The fund seeks after-inflation capital appreciation and current income.
The tables below illustrate the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy, hold and sell shares of the fund. You may pay other fees, such as brokerage commissions and other fees to financial intermediaries, which are not reflected in the tables and examples below. You may qualify for sales charge discounts in Class A Shares if you and your family invest, or agree to invest in the future, at least $50,000 in Virtus Funds. More information on these and other discounts is available: (i) from your financial professional or other financial intermediary; (ii) under “Sales Charges” on page 74 of the fund’s prospectus; (iii) with respect to purchase of shares through specific intermediaries, in Appendix A to the fund’s prospectus, entitled “Intermediary Sales Charge Discounts and Waivers;” and (iv) under “Alternative Purchase Arrangements” on page 113 of the fund’s SAI.
Shareholder Fees - Virtus Global Allocation Fund |
Class A Shares |
Class C Shares |
Institutional Class Shares |
Class P Shares |
Administrative Class Shares |
Class R6 Shares |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Sales Charge Imposed on Purchases (as a percentage of Offering Price) | 5.50% | none | none | none | none | none | |
| Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (as a percentage of Offering Price) | none | 1.00% | [1] | none | none | none | none |
| [1] | The deferred sales charge is imposed on Class C Shares redeemed during the first year only. |
Annual Fund Operating Expenses - Virtus Global Allocation Fund |
Class A Shares |
Class C Shares |
Institutional Class Shares |
Class P Shares |
Administrative Class Shares |
Class R6 Shares |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Management Fees | 0.70% | 0.70% | 0.70% | 0.70% | 0.70% | 0.70% | |
| Distribution and Shareholder Servicing (12b-1) Fees | 0.25% | 1.00% | none | none | 0.25% | none | |
| Other Expenses | 0.31% | 0.33% | 0.31% | 0.30% | 0.28% | 0.23% | |
| Acquired Fund Fees and Expenses | 0.25% | 0.25% | 0.25% | 0.25% | 0.25% | 0.25% | |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses | [1] | 1.51% | 2.28% | 1.26% | 1.25% | 1.48% | 1.18% |
| Less: Fee Waiver and/or Expense Reimbursement | [2] | (0.74%) | (0.76%) | (0.72%) | (0.68%) | (0.76%) | (0.71%) |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Expense Reimbursement | [1],[2] | 0.77% | 1.52% | 0.54% | 0.57% | 0.72% | 0.47% |
| [1] | The Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses do not correlate to the ratio of expenses to average net assets appearing in the Financial Highlights tables, which tables reflect only the operating expenses of the fund and do not include acquired fund fees and expenses. |
| [2] | The fund’s investment adviser has contractually agreed to limit the fund’s total operating expenses (excluding certain expenses, such as taxes, leverage and borrowing expenses (such as commitment, amendment and renewal expenses on credit or redemption facilities), interest, brokerage commissions, expenses incurred in connection with any merger or reorganization, unusual or infrequently occurring expenses (such as litigation), acquired fund fees and expenses, and dividend expenses, if any) so that such expenses do not exceed 0.52% for Class A Shares, 1.27% for Class C Shares, 0.29% for Institutional Class Shares, 0.32% for Class P Shares, 0.22% for Class R6 Shares and 0.47% for Administrative Class Shares through February 1, 2024. Following the contractual period, the adviser may discontinue these expense reimbursement arrangements at any time. Under certain conditions, the adviser may recapture operating expenses reimbursed and/or fees waived under these arrangements for a period of three years following the date such waiver or reimbursement occurred, provided that the recapture does not cause the fund to exceed its expense limit in effect at the time of the waiver or reimbursement, and any in effect at the time of recapture, after repayment is taken into account. |
This example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods or continued to hold them. The example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year, that the fund’s operating expenses remain the same and that the expense reimbursement agreement remains in place for the contractual period. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions your costs would be:
