The fund seeks a high level of income consistent with minimal fluctuation in principal value and liquidity.
This table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy, hold, and sell shares of the fund. You may also incur brokerage commissions and other charges when buying or selling shares of the fund, which are not reflected in the table or example below.
Shareholder Fees - T. Rowe Price Short-Term Bond Fund, Inc. - USD ($) |
Investor Class |
I Class |
Advisor Class |
Z Class |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum account fee | $ 20 | [1] | none | none | none |
| [1] | Subject to certain exceptions, accounts with a balance of less than $10,000 are charged an annual $20 fee. |
Annual Fund Operating Expenses - T. Rowe Price Short-Term Bond Fund, Inc. |
Investor Class |
I Class |
Advisor Class |
Z Class |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Management fees | 0.30% | 0.30% | 0.30% | 0.30% | |||||
| Distribution and service (12b-1) fees | none | none | 0.25% | none | |||||
| Other expenses | 0.13% | 0.03% | 0.18% | 0.01% | |||||
| Total annual fund operating expenses | [1] | 0.43% | 0.33% | 0.73% | 0.31% | ||||
| Fee waiver/expense reimbursement | none | none | none | (0.31%) | [1],[2] | ||||
| Total annual fund operating expenses after fee waiver/expense reimbursement | 0.43% | [1] | 0.33% | [1] | 0.73% | [1] | none | [2] | |
| [1] | Restated to reflect current fees. |
| [2] | T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc., has contractually agreed to waive and/or bear all the Z Class’ expenses (excluding interest; expenses related to borrowings, taxes, and brokerage; nonrecurring, extraordinary expenses; and acquired fund fees and expenses) in their entirety. T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc., expects this fee waiver and/or expense reimbursement arrangement to remain in place indefinitely, and the agreement may only be amended or terminated with approval by the fund’s Board of Directors. |
Expense Example - T. Rowe Price Short-Term Bond Fund, Inc. - USD ($) |
Investor Class |
I Class |
Advisor Class |
Z Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Year | $ 44 | $ 34 | $ 75 | none |
| 3 Years | 138 | 106 | 233 | none |
| 5 Years | 241 | 185 | 406 | none |
| 10 Years | $ 542 | $ 418 | $ 906 | none |
Normally, the fund will invest at least 80% of its net assets (including any borrowings for investment purposes) in bonds. The fund will invest in a diversified portfolio of short- and intermediate-term investment-grade corporate, government, and asset- and mortgage-backed securities. The fund may also invest in money market securities, bank obligations, collateralized mortgage obligations, and foreign securities, including securities of issuers in emerging markets. The fund’s average effective maturity will normally not exceed three years. The fund will only purchase securities that are rated within one of the four highest credit categories at the time of purchase by at least one major credit rating agency or, if unrated, deemed by T. Rowe Price to be of comparable quality. The fund may continue to hold a security that has been downgraded after purchase.
In addition, the fund uses interest rate futures primarily in an effort to manage its exposure to changes in interest rates or to adjust portfolio duration, and credit default swaps primarily in an effort to protect the value of certain portfolio holdings or to manage the fund’s overall exposure to changes in credit quality.
Investment decisions generally reflect the portfolio manager’s outlook for interest rates and the economy, as well as the prices, yields, and credit quality of various securities in which the fund may invest. For example, if interest rates are expected to fall, the fund may purchase longer-term securities (to the extent consistent with the fund’s investment program) in an attempt to seek higher yields and/or capital appreciation. Conversely, if interest rates are expected to rise, the fund may seek securities with shorter maturities.
As with any fund, there is no guarantee that the fund will achieve its objective(s). The fund’s share price fluctuates, which means you could lose money by investing in the fund. The principal risks of investing in this fund, which may be even greater in bad or uncertain market conditions, are summarized as follows:
Fixed income markets Economic and other market developments can adversely affect the fixed income securities markets. At times, participants in these markets may develop concerns about the ability of certain issuers of debt instruments to make timely principal and interest payments, or they may develop concerns about the ability of financial institutions that make markets in certain debt instruments to facilitate an orderly market. Those concerns could cause increased volatility and reduced liquidity in particular securities or in the overall fixed income markets and the related derivatives markets. A lack of liquidity or other adverse credit market conditions may hamper the fund’s ability to sell the debt instruments in which it invests or to find and purchase suitable debt instruments.
