The fund seeks a high level of current income with lower volatility than the broader high yield market.
The tables below illustrate the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy, hold and sell shares of the fund. You may pay other fees, such as brokerage commissions and other fees to financial intermediaries, which are not reflected in the tables and examples below. You may qualify for sales charge discounts in Class A Shares if you and your family invest, or agree to invest in the future, at least $50,000 in Virtus Funds. More information on these and other discounts is available: (i) from your financial professional or other financial intermediary; (ii) under “Sales Charges” on page 74 of the fund’s prospectus; (iii) with respect to purchase of shares through specific intermediaries, in Appendix A to the fund’s prospectus, entitled “Intermediary Sales Charge Discounts and Waivers;” and (iv) under “Alternative Purchase Arrangements” on page 113 of the fund’s SAI.
Shareholder Fees - Virtus Newfleet Short Duration High Income Fund |
Class A Shares |
Class C Shares |
Institutional Class Shares |
Class P Shares |
Class R6 Shares |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Sales Charge Imposed on Purchases (as a percentage of Offering Price) | 2.25% | none | none | none | none | |
| Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (as a percentage of Offering Price) | none | 1.00% | [1] | none | none | none |
| [1] | The deferred sales charge is imposed on Class C Shares redeemed during the first year only. |
Annual Fund Operating Expenses - Virtus Newfleet Short Duration High Income Fund |
Class A Shares |
Class C Shares |
Institutional Class Shares |
Class P Shares |
Class R6 Shares |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Management Fees | 0.48% | 0.48% | 0.48% | 0.48% | 0.48% | |
| Distribution and Shareholder Servicing (12b-1) Fees | 0.25% | 0.50% | none | none | none | |
| Other Expenses | 0.25% | 0.26% | 0.27% | 0.17% | 0.18% | |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses | 0.98% | 1.24% | 0.75% | 0.65% | 0.66% | |
| Less: Fee Waiver and/or Expense Reimbursement | [1] | (0.12%) | (0.13%) | (0.15%) | none | (0.11%) |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Expense Reimbursement | [1] | 0.86% | 1.11% | 0.60% | 0.65% | 0.55% |
| [1] | The fund’s investment adviser has contractually agreed to limit the fund’s total operating expenses (excluding certain expenses, such as taxes, leverage and borrowing expenses (such as commitment, amendment and renewal expenses on credit or redemption facilities), interest, brokerage commissions, expenses incurred in connection with any merger or reorganization, unusual or infrequently occurring expenses (such as litigation), acquired fund fees and expenses, and dividend expenses, if any) so that such expenses do not exceed 0.86% for Class A Shares, 1.11% for Class C Shares, 0.60% for Institutional Class Shares, 0.65% for Class P Shares and 0.55% for Class R6 Shares through February 1, 2024. Following the contractual period, the adviser may discontinue these expense reimbursement arrangements at any time. Under certain conditions, the adviser may recapture operating expenses reimbursed and/or fees waived under these arrangements for a period of three years following the date such waiver or reimbursement occurred, provided that the recapture does not cause the fund to exceed its expense limit in effect at the time of the waiver or reimbursement, and any in effect at the time of recapture, after repayment is taken into account. |
This example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods or continued to hold them. The example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year, that the fund’s operating expenses remain the same and that the expense reimbursement agreement remains in place for the contractual period. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions your costs would be:
Expense Example - Virtus Newfleet Short Duration High Income Fund - USD ($) |
Class A Shares |
Class C Shares |
Institutional Class Shares |
Class P Shares |
Class R6 Shares |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Year | $ 311 | $ 213 | $ 61 | $ 66 | $ 56 |
| 3 Years | 518 | 381 | 225 | 208 | 200 |
| 5 Years | 743 | 668 | 402 | 362 | 357 |
| 10 Years | $ 1,389 | $ 1,489 | $ 916 | $ 810 | $ 812 |
Expense Example, No Redemption - Virtus Newfleet Short Duration High Income Fund - USD ($) |
Class A Shares |
Class C Shares |
Institutional Class Shares |
Class P Shares |
Class R6 Shares |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Year | $ 311 | $ 113 | $ 61 | $ 66 | $ 56 |
| 3 Years | 518 | 381 | 225 | 208 | 200 |
| 5 Years | 743 | 668 | 402 | 362 | 357 |
| 10 Years | $ 1,389 | $ 1,489 | $ 916 | $ 810 | $ 812 |
The fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it buys and sells securities (or “turns over” its portfolio). A higher portfolio turnover rate may indicate higher transaction costs and may result in higher taxes when fund shares are held in a taxable account. These costs, which are not reflected in annual fund operating expenses or in the example, affect the fund’s performance. During the most recent fiscal year, the fund’s portfolio turnover rate was 56% of the average value of its portfolio.
