Mammalian Display Screening Propel Faster, Cost-Effective Antibody Development |
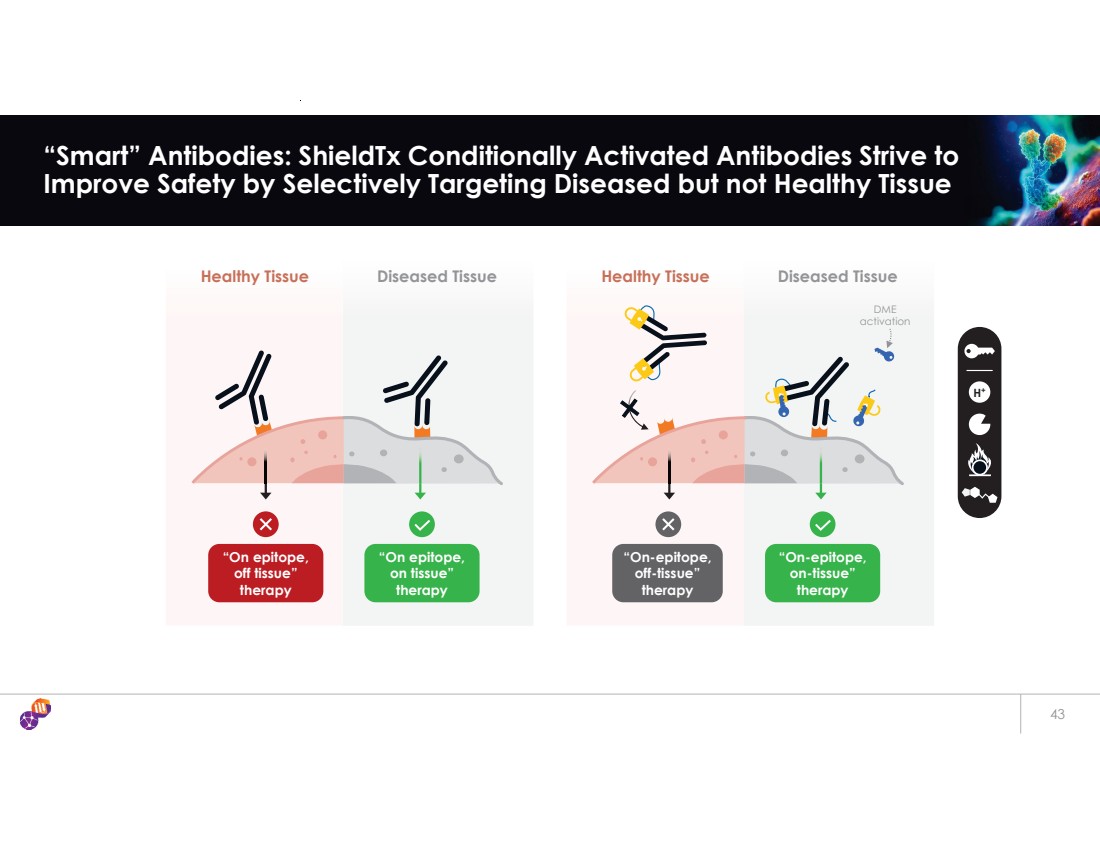
| 43 “Smart” Antibodies: ShieldTx Conditionally Activated Antibodies Strive to Improve Safety by Selectively Targeting Diseased but not Healthy Tissue H+ Diseased Tissue “On-epitope, off-tissue” therapy Healthy Tissue “On-epitope, on-tissue” therapy DME activation Diseased Tissue “On epitope, on tissue” therapy Healthy Tissue “On epitope, off tissue” therapy |
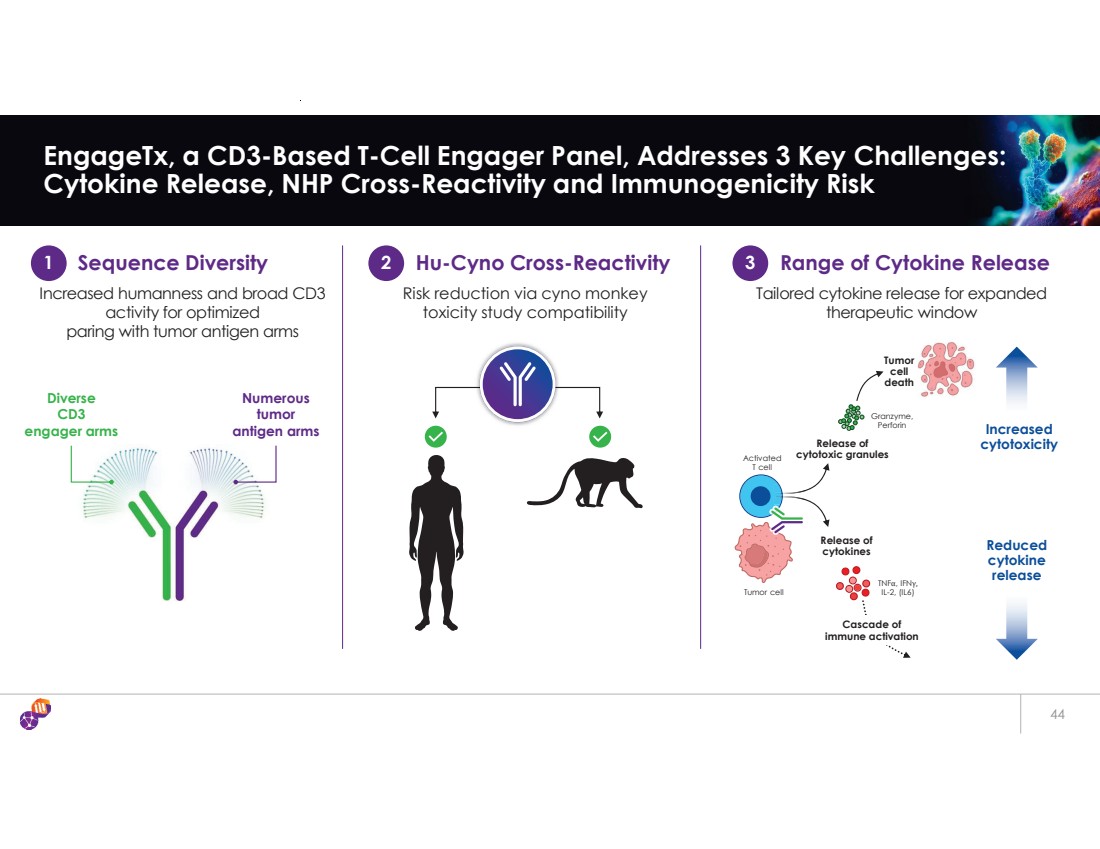
| 44 EngageTx, a CD3-Based T-Cell Engager Panel, Addresses 3 Key Challenges: Cytokine Release, NHP Cross-Reactivity and Immunogenicity Risk Numerous tumor antigen arms Diverse CD3 engager arms 1 Sequence Diversity 2 Hu-Cyno Cross-Reactivity Range of Cytokine Release 3 Increased humanness and broad CD3 activity for optimized paring with tumor antigen arms Risk reduction via cyno monkey toxicity study compatibility Tailored cytokine release