Expense Example - Virtus Global Allocation Fund - USD ($) |
Class A Shares |
Class C Shares |
Institutional Class Shares |
Class P Shares |
Administrative Class Shares |
Class R6 Shares |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Year | $ 624 | $ 255 | $ 55 | $ 58 | $ 74 | $ 48 |
| 3 Years | 932 | 639 | 328 | 329 | 393 | 304 |
| 5 Years | 1,262 | 1,151 | 622 | 621 | 736 | 580 |
| 10 Years | $ 2,193 | $ 2,557 | $ 1,459 | $ 1,451 | $ 1,703 | $ 1,369 |
Expense Example, No Redemption - Virtus Global Allocation Fund - USD ($) |
Class A Shares |
Class C Shares |
Institutional Class Shares |
Class P Shares |
Administrative Class Shares |
Class R6 Shares |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Year | $ 624 | $ 155 | $ 55 | $ 58 | $ 74 | $ 48 |
| 3 Years | 932 | 639 | 328 | 329 | 393 | 304 |
| 5 Years | 1,262 | 1,151 | 622 | 621 | 736 | 580 |
| 10 Years | $ 2,193 | $ 2,557 | $ 1,459 | $ 1,451 | $ 1,703 | $ 1,369 |
The fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it buys and sells securities (or “turns over” its portfolio). A higher portfolio turnover rate may indicate higher transaction costs and may result in higher taxes when fund shares are held in a taxable account. These costs, which are not reflected in annual fund operating expenses or in the example, affect the fund’s performance. During the most recent fiscal year, the fund’s portfolio turnover rate was 88% of the average value of its portfolio.
The fund seeks to achieve its investment objective through a combination of active allocation across asset classes and actively managed strategies within those asset classes. The fund allocates its investments across asset classes in response to changing market, macroeconomic, and other factors and events that the portfolio managers believe may affect the value of the fund’s investments. To gain exposure to different asset classes, the fund incorporates actively managed underlying strategies, both directly through dedicated teams managing separate sleeves of the fund and indirectly through investments in affiliated mutual funds, as well as through passive strategies. Under normal circumstances, the fund invests directly and indirectly in global equity securities, fixed-income securities, and long and short positions using derivatives across multiple asset classes. The fund may also invest in exchange-traded funds (“ETFs”), unaffiliated mutual funds, other pooled vehicles and derivative instruments such as futures, among others. The fund’s actively managed underlying strategies incorporate environmental, social and governance (“ESG”) factors into the selection of individual securities, and the portfolio managers also consider ESG factors in the construction of the overall portfolio. The fund’s allocations to different strategies and instruments are expected to vary over time and from time to time.
The fund’s baseline long-term allocation consists of 60% to global equity exposure (the “Equity Component”) and 40% to fixed income exposure (the “Fixed Income Component”), which is also the allocation of the blended benchmark index against which the fund’s portfolio is managed. The Equity Component can include direct or indirect exposure to equity securities of any market capitalization, any sector and from any country, including emerging markets. The fund expects to invest a significant portion of the Equity Component into Virtus NFJ Global Sustainability Fund, an affiliated mutual fund. The Fixed Income Component primarily consists of direct or indirect exposure to fixed income securities from any sector, of any credit-quality including high yield bonds, from any part of the capital structure including loans, preferred securities and convertibles, denominated in any currency and issued by any country including emerging markets. Within the Fixed Income Component, the allocation to high-yield bonds, senior loans, preferred securities, convertibles and emerging market debt will not exceed 30% of the fund’s assets on a gross exposure basis. Separately, the fund will also invest in non-U.S. currencies and take FX positions through derivatives, both long and short.