The fund seeks to achieve its investment objective by normally investing at least 80% of its net assets (plus borrowings made for investment purposes) in debt securities issued by public and private companies, which are rated below investment grade (rated Ba or below by Moody’s or BB or below by S&P or Fitch, or if unrated, determined by the fund’s subadviser to be of comparable quality) (sometimes referred to as “high-yield securities” or “junk bonds”), while maintaining an average duration of less than three years, and in derivatives and other synthetic instruments that have economic characteristics similar to such debt securities. Derivatives transactions may have the effect of either magnifying or limiting the fund’s gains and losses. To illustrate the effects of changes in interest rates on a portfolio with a similar average duration, generally, a portfolio with an average duration of three years would be expected to fall approximately 3% if interest rates rose by one percentage point.
The fund may invest up to 20% of its assets in bank loans. The fund may invest up to 20% of its assets in non-U.S. securities, which will typically be U.S. dollar-denominated but may also include securities denominated in non-U.S. currencies. The fund will invest less than 10% of its net assets in securities rated CCC or below by Standard and Poor’s.
The fund invests in high yield securities and bank loans, seeking to generate investment income while protecting from adverse market conditions and prioritizing capital preservation.
The portfolio managers apply a disciplined investment approach, making use of fundamental research, to construct a portfolio for investment. The subadviser uses an investment process that focuses on adding value through issue selection, sector/industry selection and opportunistic trading. The fund will generally overweight those sectors and industries where the subadviser identifies well-valued companies whose business profiles are viewed to be improving. In selecting specific debt instruments for investment, the portfolio managers may look to such factors as the issuer’s creditworthiness, the investment’s yield in relation to its credit quality and the investment’s relative value in relation to the high yield market. The portfolio managers seek to construct a portfolio with lower volatility than the broader high yield market in part through the fund’s approach to duration and credit quality. The portfolio managers may sell a security for a variety of reasons, such as to invest in a company offering superior investment opportunities.
The fund may utilize foreign currency exchange contracts, options, stock index futures contracts, warrants and other derivative instruments. Although the fund did not invest significantly in derivative instruments as of the most recent fiscal year end, it may do so at any time.
The fund may not achieve its objective(s), and it is not intended to be a complete investment program. The value of the fund’s investments that supports your share value may decrease. If between the time you purchase shares and the time you sell shares the value of the fund’s investments decreases, you will lose money. Investment values can decrease for a number of reasons. Conditions affecting the overall economy, specific industries or companies in which the fund invests can be worse than expected, and investments may fail to perform as the subadviser expects. As a result, the value of your shares may decrease. Purchase and redemption activities by fund shareholders may impact the management of the fund and its ability to achieve its investment objective(s). The principal risks of investing in the fund are identified below (in alphabetical order after the first six risks).
> Debt Instruments Risk. Debt instruments are subject to greater levels of credit and liquidity risk, may be speculative and may decline in value due to changes in interest rates or an issuer’s or counterparty’s deterioration or default.
> High-Yield Fixed Income Securities (Junk Bonds) Risk. High-yield or junk bonds are subject to greater levels of credit and liquidity risk, may be speculative and may decline in value due to increases in interest rates or an issuer’s deterioration or default.