Market conditions The value of the fund’s investments may decrease, sometimes rapidly or unexpectedly, due to factors affecting an issuer held by the fund, particular industries, or the overall securities markets. A variety of factors can increase the volatility of the fund’s holdings and markets generally, including political or regulatory developments, recessions, inflation, rapid interest rate changes, war, military conflict, or acts of terrorism, natural disasters, and outbreaks of infectious illnesses or other widespread public health issues such as the coronavirus pandemic and related governmental and public responses (including sanctions). Certain events may cause instability across global markets, including reduced liquidity and disruptions in trading markets, while some events may affect certain geographic regions, countries, sectors, and industries more significantly than others. Government intervention in markets may impact interest rates, market volatility, and security pricing. These adverse developments may cause broad declines in market value due to short-term market movements or for significantly longer periods during more prolonged market downturns.
Interest rates The prices of, and the income generated by, debt instruments held by the fund may be affected by changes in interest rates. A rise in interest rates typically causes the price of a fixed rate debt instrument to fall and its yield to rise. Conversely, a decline in interest rates typically causes the price of a fixed rate debt instrument to rise and the yield to fall. The prices and yields of inflation-linked bonds are directly impacted by the rate of inflation as well as changes in interest rates. Generally, funds with longer weighted average maturities and durations carry greater interest rate risk. Changes in monetary policy made by central banks and/or governments, such as the discontinuation and replacement of benchmark rates, are likely to affect the interest rates or yields of the securities in which the fund invests.
Prepayments and extensions The fund is subject to prepayment risks because the principal on mortgage-backed securities, other asset-backed securities, or any debt instrument with an embedded call option may be prepaid at any time, which could reduce the security’s yield and market value. The rate of prepayments tends to increase as interest rates fall, which could cause the average maturity of the portfolio to shorten. Extension risk may result from a rise in interest rates, which tends to make mortgage-backed securities, asset-backed securities, and other callable debt instruments more volatile.
LIBOR transition Many financial instruments use or may use a floating rate based on the London Interbank Offered Rate, or “LIBOR,” which is the offered rate for short-term Eurodollar deposits between major international banks. After June 30, 2023, LIBOR will cease
to be published and therefore all loans outstanding will be benchmarked to an alternate rate. Floating rate bank loan coupons may be benchmarked to a short-term interest rate, such as the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR), in the future. The elimination of LIBOR or changes to other reference rates or any other changes or reforms to the determination or supervision of reference rates could have an adverse impact on the market for, or value of, any securities or payments linked to those reference rates, which may adversely affect the fund’s performance and/or net asset value.
Foreign investing Investments in the securities of non-U.S. issuers may be adversely affected by local, political, social, and economic conditions overseas; greater volatility; reduced liquidity; or decreases in foreign currency values relative to the U.S. dollar. The risks of investing outside the U.S. are heightened for any investments in emerging markets, which are susceptible to greater volatility than investments in developed markets.
Credit quality An issuer of a debt instrument could suffer an adverse change in financial condition that results in a payment default (failure to make scheduled interest or principal payments), rating downgrade, or inability to meet a financial obligation. Securities that are rated below investment grade carry greater risk of default and should be considered speculative.
Derivatives The use of interest rate futures exposes the fund to additional volatility in comparison to investing directly in bonds and other debt instruments. These instruments can experience reduced liquidity and become difficult to value and may involve leverage so that small changes produce disproportionate losses for the fund. The fund’s use of interest rate futures involves the risk that anticipated interest rate movements or evaluations of yield curves will not be accurately predicted, which could harm the fund’s performance.
Liquidity The fund may not be able to meet requests to redeem shares issued by the fund without significant dilution of the remaining shareholders’ interests in the fund. In addition, the fund may not be able to sell a holding in a timely manner at a desired price. Reduced liquidity in the bond markets can result from a number of events, such as limited trading activity, reductions in bond inventory, and rapid or unexpected changes in interest rates. Markets with lower overall liquidity could lead to greater price volatility and limit the fund’s ability to sell a holding at a suitable price.