The portfolio managers may also invest up to 10% of the portfolio in any other asset class that falls outside of the Equity Component and the Fixed-Income Component, which constitute the “Other Component.” Examples include, but are not limited to, derivatives on carbon emissions and commodities. Other asset classes may be added at the portfolio managers’ discretion. The portfolio managers will typically over- or under-weight the fund’s portfolio against the baseline long-term allocation, depending on the portfolio managers’ view of the relative attractiveness of the investment opportunities available, which will change over time.
Depending on market conditions, the Equity Component may range between approximately 50% and 70% of the fund’s assets, the Fixed Income Component may range between approximately 10% and 70% of the fund’s assets and the Other Component may range between 0% and 10% of the fund’s assets. The ranges apply at the time of purchase. The fund’s exposure to each component may vary from the ranges due to market movements and it is at the portfolio managers’ discretion when to bring the fund back within the range. As a result of its derivative positions, the fund may have gross investment exposures in excess of 100% of its net assets (i.e., the fund may be leveraged) and therefore subject to heightened risk of loss. The fund’s performance can depend substantially on the performance of assets or indices underlying its derivatives even though it does not directly or indirectly own those underlying assets or indices.
The portfolio managers adjust the fund’s exposure to the Equity Component, the Fixed Income Component, and the Other Component in response to changes in their views based on their analysis of market, macroeconomic and other factors. In conjunction with their asset class analysis the portfolio managers seek to gain exposure to desired asset classes primarily through actively managed underlying strategies that apply ESG factors (including the strategy employed by Virtus NFJ Global Sustainability Fund within the Equity Component) and passive ESG ETFs and futures. They also consider ESG factors in the construction of the overall portfolio. The portfolio managers believe that investing in companies with strong records for managing ESG risks can generate long-term competitive financial returns and positive societal impact.
Within the Fixed Income Component limits described above, the fund intends to make use of an integrated ESG security selection strategy (“U.S. Fixed Income Sleeve”) that is managed by a dedicated team of portfolio managers. This strategy focuses on investments in bonds, notes, other debt instruments and preferred securities, including derivatives relating to such investments. The portfolio managers invest in a diversified portfolio of high-quality bonds that generates return primarily through security selection and sector rotation with an investment grade focus. The U.S. Fixed Income Sleeve may also invest in high yield debt (commonly known as “junk bonds”) and emerging market corporate and sovereign bonds. The strategy is based on bottom-up fundamental credit research, which accounts for the potential financial impact of ESG issues facing corporations and therefore considers ESG factors alongside financial factors in the security selection and overall risk management process. Portfolio managers have the ability to weigh risks relative to market compensation and relative to corporate strategies that seek to address identified ESG concerns.
As a portion of the Equity Component described above, the fund intends to make use of a managed volatility strategy that focuses on investments in globally diverse equity securities, including emerging market equities (“Managed Volatility Sleeve”), and is managed by a dedicated team of portfolio managers. The sleeve’s strategy focuses on the overall management of portfolio volatility and favors stocks that demonstrate lower beta. The portfolio managers apply an investment constraint requiring that the weighted average of the combined MSCI “E,” “S” and “G” scores of the individual securities within the Managed Volatility Sleeve is higher at the time of purchase than the weighted average of the combined “E,” “S” and “G” scores of the securities in the benchmark, the MSCI All Country World Index. The ESG evaluation process incorporates scores based on company sustainability disclosure, government and academic data and media searches, among other sources.
The fund may invest in any type of equity or fixed income security, including common and preferred stocks, warrants and convertible securities, mortgage-backed securities, asset-backed securities and government and corporate bonds. The fund may invest in securities of companies of any capitalization, including smaller capitalization companies. The fund also may make investments intended to provide exposure to one or more commodities or securities indices, currencies, and real estate-related securities. The fund is expected to be highly diversified across industries, sectors, and countries. The fund may liquidate a holding if it locates another instrument that offers a more attractive exposure to an asset class or when there is a change in the fund’s target asset allocation or allocation among dedicated sleeves, or if the instrument is otherwise deemed inappropriate.