> Market Volatility Risk. The value of the securities in the fund may go up or down in response to the prospects of individual companies and/or general economic conditions. Price changes may be short- or long-term. Local, regional or global events such as war or military conflict (e.g. Russia’s invasion of Ukraine), acts of terrorism, the spread of infectious illness or other public health issue, recessions, or other events could have a significant impact on the fund and its investments, including hampering the ability of the fund’s portfolio manager(s) to invest the fund’s assets as intended.
> Issuer Risk. The fund will be affected by factors specific to the issuers of securities and other instruments in which the fund invests, including actual or perceived changes in the financial condition or business prospects of such issuers.
> Interest Rate Risk. The values of debt instruments may rise or fall in response to changes in interest rates, and this risk may be enhanced for securities with longer maturities.
> Credit Risk. If the issuer of a debt instrument fails to pay interest or principal in a timely manner, or negative perceptions exist in the market of the issuer’s ability to make such payments, the price of the security may decline.
> Bank Loan Risk. In addition to the risks typically associated with high-yield fixed income securities, bank loans may be unsecured or not fully collateralized, may be subject to restrictions on resale, may be less liquid and may trade infrequently on the secondary market. Bank loans settle on a delayed basis; thus, sale proceeds may not be available to meet redemptions for a substantial period of time after the sale of the loan.
> Confidential Information Access Risk. The fund’s subadviser normally will seek to avoid the receipt of material, non-public information (“Confidential Information”) about the issuers of privately placed instruments (which may include Senior Loans, other bank loans and related investments), because such issuers may have or later issue publicly traded securities, and thus the fund may be disadvantaged in comparison to other investors who have received Confidential Information from such issuers.
> Counterparty Risk. There is risk that a party upon whom the fund relies to complete a transaction will default.
> Currency Rate Risk. Fluctuations in the exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and foreign currencies may negatively affect the value of the fund’s shares.
> Derivatives Risk. Derivatives may include, among other things, futures, options, forwards and swap agreements and may be used in order to hedge portfolio risks, create leverage or attempt to increase returns. Investments in derivatives may result in increased volatility and the fund may incur a loss greater than its principal investment.
> Foreign Investing Risk. Investing in foreign securities subjects the fund to additional risks such as increased volatility; currency fluctuations; less liquidity; less publicly available information about the foreign investment; and political, regulatory, economic, and market risk.
> Leverage Risk. When a fund leverages its portfolio by borrowing or certain types of transactions or instruments, including derivatives, fund may be less liquid, may liquidate positions at an unfavorable time, and the volatility of the fund’s value may increase.
> Liquidity Risk. Certain securities may be substantially less liquid than many other securities, such as U.S. Government securities or common stocks. To the extent the fund invests in less liquid securities or the level of liquidity in a particular market is constrained, the lack of an active market for investments may cause delay in disposition or force a sale below fair value.
> Mortgage-Backed and Asset-Backed Securities Risk. Changes in interest rates may cause both extension and prepayment risks for mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities. These securities are also subject to risks associated with the non-repayment of underlying collateral, including losses to the fund.
> Prepayment/Call Risk. Issuers may prepay or call their fixed rate obligations when interest rates fall, forcing the fund to reinvest in obligations with lower interest rates and the fund may not benefit fully from the increase in value that other fixed income investments experience when interest rates decline.
> Redemption Risk. One or more large shareholders or groups of shareholders may redeem their holdings in the fund, resulting in an adverse impact on remaining shareholders in the fund by causing the fund to take actions it would not otherwise have taken.
> Small and Medium Market Capitalization Risk. The fund’s investments in small and medium market capitalization companies may increase the volatility and risk of loss to the fund, as compared with investments in larger, more established companies.
> Unrated Fixed Income Securities Risk. If the subadviser is unable to accurately assess the quality of an unrated fixed income security, the fund may invest in a security with greater risk than intended, or the securities may be more difficult to sell than anticipated.
> U.S. Government Securities Risk. U.S. Government securities may be subject to price fluctuations. An agency may default on an obligation not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States. Any guarantee on U.S. government securities does not apply to the value of the fund’s shares.