for expanded therapeutic window Release of cytokines TNFα, IFNγ, IL-2, (IL6) Increased cytotoxicity Reduced cytokine release Release of cytotoxic granules Granzyme, Perforin Cascade of immune activation Tumor cell death Activated T cell Tumor cell |
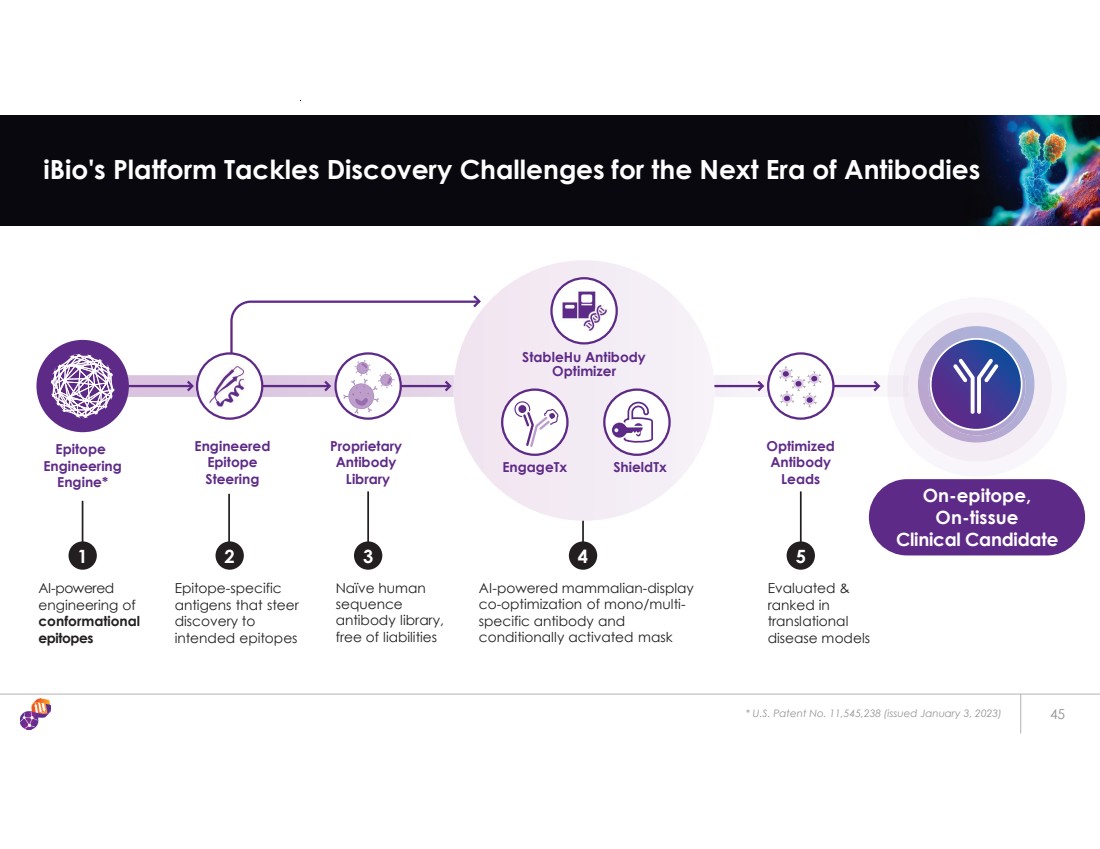
| Epitope Engineering Engine* Proprietary Antibody Library AI-powered mammalian-display co-optimization of mono/multi-specific antibody and conditionally activated mask Engineered Epitope Steering AI-powered engineering of conformational epitopes Epitope-specific antigens that steer discovery to intended epitopes 1 2 3 4 Naïve human sequence antibody library, free of liabilities Optimized Antibody Leads 5 Evaluated & ranked in translational disease models * U.S. Patent No. 11,545,238 (issued January 3, 2023) 45 iBio's Platform Tackles Discovery Challenges for the Next Era of Antibodies EngageTx ShieldTx StableHu Antibody Optimizer On-epitope, On-tissue Clinical Candidate |