In implementing these investment strategies, the fund may make substantial use of over-the-counter (OTC) or exchange-traded derivatives, including futures contracts, interest rate swaps, total return swaps, credit default swaps, options (puts and calls) purchased or sold by the fund, currency forwards, and structured notes. The fund may use derivatives for a variety of purposes, including: as a hedge against adverse changes in the market price of securities, interest rates, or currency exchange rates; as a substitute for purchasing or selling securities; to increase the fund’s return as a non-hedging strategy that may be considered speculative; and to manage portfolio characteristics. When making use of volatility-linked derivatives, the fund will enter into instruments such as variance swaps, volatility futures and similar volatility instruments that reference indexes representing targeted asset classes, such as variance swaps on the S&P 500 Index or on the Euro Stoxx 50 Index. Derivatives positions are eligible to be held in any of the Equity Component, the Fixed Income Component or Other Component of the fund. The fund may maintain a significant percentage of its assets in cash and cash equivalents which will serve as margin or collateral for the fund’s obligations under derivative transactions.
The fund may not achieve its objective(s), and it is not intended to be a complete investment program. The value of the fund’s investments that supports your share value may decrease. If between the time you purchase shares and the time you sell shares the value of the fund’s investments decreases, you will lose money. Investment values can decrease for a number of reasons. Conditions affecting the overall economy, specific industries or companies in which the fund invests can be worse than expected, and investments may fail to perform as the subadviser expects. As a result, the value of your shares may decrease. In addition, you will also be subject to the risks associated with the principal investment strategies of any underlying funds in which the fund invests. Purchase and redemption activities by fund shareholders may impact the management of the fund and its ability to achieve its investment objective(s). The principal risks of investing in the fund are identified below (in alphabetical order after the first nine risks).
> Allocation Risk. If the fund’s exposure to equities and fixed income securities, or to other asset classes, deviates from the intended allocation, or if the fund’s allocation is not optimal for market conditions at a given time, the fund’s performance may suffer.
> Market Volatility Risk. The value of the securities in the fund may go up or down in response to the prospects of individual companies and/or general economic conditions. Price changes may be short- or long-term. Local, regional or global events such as war or military conflict (e.g. Russia’s invasion of Ukraine), acts of terrorism, the spread of infectious illness or other public health issue, recessions, or other events could have a significant impact on the fund and its investments, including hampering the ability of the fund’s portfolio manager(s) to invest the fund’s assets as intended.
> Issuer Risk. The fund will be affected by factors specific to the issuers of securities and other instruments in which the fund invests, including actual or perceived changes in the financial condition or business prospects of such issuers.
> ESG Risk. The fund’s consideration of ESG factors could cause the fund to perform differently from other funds. While the subadviser believes that the integration of ESG factors into the fund’s investment process has the potential to contribute to performance, ESG factors may not be considered for every investment decision and there is no guarantee that the integration of ESG factors will result in better performance.
> Underlying Fund Risk. The fund will be indirectly affected by factors, risks and performance specific to any other fund in which it invests.
> Equity Securities Risk. The value of the stocks held by the fund may be negatively affected by the financial market, industries in which the fund invests, or issuer-specific events. Focus on a particular style or in small or medium-sized companies may enhance that risk.
> Debt Instruments Risk. Debt instruments are subject to greater levels of credit and liquidity risk, may be speculative and may decline in value due to changes in interest rates or an issuer’s or counterparty’s deterioration or default.
> Interest Rate Risk. The values of debt instruments may rise or fall in response to changes in interest rates, and this risk may be enhanced for securities with longer maturities.
> Derivatives Risk. Derivatives may include, among other things, futures, options, forwards and swap agreements and may be used in order to hedge portfolio risks, create leverage or attempt to increase returns. Investments in derivatives may result in increased volatility and the fund may incur a loss greater than its principal investment.