> Variable Distribution Risk. Periodic distributions by investments of variable or floating interest rates vary with fluctuations in market interest rates.
Please see “More Information About Risks Related to Principal Investment Strategies” in the fund’s prospectus for a more detailed description of the fund’s risks.
The bar chart and table below provide some indication of the potential risks of investing in the fund. The fund’s past performance, before and after taxes, is not necessarily an indication of how the fund will perform in the future. The current subadviser commenced providing services for the fund in July 2022 and therefore the returns shown in the table for periods prior to that date reflect the performance of other investment professionals.
The bar chart shows changes in the fund’s performance from year to year over a 10-year period. The table shows how the fund’s average annual returns compare to those of a broad-based securities market index. Updated performance information is available at virtus.com or by calling 800-243-1574.
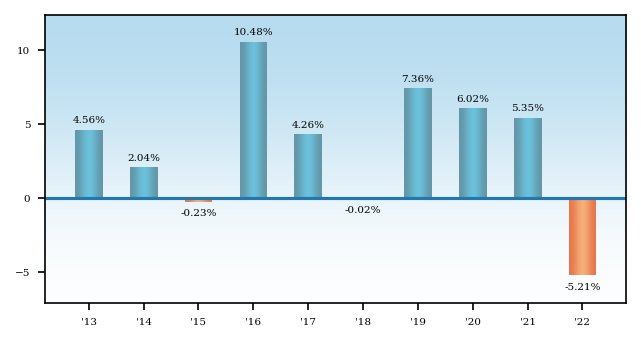
Best Quarter: | 2020, Q2: | 9.80% | Worst Quarter: | 2020, Q1: | -11.95% |
Returns reflect deduction of maximum sales charges and full redemption at end of periods shown.
Average Annual Total Returns - Virtus Newfleet Short Duration High Income Fund |
Label |
1 Year |
5 Years |
10 Years |
Since Inception |
Inception Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class A Shares | Return Before Taxes | (7.61%) | 1.86% | 2.87% | ||
| Class C Shares | Return Before Taxes | (5.64%) | 2.09% | 2.85% | ||
| Institutional Class Shares | Return Before Taxes | (5.21%) | 2.59% | 3.37% | ||
| Institutional Class Shares | After Taxes on Distributions | Return After Taxes on Distributions | (7.50%) | 0.23% | 1.00% | ||
| Institutional Class Shares | After Taxes on Distributions and Sales | Return After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | (3.07%) | 0.95% | 1.50% | ||
| Class P Shares | Return Before Taxes | (5.23%) | 2.57% | 3.32% | ||
| Class R6 Shares | Return Before Taxes | (5.21%) | 2.66% | 2.85% | Feb. 01, 2017 | |
| ICE BofA 1-3Y BB US Cash Pay High Yield Index | ICE BofA 1-3Y BB US Cash Pay High Yield Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) | (3.07%) | 3.05% | 3.59% | 3.12% | Feb. 01, 2017 |
The ICE BofA 1-3 Year BB U.S. Cash Pay High Yield Index is a subset of The ICE BofA U.S. Cash Pay High Yield Index including all securities with a remaining term to final maturity less than 3 years and rated BB1 through BB3, inclusive. The ICE BofA U.S. Cash Pay High Yield Index tracks the performance of U.S. dollar denominated below investment grade corporate debt, currently in a coupon paying period, that is publicly issued in the U.S. domestic market.
After-tax returns are calculated using the historical highest individual federal marginal income tax rates and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. After-tax returns are shown only for Institutional Class Shares; after-tax returns for other classes will vary. Actual after-tax returns depend on the investor’s tax situation and may differ from those shown. After-tax returns are not relevant to investors who hold fund shares in tax-deferred accounts or to shares held by non-taxable entities. In certain cases, the Return After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares for a period may be higher than other return figures for the same period. This will occur when a capital loss is realized upon the sale of fund shares and provides an assumed tax benefit that increases the return.