Active management The fund’s overall investment program and holdings selected by the fund’s investment adviser may underperform the broad markets, relevant indices, or other funds with similar objectives and investment strategies.
Cybersecurity breaches The fund could be harmed by intentional cyberattacks and other cybersecurity breaches, including unauthorized access to the fund’s assets, customer data and confidential shareholder information, or other proprietary information. In addition, a cybersecurity breach could cause one of the fund’s service providers or financial intermediaries to suffer unauthorized data access, data corruption, or loss of operational functionality.
The following performance information provides some indication of the risks of investing in the fund. The fund’s performance information represents only past performance (before and after taxes) and is not necessarily an indication of future results.
The following bar chart illustrates how much returns can differ from year to year by showing calendar year returns and the best and worst calendar quarter returns during those years for the fund’s Investor Class. Returns for other share classes vary since they have different expenses.
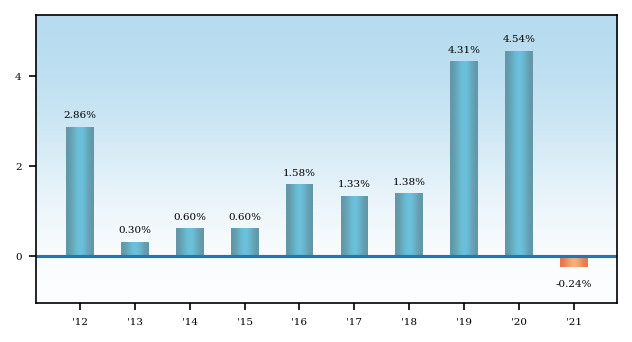
The fund’s return for the six months ended 6/30/22 was -3.96%.
Quarter Ended | Total Return | Quarter Ended | Total Return | |||||
Best Quarter | 6/30/20 | 4.20% | Worst Quarter | 3/31/20 | -1.35% |
The following table shows the average annual total returns for each class of the fund that has been in operation for at least one full calendar year, and also compares the returns with the returns of a relevant broad-based market index, as well as with the returns of one or more comparative indexes that have investment characteristics similar to those of the fund, if applicable.
In addition, the table shows hypothetical after-tax returns to demonstrate how taxes paid by a shareholder may influence returns. After-tax returns are calculated using the historical highest individual federal marginal income tax rates and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. Actual after-tax returns depend on an investor’s tax situation and may differ from those shown. After-tax returns shown are not relevant to investors who hold their fund shares through tax-deferred arrangements, such as a 401(k) account or an IRA. After-tax returns are shown only for the Investor Class and will differ for other share classes.
Average Annual Total Returns - T. Rowe Price Short-Term Bond Fund, Inc. |
Label |
1 Year |
5 Years |
10 Years |
Since Inception |
Inception Date |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investor Class | (0.24%) | 2.25% | 1.71% | Mar. 02, 1984 | |||
| Investor Class | After Taxes on Distributions | (0.72%) | 1.44% | 0.99% | ||||
| Investor Class | After Taxes on Distributions and Sales | (0.14%) | 1.37% | 0.99% | ||||
| I Class | 0.04% | 2.38% | 2.26% | Dec. 17, 2015 | |||
| Advisor Class | (0.35%) | 1.97% | 1.43% | Dec. 31, 2004 | |||
| Z Class | Feb. 22, 2021 | ||||||
| Bloomberg 1-3 Year U.S. Government/Credit Bond Index | Bloomberg 1-3 Year U.S. Government/Credit Bond Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses, or taxes) | ||||||
| Bloomberg 1-3 Year U.S. Government/Credit Bond Index | (0.47%) | 1.85% | 1.39% | 1.75% | [1] | ||
| Lipper Short Investment Grade Debt Funds Average | Lipper Short Investment Grade Debt Funds Average | ||||||
| Lipper Short Investment Grade Debt Funds Average | 0.07% | 2.13% | 1.81% | 2.14% | [2] | ||
| [1] | Return since 12/17/15. |
| [2] | Return since 12/31/15. |