> Call Risk. A fixed-income security may be redeemed before maturity (“called”) below its current market price, and a call may lead to the reinvestment of proceeds at a lower interest rate, or with higher credit risk or other less favorable characteristics.
> Commodity and Commodity-linked Instruments Risk. Commodities and commodity-linked instruments will subject the fund’s portfolio to greater volatility than investments in traditional securities.Commodity-linked instruments may experience returns different than the commodity they attempt to track and may also be exposed to counterparty risk.
> Convertible Securities Risk. The value of a convertible security may decline as interest rates rise and/or vary with fluctuations in the market value of the underlying securities. The security may be called for redemption at a time and/or price unfavorable to the fund.
> Counterparty Risk. A counterparty to a derivatives contract, repurchase agreement, a loan of portfolio securities or an unsettled transaction may be unable or unwilling to make timely settlement payments or otherwise honor its obligations to the fund.
> Credit Risk. If the issuer of a debt instrument fails to pay interest or principal in a timely manner, or negative perceptions exist in the market of the issuer’s ability to make such payments, the price of the security may decline.
> Currency Rate Risk. Fluctuations in the exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and foreign currencies may negatively affect the value of the fund’s shares.
> Emerging Markets Risk. Foreign investing risk may be particularly high to the extent that the fund invests in emerging market securities. Emerging markets securities may be more volatile, or more greatly affected by negative conditions, than those of their counterparts in more established foreign markets.
> ETF Risk. The risks associated with investing in ETFs generally reflect the risks of owning shares of the underlying securities the ETF is designed to track, although lack of liquidity in an ETF could result in its value being more volatile than the underlying portfolio of securities.
> Focused Investment Risk. To the extent the fund focuses its investments on a limited number of issuers, sectors, industries or geographic regions, it may be subject to increased risk and volatility.
> Foreign Investing Risk. Investing in foreign securities subjects the fund to additional risks such as increased volatility; currency fluctuations; less liquidity; less publicly available information about the foreign investment; and political, regulatory, economic, and market risk.
> High-Yield Fixed Income Securities (Junk Bonds) Risk. High-yield or junk bonds are subject to greater levels of credit and liquidity risk, may be speculative and may decline in value due to increases in interest rates or an issuer’s deterioration or default.
> Index Risk. Investments in index-linked derivatives are subject to the risks associated with the applicable index.
> Leverage Risk. When a fund leverages its portfolio by borrowing or certain types of transactions or instruments, including derivatives, fund may be less liquid, may liquidate positions at an unfavorable time, and the volatility of the fund’s value may increase.
> Liquidity Risk. Certain securities may be substantially less liquid than many other securities, such as U.S. Government securities or common stocks. To the extent the fund invests in less liquid securities or the level of liquidity in a particular market is constrained, the lack of an active market for investments may cause delay in disposition or force a sale below fair value.
> Mortgage-Backed and Asset-Backed Securities Risk. Changes in interest rates may cause both extension and prepayment risks for mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities. These securities are also subject to risks associated with the non-repayment of underlying collateral, including losses to the fund.
> Portfolio Turnover Risk. High levels of portfolio turnover increase transaction costs and taxes and may lower investment performance.
> Real Estate Investment Risk. The fund may be negatively affected by changes in real estate values or economic conditions, credit risk and interest rate fluctuations, changes in the value of the underlying real estate and defaults by lessees and/or borrowers.
> Redemption Risk. One or more large shareholders or groups of shareholders may redeem their holdings in the fund, resulting in an adverse impact on remaining shareholders in the fund by causing the fund to take actions it would not otherwise have taken.
> Small and Medium Market Capitalization Risk. The fund’s investments in small and medium market capitalization companies may increase the volatility and risk of loss to the fund, as compared with investments in larger, more established companies.
> Variable Distribution Risk. Periodic distributions by investments of variable or floating interest rates vary with fluctuations in market interest rates.
Please see “More Information About Risks Related to Principal Investment Strategies” in the fund’s prospectus for a more detailed description of the fund’s risks.
The bar chart and table below provide some indication of the potential risks of investing in the fund. The fund’s past performance, before and after taxes, is not necessarily an indication of how the fund will perform in the future.
The bar chart shows changes in the fund’s performance from year to year over a 10-year period. The table shows how the fund’s average annual returns compare to those of two broad-based securities market indexes and a composite benchmark that reflects the market sectors in which the fund invests. Updated performance information is available at virtus.com or by calling 800-243-1574.
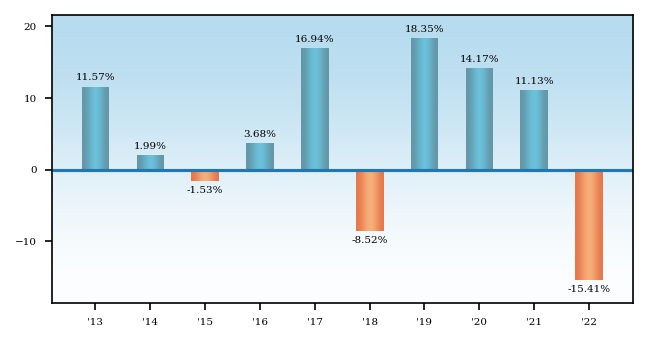
Best Quarter: | 2020, Q2: | 13.26% | Worst Quarter: | 2020, Q1: | -12.48% |
Returns reflect deduction of maximum sales charges and full redemption at end of periods shown.
Average Annual Total Returns - Virtus Global Allocation Fund |
Label |
1 Year |
5 Years |
10 Years |
Since Inception |
Inception Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class A Shares | Return Before Taxes | (20.30%) | 1.61% | 3.83% | ||
| Class C Shares | Return Before Taxes | (16.22%) | 2.00% | 3.65% | ||
| Institutional Class Shares | Return Before Taxes | (15.41%) | 3.05% | 4.67% | ||
| Institutional Class Shares | After Taxes on Distributions | Return After Taxes on Distributions | (16.77%) | 0.66% | 2.55% | ||
| Institutional Class Shares | After Taxes on Distributions and Sales | Return After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | (8.33%) | 1.79% | 3.01% | ||
| Class P Shares | Return Before Taxes | (15.43%) | 3.01% | 4.67% | ||
| Administrative Class Shares | Return Before Taxes | (15.65%) | 3.10% | 4.60% | ||
| Class R6 Shares | Return Before Taxes | (15.40%) | 3.10% | 5.00% | Sep. 08, 2015 | |
| MSCI All Country World Index (net) | MSCI All Country World Index (net) (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) | (18.36%) | 5.23% | 7.98% | 8.11% | Sep. 08, 2015 |
| Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index | Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) | (13.01%) | 0.02% | 1.06% | 0.86% | Sep. 08, 2015 |
| 60% MSCI All Country World Index (net) / 40% Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index | 60% MSCI All Country World Index (net) / 40% Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) | (16.02%) | 3.45% | 5.39% | 5.43% | Sep. 08, 2015 |
The MSCI All Country World Index (net) is a free float-adjusted market capitalization-weighted index that measures equity performance of developed and emerging markets. The Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index measures the U.S. investment grade fixed rate bond market. The indexes are calculated on a total return basis. The indexes are unmanaged and not available for direct investment.
After-tax returns are calculated using the historical highest individual federal marginal income tax rates and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. After-tax returns are shown only for Institutional Class Shares; after-tax returns for other classes will vary. Actual after-tax returns depend on the investor’s tax situation and may differ from those shown. After-tax returns are not relevant to investors who hold fund shares in tax-deferred accounts or to shares held by non-taxable entities. In certain cases, the Return After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares for a period may be higher than other return figures for the same period. This will occur when a capital loss is realized upon the sale of fund shares and provides an assumed tax benefit that increases the return.